Key Takeaways
- With the rise of digitalization, healthcare has become one of the most vulnerable sectors to cyberattacks.
- The medical sector experienced 569 cyber attacks in 2022, with 335 targeting network servers.
- Insufficient cybersecurity in healthcare can lead to unauthorized access, data breaches, and disruption of critical medical services, jeopardizing patient safety.
- For medical providers, prioritizing cybersecurity is crucial to safeguard data privacy, prevent breaches, ensure regulatory compliance, and foster patient trust.
As the medical industry continues its digital transformation journey, the significance of cybersecurity in healthcare keeps growing. In 2022, the Office for Civil Rights reported 569 cyber attacks on the medical sector, where 335 were committed on the network server. The most popular data breach was a hacking/IT incident (453 cases).
Cyberattacks in healthcare are dangerous because they can compromise patient safety, breach confidentiality, and disrupt operations. Moreover, they often lead to financial and reputation losses. Therefore, you should consider data security threats when developing or improving your software. At Acropolium, we create secure healthcare solutions compliant with HIPAA, HITECH, GDPR, and other standards and regulations.
In this article, we want to share our practical experience building HIPAA-compliant sexual health, bioscience big data processing, and addiction recovery software. We’ll discuss the importance of privacy and security in healthcare, offer practical tips, and highlight the best practices and industry standards.
Safeguarding Patient Data: Why is Cybersecurity Important in Healthcare
Why is privacy important in healthcare? Well, that’s mostly because medical service providers store and transmit sensitive information. It includes patient and doctor names, social security numbers, medical histories, and insurance data. As a result, cybercriminals can use it for malicious purposes, such as identity theft, or sell this information on the black market.
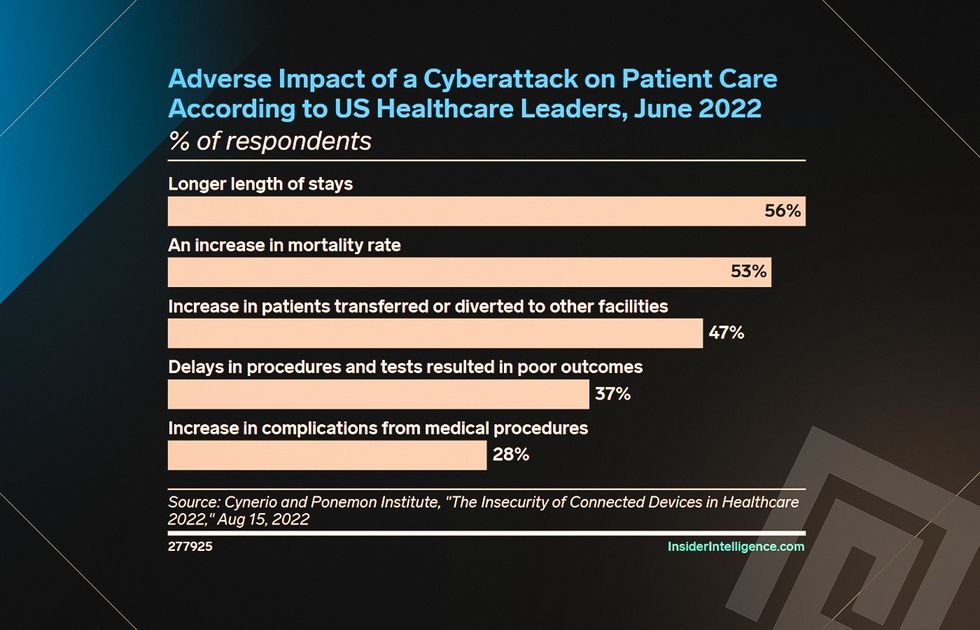
According to reports about cybersecurity in healthcare in 2022, hackers significantly influence patient care. It results in numerous adverse effects, including the following ones:
- Longer patient stays (56%),
- Increased mortality rate (53%),
- More patients transferred or diverted to other facilities (47%)
Cyber attacks also lead to reputation and financial damage. That’s due to data recovery costs, legal fees, and loss of revenue from disrupted operations.
As a medical provider, you should prioritize cybersecurity to reach the following goals:
- Protect data privacy in healthcare
- Prevent its breaches
- Ensure compliance with regulations
- Mitigate risks
- Enhance patient trust
Types of Cybersecurity Issues in Healthcare
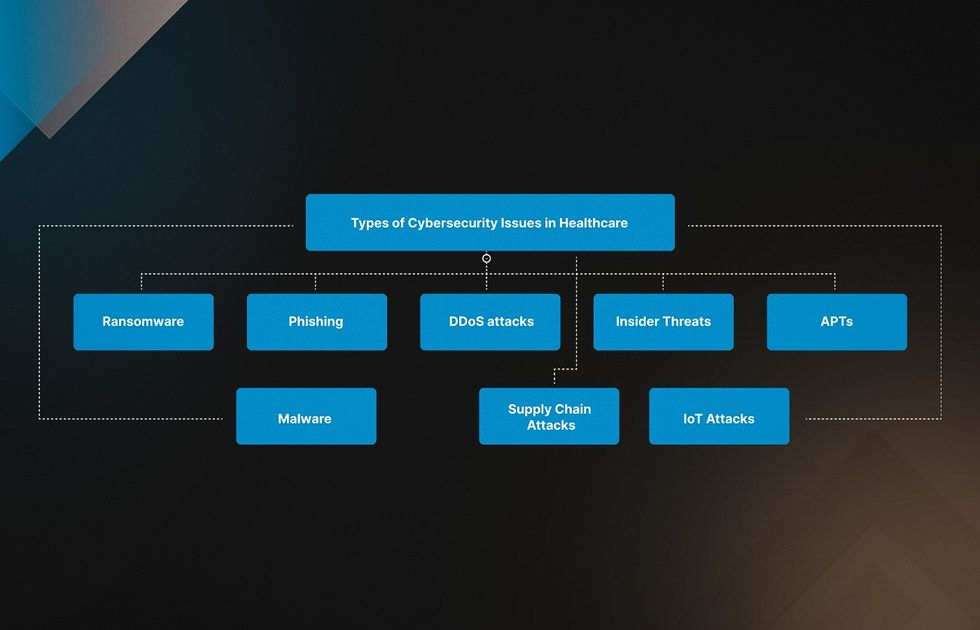
According to healthcare cybersecurity statistics, three significant vulnerabilities include third-party vendor risks, cloud breaches, and Internet of Things (IoT) attacks. At the same time, cyber threats come in many forms and can have severe consequences due to the sensitive data involved. Let’s look at the most widespread risks you may encounter.
- Ransomware. Attackers use ransomware to encrypt data on a computer system, making it inaccessible to users. They then demand payment (usually in cryptocurrency) for the decryption key to unlock the data. For example, in 2022, a ransomware attack on CommonSpirit, a hospital in Chicago, compromised the data of 623,000 patients.
- Phishing. Cybercriminals use phishing emails or messages pretending to be from a legitimate source, such as a healthcare organization or a trusted vendor. They harm cyber security in the medical field by tricking the recipient into revealing sensitive information or clicking on malicious links.
- Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks. A DDoS attack floods a target system with traffic, making it overwhelmed and unavailable to legitimate users. It can disrupt healthcare services or distract IT staff while launching other attacks.
- Insider Threats. Such attacks come from within an organization. A disgruntled employee or contractor can compromise sensitive information. It may involve data theft, sabotage of systems, or accidental patient information exposure.
- Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs). APTs are sophisticated, targeted attacks aiming to gain permanent access to a system. They can be challenging to detect due to the multiple stages and tactics involved, such as spear-phishing, malware, and social engineering.
- Malware. Malware is malicious software designed to cause harm to a computer system, such as stealing data, disrupting services, or damaging hardware. Privacy and security in healthcare can be violated through email attachments, malicious websites, or infected software downloads.
- Supply Chain Attacks. They target third-party vendors or suppliers providing services or software to healthcare organizations. Attackers may exploit vulnerabilities in the supply chain to gain access to a target network or to deliver malware.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Attacks. 53% of connected medical devices or sensors are vulnerable to attacks. Consider healthcare IoT cybersecurity and pay extra attention to IV pumps and VoIP systems with weak passwords.
Tips and Strategies: How to Prevent Data Breaches in Healthcare

As the number of cyber threats facing medical organizations continues to rise, you should consider the importance of patient safety in healthcare. Here are some essential steps to consider when creating a medical app.
Risk Assessments
Regularly performing risk assessments helps healthcare organizations spot potential vulnerabilities and threats. Thus, you can prioritize your medical cyber security efforts accordingly. In particular, providers identify areas requiring more attention and resources by evaluating risks related to hardware, software, and human factors.
Vulnerability Management
Thanks to a vulnerability management program, a healthcare organization can recognize and address weaknesses in its systems and software before attackers exploit them. It involves constant system monitoring, security patches, and updates to reduce the exploitation risk.
Incident Response Planning
Incident response planning is critical to improving cyber security in healthcare industry. This method includes detecting, containing, and mitigating the attack’s effects. It should also involve communication protocols for notifying stakeholders like patients, partners, and regulatory authorities.
Employee Training and Awareness
Healthcare organizations should ensure employee awareness to reduce the risk of data breaches and other threats. All staff, including doctors, nurses, and administrative personnel, should undergo regular training. This way, they will learn how to identify and avoid phishing emails, create strong passwords, and securely handle and store sensitive data.
Best Practices for HealthCare Cybersecurity
As you see, implementing best practices for health data security is critical to safeguard patient data and reduce the risk of cyberattacks. Here are some more advanced techniques to consider:
Prevent Unauthorized Access
Cybersecurity requirements for medical devices and systems include using strong passwords. They should be nearly impossible to guess or crack. Besides, it’s worth regularly changing your system’s credentials. Encryption can secure data in transit and at rest. Meanwhile, multi-factor authentication ensures that only authorized users can access confidential data.

Strengthen Network Security
Firewalls and intrusion detection systems are vital for network security components. Firewalls block unauthorized access to a network. In turn, intrusion detection systems detect and respond to potential cyber threats.
Prioritize Regular Software Updates and Patching
Regular system updates and patching are effective measures against known vulnerabilities. They reduce the risk of cyberattacks and introduce the most powerful security solutions to date.
Here are some examples of healthcare cybersecurity software:
- Encryption: VeraCrypt, BitLocker
- Antivirus tools: Norton Antivirus, McAfee Antivirus
- Firewalls: ZoneAlarm, Norton Firewall
- Data loss prevention: Symantec DLP, Forcepoint DLP
- Access management: Okta, Microsoft Active Directory
- Intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS): Cisco Secure IDS, IBM Security Network IPS
Implementing Healthcare Cybersecurity Solutions: Protecting Key Critical Tools

Medical providers can improve security in healthcare information systems using specific software solutions. When choosing such a tool for your needs, consider its ease of use, integrations with existing systems, and security policies customization.
Maximizing Cybersecurity with EHR Systems
In modern healthcare, electronic health records (EHRs) are critical for storing and sharing patient health information. However, while beneficial, they pose significant cyber security risks in healthcare. That’s because they store sensitive data hackers would love to get their hands on.
EHR security measures include strong access controls (good passwords, single sign-on (SSO), and two-factor authentication), data encryption, and regular risk assessments. It’s also worth providing regular employee training on data security. Finally, you can adopt monitoring and alerting systems to detect and respond to suspicious activity.
Advancing Cloud Security
When choosing a cloud security healthcare solution, providers should assess the offered features. They include data encryption in transit and at rest, multi-factor authentication, and regular updates.
On-premise access provides more control and visibility over data and infrastructure. In contrast, cloud-based access offers greater flexibility and scalability. To choose a suitable solution, consider data sensitivity, compliance requirements, budget, and expertise. Then, evaluate the features and practices of healthcare cybersecurity companies.
Key Considerations for Implementing Healthcare Data Security Solutions
The importance of data security in healthcare is extremely high. And unfortunately, medical management providers often face significant challenges in protecting their sensitive data. A comprehensive solution should meet the following key criteria to address those obstacles.
Compatibility
When selecting data security software, ensure it’s compatible with the existing systems and infrastructure. It should include electronic health record (EHR) systems and other healthcare applications. This way, you will guarantee seamless integration and avoid any disruptions in the workflow.
Scalability
If your healthcare company expands, you can benefit from a cloud-based data security solution. It will allow you to scale up without investing in entirely new systems. Thus, you will keep protecting your data without any additional strain on resources.
Integration
The chosen software should integrate with other tools and services. These are firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, security information systems, and event management (SIEM) solutions. Such integrations enhance the overall cybersecurity for hospitals and healthcare facilities. Besides, they ensure all systems work consistently.
Reporting and Analytics
Healthcare providers can monitor and inspect security events and trends with detailed reporting and analytics capabilities. This way, your organization will identify potential vulnerabilities and proactively address them before they snowball into issues. As a result, you will establish the utmost protection of health information security and privacy.
User-Friendliness
Cybersecurity services for healthcare that are too difficult to navigate may be challenging for employees. And if your workers tend to neglect such tools, they will leave the organization vulnerable to attacks. Therefore, the preferred solution should be intuitive, convenient, and easy to use.
Healthcare Security Standards and Regulations
Medical organizations must comply with several regulations and healthcare data security standards. For instance, these are the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act, and the NIST Cybersecurity Framework. Compliance with those rules is essential for improving patient data security and avoiding penalties.
Why Acropolium is the Right Choice among Healthcare Security Solution Companies

Acropolium is a reliable healthcare cyber security services vendor. Our dedicated team creates bespoke software for healthcare startups, clinics, telehealth companies, research laboratories, and other medical providers.
In particular, our company provides the following services:
- Healthcare cybersecurity consulting and audit for your existing software architecture
- Custom solutions powered by IoT, AI/ML, GPS, video streaming, and chatbots
- Blockchain verification and SSO for health records and internal processes
- Compliance with HIPAA, HITECH, HL7, FHIR, GDPR, and ISO 9001 standards
Let’s look at our latest cases to study Acropolium’s experience in data protection in healthcare.
HIPAA Compliant Medical App Development
The client turned to us to create a new HIPAA-compliant sexual health program. We encountered poor code quality and a large technical debt to the existing solution. After a large-scale audit, we optimized the code and infrastructure and prepared the system for scaling. We also made the app HIPAA-compliant and added some new features.
These steps reduced the project budget by 40% and response time by 56%. And thanks to the new functions, customer loyalty increased by 38%.
Bioscience Cloud-based Big Data Processing App Development
A proteomics company needed a graphical interface for the developed backend. The client also asked us to integrate AI/ML into processing and analyzing biomaterials. Finally, they needed advice on the backend optimization. The main challenge was inefficient communication with the external developer, causing chaotic testing and constant iterations.
We implemented the Scrum methodology to improve communication, achieve the expected results, and make timely changes to the project. As a result, our team reduced the development time by 30%. In addition, due to AI/ML implementation, we increased the accuracy of data processing by 40% and lowered the response time by 38%.
Addiction Recovery Mobile App Development
Acropolium also created a cross-platform application for a private center for psychological assistance to addicted people. It was necessary to identify diseases and provide care, minimizing offline communication on sensitive topics.
We used the Firebase BaaS solution to save 40% of development time and costs. This way, we could focus on the application’s business logic. Today, end users can take a mini drug test, contact specialists, and even point out drug outlets to help the police. Thus, the flow of new patients to rehabilitation increased by 36%.
Final Thoughts
Healthcare providers face many internal and external cyber threats leading to loss of money and reputation. This article overviewed the most efficient strategies and steps to protect your healthcare information security and privacy, including using special software. Remember that such a solution must be user-friendly, scalable, and compatible with existing systems.
Acropolium specialists create reliable healthcare data security software on a subscription-based model with a monthly fee. Contact us to discuss your specific project and discover its timeline and budget.







![Online Pharmacy App Development [2024 Guide]](/img/articles/pharmacy-app-development/img01.jpg)

![Kiosk Software Development for Healthcare Industry [Guide with Case]](/img/articles/kiosk-software-development/img01.jpg)
![Cloud Computing in Healthcare [5 Real Use Cases Included]](/img/articles/cloud-computing-healthcare/img01.jpg)
![Chatbots in Healthcare [10 Use Cases] + Development Guide](/img/articles/chatbots-in-healthcare/img01.jpg)
