
Key Takeaways
- Conversational AI in banking enables natural, secure voice interactions that reduce customer wait times, automate routine tasks, and ensure 24/7 availability.
- By integrating with CRM systems, voicebots adjust tone, responses, and recommendations based on a customer’s history and profile.
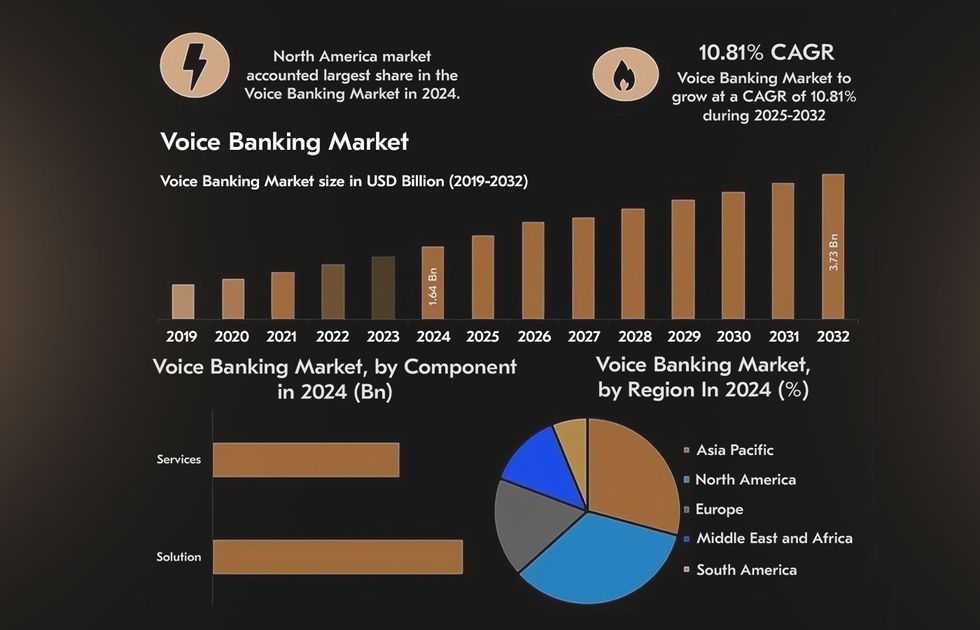
- The voice banking market was valued at $1.64B in 2024 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 10.81%, reaching $3.73B by 2032.
- Voice AI systems implement encryption, voice biometrics, and audit trails to meet financial regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and PSD2, while reducing the risk of fraud.
The constantly rising customer expectations for around‑the‑clock assistance and tailored experiences have driven banks to explore voicebots in banking. By combining natural language understanding with secure backend integrations, these systems transform call centers into proactive service hubs.
Institutions gain faster response times, seamless voice‑driven workflows, and the agility to meet evolving regulatory and security demands, all while delivering human‑like interactions that feel intuitive and reliable. In fact, modern businesses allocate over 5% of their digital spending to generative and analytical AI technologies — and finance is among them.
Known as a top AI company specializing in fintech software development, Acropolium has delivered dozens of successful AI integrations and custom financial tools. Today, we will share our insights to introduce the power of voice-assisted banking with its benefits, use cases, and challenges.
What’s a Voicebot in Banking?
A voicebot in banking is an AI‑driven conversational agent that utilizes speech recognition and natural language processing (NLP) to interact with customers over the phone or voice‑enabled channels. When a user speaks, the system transcribes intent, consults the bank’s databases or core systems, and delivers spoken responses.
Whether providing account balances, resetting passwords, or routing complex queries to specialists, this financial technology simplifies banking workflows. At the same time, it’s a go-to in industries like logistics and automotive.
Unlike rigid IVR menus, modern voicebots learn from interactions to refine their understanding, enabling banks to automate high‑volume tasks and deliver consistent, context‑aware support.
In 2024, the voice banking market reached a value of $1.64 billion. Projections show it could grow at a CAGR of 10.81% through 2032, reaching around $3.73 billion. As current limitations are addressed, banks are expected to automate between 15% and 35% of their operations, gaining speed and precision that surpass traditional human-led processes.
How Businesses Benefit from Using Voice AI in Banking
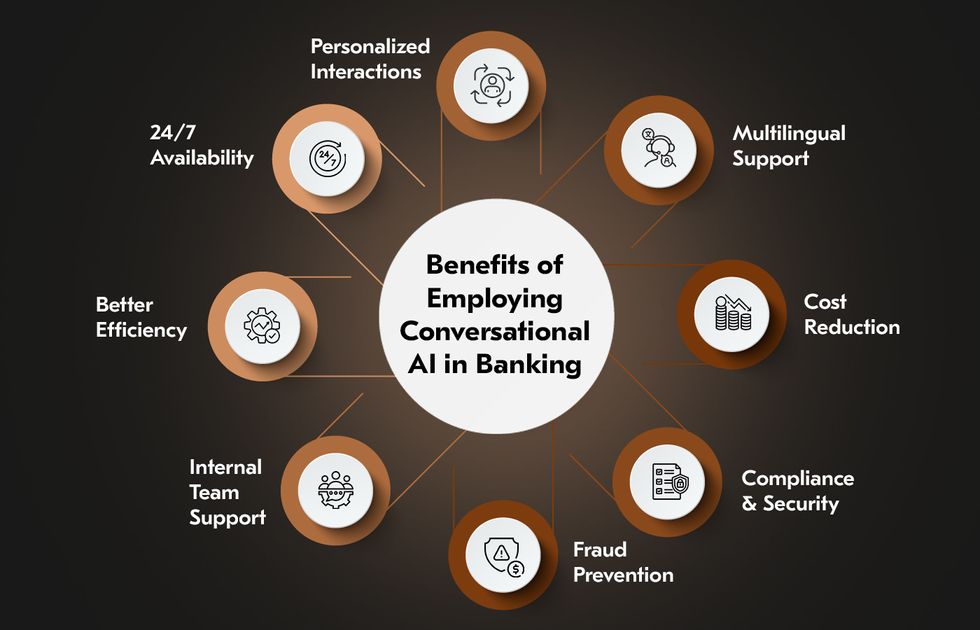
As the financial sector moves further into automation and digital-first services, voice AI integration is becoming a key component in addressing growing customer demands. Beyond speed, it enables more intuitive, inclusive, and secure interactions.
Let’s explore how financial institutions are leveraging voice technology to simplify processes and strengthen customer relationships over time.
24/7 Availability & Faster Service
A voicebot in banking handles routine requests — balance checks, transaction histories, branch locations — around the clock, eliminating hold times and peak‑hour bottlenecks. Customers enjoy immediate resolutions, while live agents focus on high‑value or escalated cases.
Personalized Customer Interactions
By integrating CRM data and transaction history, voicebots address callers by name and recall past concerns. Dynamic scripts adapt to segment profiles by premium, small‑business, or retail, delivering bespoke offers, targeted alerts, and financial advice that drives deeper engagement.
Multilingual & Accessible Support
Since global banks serve diverse populations, conversational AI in banking switches seamlessly between languages, dialects, and accents. They also support voice‑driven accessibility modes for visually impaired customers, ensuring compliance with inclusivity standards and broadening market reach.
Operational Efficiency & Cost Reduction
Automating high‑volume inquiries shifts half of the call‑center workload to AI in web applications, slashing staffing costs and reducing average handle time. Real‑time monitoring dashboards track call volumes and system health, enabling proactive scaling and performance tuning.
Compliance, Security & Fraud Prevention
Advanced voice‑biometric authentication analyzes vocal patterns to verify identity, reducing PIN resets and fraudulent access. Smart contracts and encrypted voice transcripts create immutable audit trails, simplifying regulatory reporting and demonstrating adherence to KYC/AML mandates.
Support for Internal Teams
Beyond external service, financial businesses deploy conversational AI for banking to assist staff. Internal voice assistants streamline tasks like retrieving policy documents, executing trade‑order templates, or scheduling compliance training. This way, they’re improving productivity and knowledge sharing across departments.
Conversational AI Use Cases in Banking: Real-World Examples
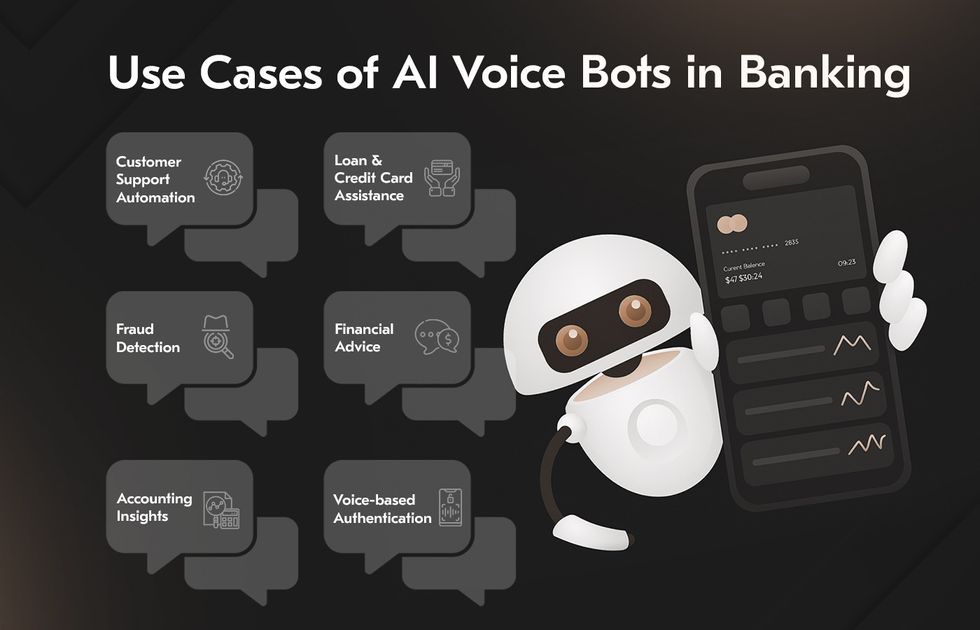
Understanding what AI can do in theory is only half the story. What really matters is how it performs in real environments across real customer interactions and operational workflows. Banks across the globe are already using AI voice assistant banking tools to manage high volumes of requests, boost customer satisfaction, and reinforce security.
Customer Support Automation
Voicebots rely on automatic speech recognition to transcribe spoken language into text. Natural language understanding (NLU) then interprets the user’s intents. Once intent is detected, backend integrations (via APIs) fetch relevant data from the bank’s core systems and return a voice response through text-to-speech (TTS) synthesis.
Bank of America’s Erica uses machine learning to process more than 2 million interactions per day. Erica combines historical user data with contextual inputs (e.g., time, location) to offer instant responses. It can proactively detect patterns like recurring charges and surface alerts or actions without being prompted.
Loan & Credit Card Assistance
Conversational AI in banking trained on loan and credit policy data can respond to voice prompts like “Am I eligible for a personal loan?” or “What’s the status of my credit card application?” Voicebots access CRM systems or document repositories in real time, retrieving application statuses, eligibility conditions, or payment timelines. AI also personalizes the conversation based on previous interactions and financial profiles.
Axis Bank’s voice assistant, Aha!, supports natural conversations in English, Hindi, and Hinglish. Built with multilingual NLP models, it helps customers check loan options, EMIs, and documentation needs without waiting on agents. It handles over 100,000 voice requests daily.
Fraud Detection Alerts
Voice AI in banking systems monitors real-time transaction patterns and detects anomalies (e.g., unusual locations, transaction sizes, or timing). If flagged, a voicebot immediately contacts the user via outbound call or IVR. Using NLU, it confirms suspicious activity and awaits verbal confirmation. If unrecognized, the voicebot can automatically trigger blocks or escalate the case.
Several U.S. and European banks use AI-enhanced IVRs that issue alerts like, “We noticed a $1,200 purchase at an unusual location, was this you?”. Confirming by voice speeds up response time and helps prevent further unauthorized activity.
Financial Advice & Account Insights
Voice-assisted banking equipped with contextual AI and machine learning analyze user transaction data and behavior. They interpret spoken questions like “What did I spend on dining last month?” and retrieve categorized spending data. Some models use reinforcement learning to refine suggestions (e.g., when offering savings plans or reminders).
Capital One’s Eno uses deep NLP models to understand over 2,200 variations of common banking queries. While text-based at launch, its core architecture enables voice-driven account insights, spending summaries, and smart notifications like duplicate charges.
Voice-based Authentication
Voice biometrics works with 100+ physical and behavioral voice characteristics (pitch, tone, cadence, and speaking style) to verify identity. Machine learning models create unique voiceprints for each user. When someone calls in, the voicebot compares the current voice sample to the stored voiceprint in real-time to authenticate securely.
HSBC has adopted voice authentication in call centers, reducing login times and password resets, which has reduced banking fraud by 50%. Voiceprint matching can occur within seconds, dramatically improving both user experience and security.
Challenges of Implementing Voice Bots in Banking

Despite its clear potential, implementing conversational AI in banking isn’t without complications. From data privacy concerns to technical limitations in speech recognition, banks face a variety of hurdles when integrating voice AI into legacy systems.
A successful rollout requires more than just software. It demands strategy, adaptability, and a deep understanding of both customer behavior and regulatory landscapes.
Data Privacy and Regulatory Compliance
Banks operate in highly regulated environments where customer conversations often involve sensitive personal and financial data. To remain compliant with regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and region-specific laws such as GLBA or PSD2, conversational AI for banking must ensure strict encryption standards (AES-256 or higher), access control, and data minimization strategies.
To meet these requirements, banks typically implement end-to-end encryption, strict access controls, and detailed audit trails. Using compliance-certified cloud environments helps ensure that regional data storage laws are respected. It’s equally important to build user consent flows into the voice interface, with clear disclosures about recording, biometric processing, and data retention.
Integration with Legacy Systems
Many financial institutions still rely on mainframes and monolithic systems that predate modern APIs, making voicebot integration complex. These legacy systems often lack the speed, structure, and interfaces needed for real-time conversational AI. To overcome this, voice-assisted banking employs middleware layers, microservices, and integration platforms that act as bridges between voice interfaces and backend systems.
Where APIs don’t exist, robotic process automation (RPA) can mimic user behavior to retrieve or submit information through older interfaces. In cases where real-time responsiveness is limited, asynchronous data exchange patterns can help maintain fluid voice conversations.
Language, Accent, and Dialect Variability
Serving a diverse customer base means voicebots must understand not just multiple languages, but also regional accents, dialects, and informal speech. Conversational AI in banking needs to be trained on real-world audio from the bank’s target demographics, including samples with background noise, overlapping speech, and varied speaking styles.
Rather than relying on generic speech-to-text engines, many institutions work with NLP vendors that offer localized language models and domain-specific training. Ongoing model fine-tuning using real conversational data helps maintain clarity and responsiveness.
User Trust and Adoption
While AI-powered voice bots in banking offer efficiency, they can struggle with user confidence, especially in finance, where accuracy and discretion are non-negotiable. Customers may hesitate to share personal information with an unfamiliar voice interface or may feel unsure about how their data is being used. Building trust begins with transparency.
Voicebots should clearly explain their role, data usage, and the customer’s rights during the first interaction. Giving users the option to speak to a human agent at any time builds a sense of control, while empathetic speech patterns and familiar terminology make the bot feel more approachable.
Maintaining Accuracy and Relevance
Like any AI system, a voicebot in banking requires continuous monitoring and adaptation to remain useful. Without regular updates, models can quickly become outdated, failing to recognize new phrases, product names, or shifts in customer behavior. Banks manage this by establishing robust feedback loops, where real-world interaction data feeds back into the training pipeline.
Intent libraries and dialogue flows must be updated as new services launch or policies change. Real-time analytics allow banks to identify common failure points, such as misunderstood queries or high dropout rates, and address them promptly. Additionally, A/B testing different voice flows can help refine phrasing, pacing, and logic to match user expectations.
Why Choose Acropolium?
With over 22 years of delivering enterprise‑grade software, Acropolium combines full‑cycle development expertise with leadership in AI and voice solutions. Our ISO‑certified processes ensure every project meets stringent security and compliance standards — from PoC to global rollout.
Named top ML and AI software developers, our dedicated teams architect voice-assisted banking platforms that integrate seamlessly with legacy infrastructures, leverage advanced NLP models, and support rapid iteration. This way, we empower banks to modernize their customer experience while controlling cost and risk.
Final Thoughts
Voice bots in banking are now core components of modern banking operations. It streamlines interactions, supports compliance efforts, and helps reduce the burden on internal teams without compromising service quality.
These systems are increasingly embedded across customer service lines, internal workflows, and fraud detection processes. With Acropolium’s subscription-based cooperation model, banks can access full-cycle development for regulatory compliance, integration with obsolete systems, and long-term scalability with reduced development costs.
Reach out to explore how our expertise supports continuous, secure innovation in voice-driven banking.







![Top AI Applications in Finance for 2025: [Benefits & Success Stories]](/img/articles/artificial-intelligence-applications-in-finance/img01.jpg)
![AI in Portfolio Management: Use Cases & Benefits [2025 Guide]](/img/articles/ai-for-portfolio-management-use-cases/img01.jpg)
![Learn how [Online Payment Processing Software] works and how to process online payments on website](/img/articles/how-to-process-online-payments/img01.jpg)
![Cryptocurrency Exchange Software Development [2025 Guide]](/img/articles/why-you-need-custom-cryptocurrency-exchange-software-and-how-to-get-it-right/img01.jpg)

![Why Invest in Cryptocurrency Wallet Development [Guide]](/img/articles/investing-in-cryptocurrency-wallet-development-cost-and-benefits/img01.jpg)