Marketing decisions rarely start with a blank page. They begin midstream, surrounded by dashboards, campaign calendars, customer signals, and pressure to act quickly. A performance drop appears in one channel, engagement rises unexpectedly in another, and a product launch deadline remains unchanged. At that moment, teams are forced to decide what matters, what can wait, and what should often change with incomplete information and little time to test assumptions.
AI in marketing impacts how decisions are formed and executed. AI systems continuously process behavioral, contextual, and performance data to surface patterns and generate predictions that inform subsequent actions. Campaigns adapt as they run, personalization adjusts at the individual level, and performance signals feed directly into planning. Questions that once required manual analysis can now be answered continuously: which customers matter most right now, which channels deserve investment, and which signals indicate risk or opportunity.
The purpose of this article is to explain how AI is actually used in marketing today, where it delivers measurable value, and what changes when it becomes part of core scalable marketing operations. It examines practical use cases, benefits, and limitations.
If you are evaluating how AI could improve marketing decisions, execution speed, or customer engagement in your organization, contact us to discuss your use case. Acropolium works with teams to design and implement AI and ML solutions that integrate into existing marketing workflows and support clear, trackable performance improvements.
What is Artificial Intelligence in marketing?
AI in marketing refers to the use of Machine Learning, Natural Language Processing, and generative AI to support marketing decisions, automate execution, and continuously improve performance through data-driven insights. Its role goes beyond task automation and content generation. AI systems perform cognitive functions such as pattern recognition, prioritization, prediction, and decision support at a scale and speed that human teams cannot sustain.
A practical question many organizations ask is: What does AI actually change in marketing operations? AI evaluates vast volumes of customer, market, and performance data to recommend or execute actions that are statistically most likely to produce desired business outcomes.
You may ask then why AI in marketing matters now rather than later. Digital marketing environments generate more data than manual analysis can handle, with customer behavior fragmented across channels, devices, and touchpoints. Artificial Intelligence marketing solutions connect analysis directly to execution, reducing the gap between insight and action. It allows marketing teams to move from reactive reporting to predictive customer insights and planning, answering questions such as which customers are most likely to convert, which segments carry churn risk, and where budget reallocations will have the most significant impact.
What are the benefits of AI in marketing?
The implementation of AI for marketing delivers measurable business impact when applied to concrete decision points across planning, execution, and optimization. Its value comes from improving how organizations allocate capital, scale execution, and respond to customer behavior through data-driven systems rather than manual coordination.
Financial growth
AI improves the precision of marketing investment decisions and reduces revenue leakage across the funnel, thereby enhancing financial performance. Automated decision-making systems continuously assess which audiences, channels, and messages drive the most conversions and long-term value, enabling budget adjustments while campaigns are still active. Predictive analytics help forecast conversion likelihood, with reported revenue uplift ranging from 3% to 15% among AI adopters.
For example, organizations that apply AI-driven lead scoring and budget allocation can identify high-probability opportunities earlier in the buying cycle. Artificial Intelligence in digital marketing allows sales and marketing teams to focus resources on prospects with higher conversion likelihood and expected lifetime value, improving revenue predictability and reducing spend on low-impact activities.
Operational efficiency
AI changes day-to-day marketing execution by reducing manual effort in data handling, reporting, and routine production. Systems operate continuously and consistently, removing delays caused by handoffs between tools or teams. The impact of AI on marketing allows marketing operations to respond faster to performance signals without increasing organizational complexity.
AI marketing examples show how integrating AI into campaign execution workflows can automate reporting, testing, and optimization tasks that previously required daily manual intervention. Enterprise users report saving 40–60 minutes per day by delegating analytical and technical tasks to AI systems.
Personalization
AI improves customer engagement by enabling more precise and timely personalization across channels. Instead of relying on static segments, systems adjust messaging, offers, and timing based on observed behavior and contextual signals. AI applications in marketing enable the deployment of real-time recommendation engines and tailor product suggestions and content as customers interact with digital properties. This increases relevance without requiring manual rule updates or frequent segmentation redesign.
Strategic advantage
AI for marketing supports more informed strategic decisions by linking performance outcomes to specific actions and market signals. Rather than reacting to lagging indicators, marketing teams gain early visibility into emerging trends, demand shifts, and competitive movement. For example, firms can analyze unstructured data from reviews, social platforms, and forums can identify sentiment changes or unmet needs before they appear in traditional reports.
How is Artificial Intelligence used in marketing today?
In 2026, AI operates as an embedded marketing infrastructure that supports planning, execution, and performance control across the whole campaign lifecycle. Instead of producing isolated outputs, AI systems manage interconnected workflows spanning data analysis, personalization, automation, and optimization. Marketing teams increasingly delegate repeatable decision paths to autonomous systems while retaining responsibility for intent, constraints, and governance. 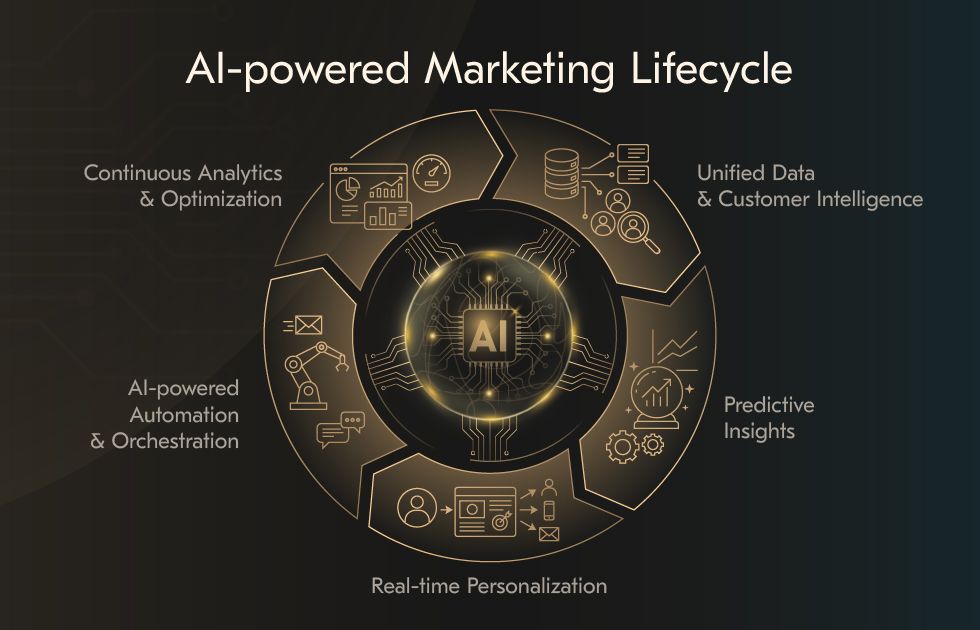
Data analysis and customer insights
AI-driven data analysis in 2026 focuses on converting large volumes of unstructured and semi-structured data into actionable insights that directly inform execution. Marketing teams rely on predictive models that estimate future behavior rather than summarize past performance.
Key applications include:
Predictive customer AI marketing insights: ML models estimate next-best actions, purchase probability, and customer lifetime value in near real time.
Sentiment and emotion analysis: Systems analyze text, voice, and interaction patterns across reviews and social channels to infer attitudes and engagement signals.
Unified customer intelligence: AI integrates data from CRM platforms, digital properties, and engagement channels into a consistent customer-level view that supports coordinated decision-making.
Personalization across marketing channels
Personalization in 2026 operates at the level of the individual interaction rather than static audience segments. AI systems continuously adjust messaging, format, and timing based on behavioral and contextual signals across channels. Personalization remains bounded by predefined rules to ensure consistency and compliance.
Common personalization practices include:
Micro-segmentation: AI adjusts targeting dynamically at the individual level rather than relying on long-lived demographic groups.
Adaptive content delivery: Websites, emails, and applications update content elements in response to real-time behavior.
Lookalike audience modeling: Systems identify patterns among high-value customers to reach similar profiles with greater precision.
AI-powered marketing automation
Marketing automation platforms in 2026 reliy heavily on agent-based systems that coordinate multi-step workflows. These systems handle campaign performance optimization, setup, and execution with minimal manual input. Automation focuses on consistency and responsiveness rather than full autonomy without oversight.
Typical AI powered marketing automation capabilities include:
Autonomous campaign orchestration: AI systems coordinate goals, channel execution, and optimization across multiple touchpoints.
Send-time and channel optimization: Delivery timing and channel selection are adjusted based on individual engagement patterns.
Conversational engagement: AI-powered assistants manage routine interactions and guide customers through defined journey stages.
AI in marketing analytics and performance tracking
AI marketing analytics emphasize continuous monitoring and predictive evaluation. AI in digital marketing connects performance signals to decisions as campaigns run, enabling teams to intervene early rather than react after completion. Measurement becomes part of execution rather than a separate reporting activity.
Key real-time marketing analytics use cases include:
Real-time performance visibility: Dashboards update continuously and support immediate adjustment of spend, messaging, or targeting.
Predictive outcome modeling: Teams simulate campaign performance under different conditions before launch to reduce uncertainty.
Advanced attribution modeling: AI assigns value across touchpoints with greater accuracy, clarifying which actions contribute most to results.
What are the core AI marketing strategies?
Building an AI-driven marketing strategy
An AI driven marketing begins with clarity on what the organization expects AI to improve and why those improvements matter commercially. Before models or tools are introduced, marketing teams must define the decisions AI will influence and the outcomes those decisions are expected to produce. Leadership agreement on priorities such as customer lifetime value, qualified demand, or retention ensures AI optimization efforts move in a single direction.
Structured frameworks that map AI capabilities across planning, production, personalization, promotion, and performance help maintain coherence as adoption expands. A focused audit of current processes in data-driven growth strategies then highlights early opportunities where automation or prediction can deliver value without disrupting existing workflows.
Integrating AI into digital marketing workflows
Once strategic intent is defined, attention naturally shifts to execution. Artificial Intelligence in marketing creates value only when insights translate into action, which requires integration across data sources, tools, and teams. Integration starts with unifying customer, performance, and engagement data so AI systems operate on consistent inputs. Data quality controls and standard definitions reduce error and bias as the scale increases.
Aligning AI marketing tools with business goals
With workflows connected, tool selection becomes a question of alignment rather than capability alone. AI platforms must support existing marketing systems, scale with data volume, and reinforce defined objectives. Tools for AI marketing strategy that optimize metrics disconnected from business outcomes introduce noise rather than value. Alignment also depends on organizational readiness. Marketing teams need a practical understanding of how AI systems influence decisions and how outputs should be interpreted.
How companies apply AI across marketing teams
Marketing strategy and planning
AI reshapes marketing strategy by enabling forward-looking decisions rather than retrospective analysis. By analyzing historical performance, market signals, and behavioral patterns, AI in digital marketing enables teams to anticipate outcomes and evaluate trade-offs before committing resources. Strategy becomes less dependent on fixed campaign cycles and more oriented toward continuous prioritization and adjustment.
Typical applications in strategy and planning include:
Predictive strategy modeling: Estimating purchase probability, customer lifetime value, or demand shifts based on behavioral and contextual data.
Market research at scale: Analyzing unstructured data from reviews, social platforms, and forums to detect sentiment and emerging trends.
Automated campaign planning: Recommending audiences, budgets, and timing based on historical performance patterns.
Strategic prioritization: Identifying which problems or opportunities merit attention while algorithms handle execution-level optimization.
Creative and content operations
Generative AI systems support faster production of content variants while preserving defined brand standards. This allows teams to respond to demand across channels without expanding manual effort in proportion. Creative direction remains human-led, while AI supports production and adaptation. Typical AI-driven use cases in content operations include:
Content generation: Drafting text-based assets such as articles, messaging, and product descriptions aligned with brand guidelines.
Visual and video creation: Producing images and video variations to support multi-channel campaigns.
Granular personalization: Generating multiple creative variants tailored to specific audiences or contexts.
Localization support: Translating and adapting content across regions and languages with consistent tone and structure.
Performance marketing and analytics
AI enhances performance marketing by processing large volumes of data that exceed the capacity of manual analysis. Systems continuously assess signals across channels to optimize spend, messaging, and placement. Performance evaluation shifts from periodic reporting to ongoing adjustment based on live results. This improves responsiveness and reduces reliance on static assumptions. The application of Artificial Intelligence in marketing performance include:
Programmatic media buying: Automating ad placement decisions based on context, behavior, and historical outcomes.
Automated testing: Running and adjusting A/B or multivariate tests across ads, landing pages, and messaging.
Search optimization: Supporting keyword analysis, metadata updates, and internal linking in response to search behavior changes.
Predictive lead scoring: Prioritizing prospects based on engagement patterns and conversion likelihood.
CRM and lifecycle marketing
AI strengthens lifecycle marketing by enabling a more coherent view of customer behavior across touchpoints. Systems analyze interactions over time to inform timing, messaging, and omnichannel engagement optimization. AI supports more consistent engagement throughout acquisition, onboarding, retention, and reactivation phases. In many organizations, this capability is implemented through email marketing software development, where AI models are embedded directly into campaign logic, sequencing rules, and lifecycle triggers.
Common lifecycle-focused applications include:
Personalized customer journeys orchestration: Recommending following actions or content based on stage, behavior, and prior interactions.
Send-time optimization: Determining the most effective timing and channel for individual recipients.
Churn risk detection: Identifying early signs of disengagement to support proactive retention efforts.
Conversational support: Using AI-driven assistants to manage routine interactions and guide users through processes.
Product marketing and go-to-market
In product marketing, AI supports decision-making related to positioning, pricing, and launch strategy. By analyzing usage data, feedback, and market signals, AI in digital marketing helps teams evaluate product-market alignment and prioritize initiatives. Typical applications in go-to-market activities include:
Market-fit assessment: Estimating demand and adoption likelihood before or during launch.
Dynamic pricing models: Adjusting pricing based on demand signals, competition, and contextual factors.
Feature prioritization: Analyzing feedback and usage data to inform roadmap and packaging decisions.
Lookalike audience modeling: Identifying new audiences based on characteristics of high-value customers.
What are the risks and limitations AI powered marketing usage?
AI in marketing can bring structural risks that must be addressed at the system, data, and organizational levels. These challenges surface when using AI in marketing and are deployed at scale, integrated into live customer interactions, or allowed to influence high-impact decisions without adequate controls.
Algorithmic bias
AI systems learn from historical data, and that data often reflects existing imbalances in representation, access, or behavior. When such patterns are absorbed without correction, AI can reinforce biased targeting, pricing, or content delivery across demographics such as age, gender, or socioeconomic groups. Bias is rarely intentional, but its impact can be material. Without continuous auditing, representative datasets, and explicit fairness constraints, biased outputs can persist unnoticed.
Data protection
AI-driven marketing depends on large volumes of personal and behavioral data collected across channels and touchpoints. This data is inherently sensitive and often subject to strict regulatory requirements. Improper handling, weak access controls, or unclear data lineage increase the likelihood of breaches and unauthorized use. Third-party tools, integrations, and shared data environments expand the attack surface. Once trust is lost through misuse or exposure, recovery is slow and costly, regardless of technical remediation.
Manipulation, misuse, and loss of control
Advanced AI systems can influence behavior at scale, raising concerns about manipulation and misuse. Poorly governed systems may optimize for engagement or conversion in ways that distort user choice or encourage exploitative patterns. The same technologies can also be repurposed for malicious activities, including the misuse of synthetic content or the unauthorized replication of protected materials.
Infrastructure costs
Training and operating large AI models require substantial computational resources. Data centers consume significant energy, and sustained AI usage increases infrastructure demand. Infrastructure cost management becomes part of responsible deployment. Decisions on model size, retraining frequency, and workload distribution directly affect sustainability and operating budgets.
Limitations in human understanding
Current AI systems operate within narrow cognitive boundaries. They lack self-awareness, contextual judgment, and emotional understanding in the human sense. In marketing scenarios that require nuance, ethical reasoning, or long-term relationship management, this limitation becomes visible. Over-reliance on automated outputs risks decisions that are technically optimized but contextually inappropriate.
Addressing these risks requires deliberate operating choices and clear ownership. Here are the mitigation strategies for responsible AI in marketing:
Human oversight by design: AI systems should operate under defined review and approval mechanisms. Human experts remain responsible for validating outputs, correcting errors, and ensuring decisions align with brand standards, legal obligations, and ethical expectations.
Transparency in data and AI usage: Clear communication about how customer data is collected, processed, and used reduces risk and builds long-term trust.
Ethical governance and regular audits: Organizations should define ownership of AI decisions and conduct regular audits to detect bias, drift, or unintended effects.
Strict compliance with data protection regulations: Adherence to frameworks requires secure data storage, controlled access, and clear data lifecycle management. Compliance must be embedded into system design rather than handled as a post-deployment check.
Cross-functional collaboration: Effective risk management requires close coordination among marketing, legal, IT, security, and data teams.
What is the future of AI in marketing?
Looking ahead, AI in marketing will increasingly function as a permanent decision layer rather than a supporting tool. Its role will center on coordinating planning, execution, and measurement with greater continuity and fewer manual interruptions. As adoption deepens, patterns of use are becoming clearer across organizations that deploy AI at scale.
The most visible AI marketing trends are:
Rise of autonomous and agentic marketing systems
Marketing technology is progressing toward autonomous systems capable of managing campaigns end-to-end. These systems will define objectives, translate them into execution plans, generate content variations, allocate budgets, and optimize performance continuously based on live signals. Agentic AI architectures enable this by coordinating multiple specialized components that plan actions, monitor outcomes, and adjust behavior in real time.
As agent-based systems mature, a growing share of marketing workload will shift to autonomous execution layers. Campaign briefing, journey orchestration, and performance monitoring will increasingly occur within a single system rather than across disconnected tools. AI and marketing execution speed increases, while human involvement moves upstream to defining constraints, approval thresholds, and escalation logic.
Hyper-personalization marketing
Personalization is moving beyond broad segments toward individual-level adaptation across channels. AI for marketers already adjusts messaging based on behavioral and timing signals, but future implementations will rely more heavily on real-time context and inferred customer intent. Micro-segmentation enables marketing decisions to be made at the level of individual interactions rather than at the level of audience groups.
Interactive marketing environments
AI will play a central role in expanding marketing into interactive and immersive environments. Integration with augmented and virtual interfaces enables more contextual product exploration, guided demonstrations, and scenario-based engagement. AI manages personalization, continuity, and complexity within these environments. These interactions depend on the persistent state and learning across sessions.
How to implement AI in marketing strategy: 5 core steps
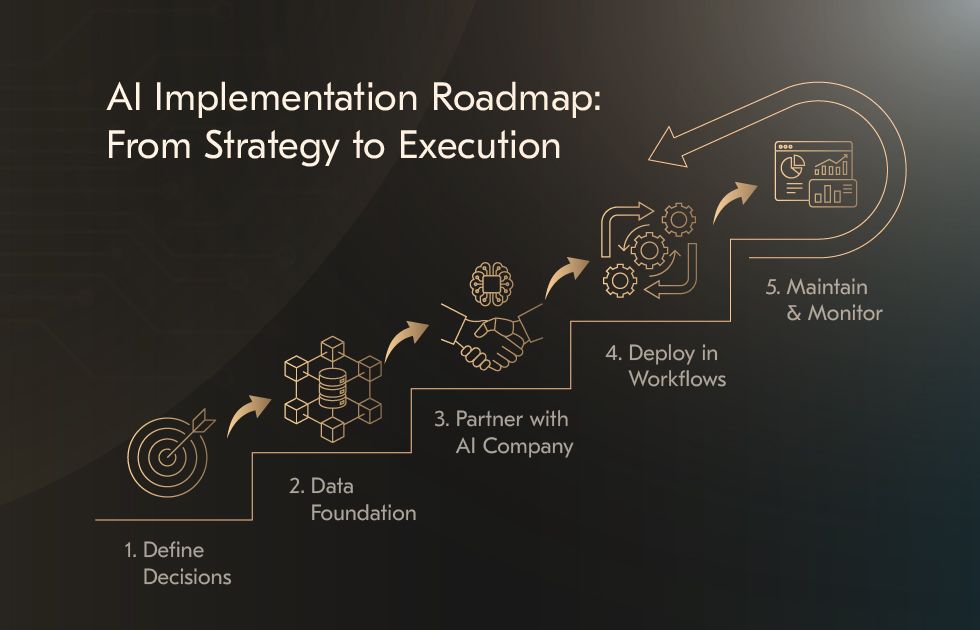
Step 1: Define the decisions AI needs to support
Implementation begins by identifying which marketing decisions would benefit from greater speed, consistency, or analytical depth. These typically sit at points where teams rely on partial data, manual judgment, or delayed reporting, such as lead prioritization, channel allocation, segmentation, or performance attribution. Defining these decision points creates focus and prevents AI from being applied too broadly or abstractly.
Step 2: Establish a data foundation
Once the decision scope is defined, attention shifts to the data required to support it. Marketing data often spans CRM systems, analytics platforms, advertising tools, and product usage sources, each with its own structure and cadence. These inputs must be standardized and linked to support reliable customer behavior modeling. Clear ownership, validation rules, access controls, and compliance mechanisms ensure AI outputs remain dependable over time. Addressing privacy and regulatory requirements at this stage prevents rework and limits downstream risk.
Step 3: Strengthen execution with an experienced AI development company
At this point, many organizations choose to partner with an experienced AI development company to accelerate progress. A specialized partner brings applied knowledge of marketing software development and AI use cases, established architectural patterns, and implementation discipline. This support reduces experimentation risk and shortens the path from strategy to production.
In practice, this often takes the form of software development as a service, where AI capabilities are designed, built, and integrated into existing marketing systems rather than delivered as standalone tools.
An experienced partner knows how to use AI in marketing for your specific use case and can assist with data preparation, model selection, system integration, and governance design. More importantly, the partnership helps translate strategic objectives into AI systems that fit existing marketing processes rather than disrupting them.
Step 4: Deploy AI within existing workflows
With expertise and structure in place, AI can be deployed through controlled, incremental implementations. Initial AI use cases in marketing should remain narrow and measurable, allowing teams to observe how AI influences decisions and outcomes. This phase supports validation, refinement, and internal alignment. Integration with current marketing tools is integral. AI should support planning, execution, and reporting within existing workflows. Incremental rollout builds confidence while preserving operational stability.
Step 5: Maintain oversight and continuous performance review
Ongoing oversight ensures long-term value. Human review remains necessary to validate outputs, manage exceptions, and preserve brand and compliance standards. Regular performance monitoring helps identify drift, bias, or declining relevance as data and market conditions change. Feedback loops close the implementation cycle.
If you are planning to introduce AI into your marketing operations or scale existing initiatives, Acropolium can help you design, build, and integrate AI systems that fit your data, workflows, and growth objectives. Get in touch with us to discuss how AI can support your marketing strategy.







![How to Integrate AI into Your Business: [A Comprehensive Guide]](/img/articles/how-to-integrate-ai-into-your-business-a-comprehensive-guide/img01.jpg)
![AI in Automotive Industry: [9 Use Cases + Examples]](/img/articles/ai-in-automotive-industry/img01.jpg)

![AI in Retail: [Use Cases & Applications for 2025]](/img/articles/ai-in-retail-use-cases/img01.jpg)