Key Takeaways
- Big data technologies process massive datasets to derive insights by integrating AI, machine learning, and IoT.
- Industries that use big data include healthcare, finance, retail, logistics, manufacturing, education, hospitality, marketing, media, and government.
- Among the big data usage examples are real-time monitoring, customer personalization, operational efficiency, risk management, and predictive maintenance.
Data is the new oil. Yet, companies in all industries still need to turn it into useful products, like oil is transformed into gas or plastic. That is, businesses face the challenges of managing vast amounts of unstructured and structured data. While traditional systems struggle to process complex datasets, the benefits of big data in business enable organizations to derive actionable insights, improve customer experiences, and make informed decisions.
Technologies like AI, machine learning, and IoT accelerate this transformation, offering real-time data analysis and predictive capabilities. In this article, we will talk about big data use cases for different industries and successful examples of companies using big data.
What Is Big Data Technology?
What is big data used for? Big data technologies are specialized tools, platforms, and techniques that process, store, and analyze massive and complex datasets. It enables organizations to get professional AI-powered consultations, make informed decisions, and drive innovation. Big data often works with, artificial intelligence, machine learning and the Internet of Things.
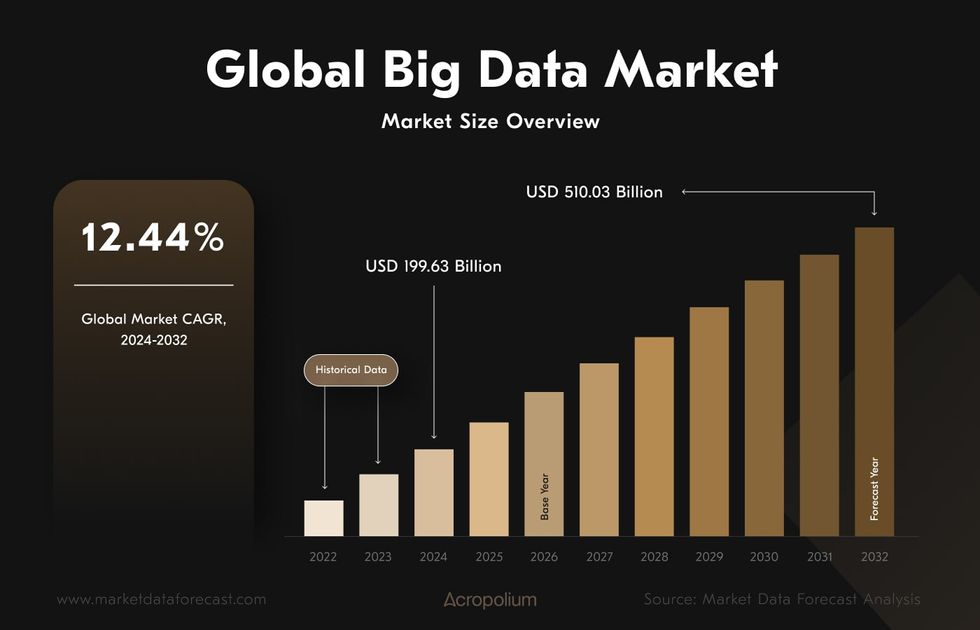
The global big data analytics market is projected to grow from $199.63 billion in 2024 to $510.03 billion by 2032, growing at a 12.44% CAGR. Popular examples of big data technologies include Hadoop, Apache Spark, and NoSQL databases.
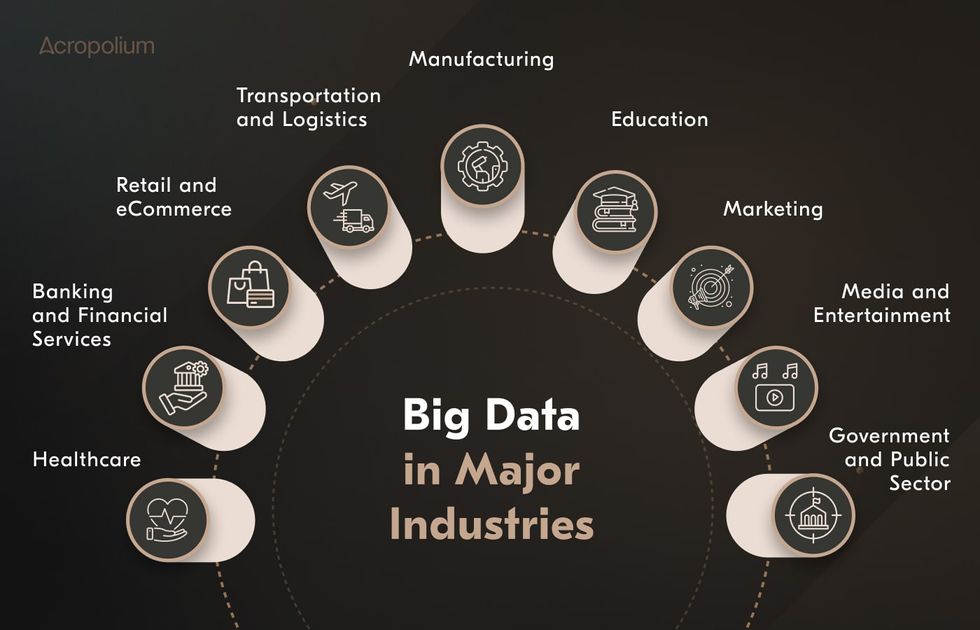
Now, let’s discover what industries use big data.
Big Data Use Cases by Industry
Examples of big data in business include healthcare, banking, retail, transportation and logistics, government, manufacturing, education, marketing, and media and entertainment.
Of course, these areas experience varying degrees of technology impact. In particular, when it comes to spending, 18% of tech companies invest more than 20% of their budgets on analytics tools. Other industries with significant investments include retail, healthcare, financial services, media, and business and legal services.

But what is big data analytics used for? Let’s look at the fields that benefit the most from technology, discussing popular use cases and big data examples in business.
Big Data in Healthcare
The technology improves the quality of care, reduces costs, and supports innovation through the following use cases for big data:
- Diagnostics. AI and big data improve diagnostic accuracy (for example, in radiology or telemedicine) by analyzing large volumes of data.
- Personalized medicine. Healthcare providers create customized treatment plans based on individual needs and conditions by analyzing patient data.
- Drug development. Large dataset analysis accelerates the discovery of new drugs and treatments by identifying promising compounds.
- Predictive analytics. Big data uses in business include forecasting patient health trends, enabling early interventions, and efficient resource allocation.
Big data examples in healthcare:
- By centralizing data and fostering AI expertise, Pfizer saves millions and accelerates innovation. The Scientific Data Cloud simplifies data access for scientists, while AI-powered VOX boosts research efficiency and product delivery. Also, big data and AI supported the company’s goal of launching 19 medicines and vaccines in 18 months.
Big Data in Banking
The application of big data in finance helps institutions optimize processes and increase efficiency.
- Fraud detection. With large datasets, financials identify suspicious patterns and predict potential fraud.
- Credit scoring. Businesses that use big data assess creditworthiness by analyzing transaction history and other data sources (digital footprints, payment behavior, mobile usage, etc.)
- Regulatory compliance. Enable tracking transactions, maintaining records, and monitoring suspicious activity to ensure compliance.
- Algorithmic trading. Banks and investment firms can identify market trends and make real-time trading decisions based on financial data.
Big data analytics banking examples:
- JPMorgan Chase uses big data to detect fraud by analyzing normal and fraudulent transactions. AI simulators generate synthetic data with predefined probabilities to identify anomalies.
Big Data in Retail
Let’s see how big data retail use cases drive more efficient, personalized, and customer-centric retail operations:
- Personalization. Retailers use big data in industry to analyze customer behaviors and preferences, enabling personalized product recommendations.
- Dynamic pricing. Make real-time price adjustments based on demand, competitor prices, and market trends to remain competitive while maximizing profits.
- Inventory optimization. By analyzing past sales, seasonal trends, and other variables, you will predict demand patterns and optimize inventory levels.
- Supply chain efficiency. E-commerce businesses evaluate real-time data from suppliers, transportation, and demand forecasting to reduce costs and improve delivery times.
Big data in retail examples:
- Walmart uses advanced technologies to create personalized shopping experiences across stores, Sam’s Clubs, web apps, and virtual environments. For example, the Content Decision Platform allows you to design unique homepages and tailored content.
Big Data in Transportation and Logistics
The benefits of big data in business involve enhancing efficiency, safety, and customer experience. Consider these crucial big data analytics use cases:
- Route optimization. Collect and use real-time data from traffic sensors, GPS, and historical trends to optimize delivery routes and reduce travel time.
- Fleet management. Logistics companies optimize fleet performance, reduce costs, and enhance safety by monitoring vehicle and driver metrics.
- Load optimization. Companies using big data analytics evaluate load configurations to maximize the use of space in trucks and containers.
- Logistics visibility. Tracking products in real time improves transparency, reduces delays, and enhances inventory management.
Real life examples of big data in logistics:
- Maersk uses big data to reduce waste, access new markets, and manage disruptions. Its 700 vessels generate approximately 5,000 data tags each, while over 70 port facilities are equipped with 750,000 IoT devices.
Big Data in Manufacturing
Big data industries like manufacturing should revolutionize production processes, increasing efficiency and improving product quality.
- Predictive maintenance. Big data applications help reduce downtime and maintenance costs by analyzing data from machinery sensors.
- Demand forecasting. By assessing customer and market data, businesses predict demand fluctuations to adjust production schedules and reduce overproduction or stockouts.
- Quality control. Identify defects early in the production process to correct issues quickly and reduce scrap rates.
- Supply chain optimization. Track materials and products in real time, ensuring optimal stock levels, reducing waste, and improving delivery schedules.
Big data analytics examples in manufacturing:
- Tesla redefines car manufacturing, collecting sensor data from millions of miles to enhance performance, detect faults, and refine autonomous driving features. Real-time analysis enables over-the-air updates, improving vehicles and offering services like remote diagnostics.
Big Data in Education
Education needs to be more effective and personalized, and big data for industry can greatly contribute to this through:
- Personalized learning. By analyzing student data, educators tailor learning experiences to meet individual needs and enhance engagement.
- Predictive analytics. Migrate to modern architecture and implement big data to enable early intervention for at-risk students and support data-driven decision-making for administrators.
- Student retention. Educational companies that use big data identify students who may be at risk of dropping out to implement interventions.
- Curriculum development. Exploring student success trends allows institutions to refine courses, address content gaps, and create tailored learning materials.
Big data applications examples in education:
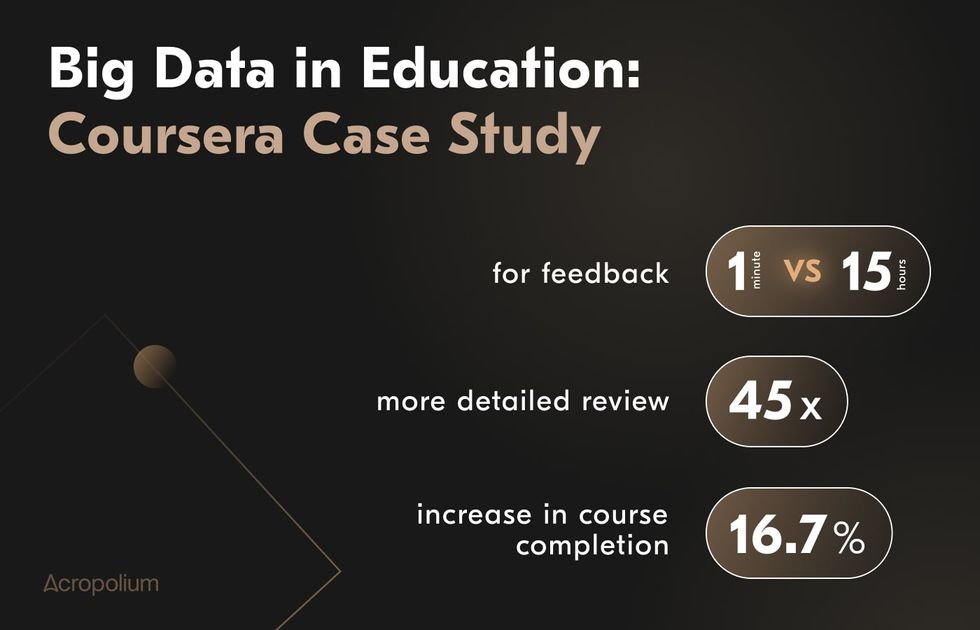
- Coursera’s peer reviews streamline feedback with faster (1 minute vs. 15 hours), more detailed (45x more feedback), and scalable evaluations. Early tests show a 16.7% increase in course completions, while AI’s grading supports deeper learning and retention.
Big Data Analytics in Marketing
Why is big data analytics important for marketing? Advanced technologies are crucial for enhancing customer engagement and driving business growth. Consider the following big data business use cases:
- Customer segmentation. Create targeted marketing strategies and personalized campaigns by segmenting audiences more accurately.
- Campaign optimization. Using big data impact on business, you will refine their strategies in real time, optimizing spending and maximizing return on investment.
- Predictive analytics. Partner with offshore development companies to efficiently anticipate trends, optimize inventory, and improve customer satisfaction by offering relevant products and services.
- Customer sentiment analysis. Gauge consumer sentiment and adjust strategies to improve brand perception.
Marketing big data analytics applications examples:
- Coca-Cola integrates regional customer data into a unified platform, allowing for real-time global insights. This enables the company to understand global trends and deliver personalized marketing strategies based on individual consumer preferences.
Big Data in Media and Entertainment
Thinking about ways to improve content delivery and personalize experiences? Big data use cases in media and entertainment will optimize operational processes:
- Content creation. The big data analytics industry understands trends and preferences in real time, enabling creators to produce content that resonates with audiences.
- Audience insights. By collecting data from viewers across multiple platforms, companies gain valuable insights into audience demographics and behaviors.
- Tailored content. Analyze viewing habits and preferences to craft personalized content, increasing engagement and retention.
- Live event analytics. Integrate big data solutions to assess real-time data from live events, including audience sentiment, social media interactions, and viewership statistics.
Big data examples in the entertainment industry:
- Netflix personalizes content recommendations and thumbnails based on viewing habits. Similarly, Spotify uses data to tailor music suggestions for its 246 million premium subscribers, improving engagement and satisfaction across platforms.
Big Data Applications in Government and Public Sector
More responsive services for citizens are real. All you need is to use big data in different industries like government and the public sector.
- Smart cities. Build SaaS MVP and analyze data from sensors and IoT devices to optimize traffic management, energy consumption, and public transportation bespoke systems.
- Crime prevention. Crime patterns, criminal activity prediction, and resource allocation are examples of how big data helps reduce crime rates and improve public safety.
- Environmental protection. Governments partner with trusted big data vendors to monitor environmental changes, track pollution, predict risks, and enforce regulations.
- Resource allocation and budgeting. Big data allows governments to track spending, assess the effectiveness of public programs, and identify areas of inefficiency.
Government big data application examples:
- Singapore harnesses IoT to innovate in mobility, housing, healthcare, and governance, seamlessly integrating digital and physical spaces via 5G. In 2022, its IoT market earned $5.47 billion, with 28% of residents adopting IoT devices, cementing its global leadership in digital innovation.
Key Big Data Analytics Applications
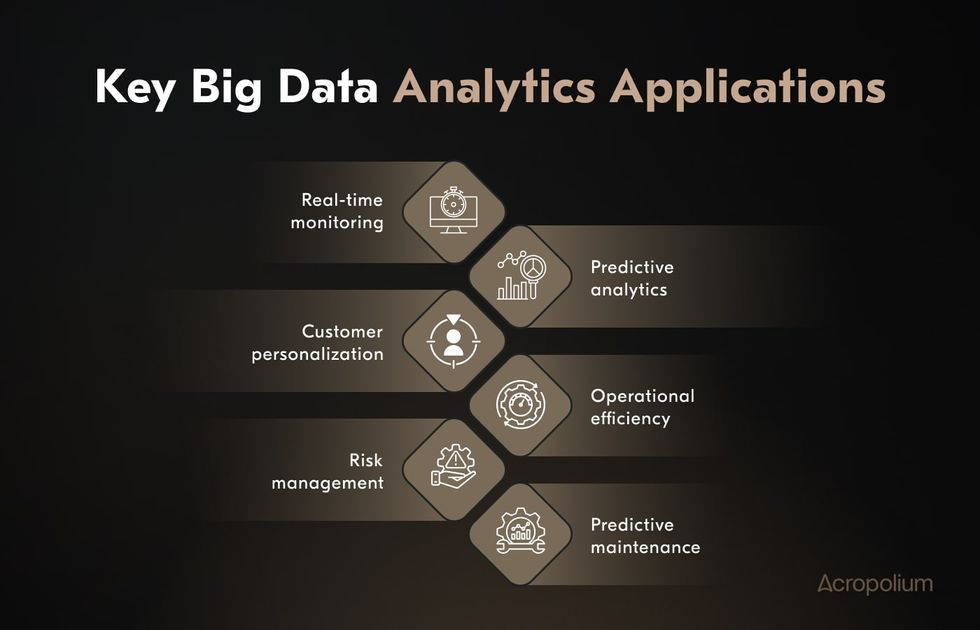
So, what can big data be used for? Let’s summarize big data applications in business across various industries:
- Real-time monitoring. Track performance, quality, or service delivery for instant insights and adjustments.
- Predictive analytics. Forecast trends, consumer behavior, and market dynamics to enable proactive decision-making.
- Customer personalization. Tailor products, services, and marketing strategies based on individual preferences and behaviors.
- Operational efficiency. Streamline supply chains, reduce costs, and improve resource allocation.
- Risk management. Identify and mitigate risks like fraud, cybersecurity threats, and operational disruptions.
- Predictive maintenance. Monitor the lifecycle and performance of physical assets to reduce downtime and maintenance costs.
Final Thoughts
Now you know how big data can help businesses, enhancing productivity and decision-making. And if you’re looking for a trusted partner, Acropolium delivers GDPR-compliant apps, adhering to ISO-certified processes and leveraging serverless solutions. For example, we successfully implemented a hotel revenue optimization system and oil and gas analytics solution.
Our IT outsourcing agency offers comprehensive consulting, SaaS MVP, migration, and integration subscription-based support at a fixed monthly fee. Contact Acropolium’s dedicated team to discuss how is big data used in business.







![Blockchain App Development [7 Reasons to Build a Blockchain App]](/img/articles/blockchain-application-development/img01.jpg)
![How to Write Software Requirements Specification [SRS Document Template]](/img/articles/software-requirements-specification/img01.jpg)
![Renewable Energy Software Development in 2025 [Use Cases & Solutions]](/img/articles/software-for-renewable-energy-sector/img01.jpg)
![8 Machine Learning Use Cases in Key Industries [2025 Guide]](/img/articles/use-cases-for-machine-learning-adoption-in-key-industries/img01.jpg)