
Healthcare is changing faster than most organizations can adapt. Providers are under pressure to deliver faster, safer, and more personalized care while operating within some of the most heavily regulated environments in any industry. Off-the-shelf software can address specific needs but rarely adapts to the complex workflows, interoperability requirements, and compliance obligations that define modern healthcare. Here, custom healthcare software development becomes critical.
Unlike standardized SaaS tools, tailored solutions can reflect the realities of medical workflows, adapt to strict compliance requirements, and integrate with complex IT environments. They are not built to provide “one-size-fits-all” convenience, but to address the specific challenges of determining whether a hospital runs smoothly, a clinic stays compliant, or a new digital health startup survives in a competitive market.
If your organization is considering such a step, choosing the right partner is critical. The complexity of healthcare demands more than technical expertise. It requires a development team that pays attention to regulations, security, and clinical realities. Looking for a reliable healthcare software development company? Get in touch.
Why you need custom healthcare software in 2026
In 2025, healthcare organizations are under intense pressure to digitize operations, meet stringent regulatory requirements, and deliver patient care that is secure, personalized, and efficient. Standardized solutions often impose rigid workflows, but custom systems are designed to align directly with the needs of providers, administrators, and patients.
SaaS tools are limited in their ability to adapt to specialized workflows, ensure full regulatory compliance in complex environments, or integrate with legacy infrastructure. Control over patient data security and long-term scalability remains constrained, as organizations depend on the vendor’s roadmap and security practices. Custom healthcare software offers a different path. Tailoring functionality, architecture, and compliance mechanisms to the exact needs of an organization provides long-term control. Custom healthcare IT solutions can be designed to integrate seamlessly with existing electronic health records, enterprise systems, or insurance databases.
Who benefits from custom healthcare software?
Custom development is not a one-size-fits-all strategy. Its value depends on the complexity and scale of the organization:
Clinics and specialty practices often require tailored EHR systems, billing tools, or patient engagement portals that reflect the nuances of their practice rather than the generalized workflows of commercial platforms. A dermatology clinic, for example, may need imaging storage tightly integrated with records, while a mental health practice might prioritize secure telehealth and session documentation.
Hospitals and health systems face the greatest need for customization. They must integrate various systems (emergency, inpatient, outpatient, diagnostic, pharmacy, and administrative) into a single interoperable platform. For these organizations, custom solutions reduce inefficiencies caused by siloed systems and ensure compliance with diverse regulations.
Startups and digital health innovators use custom software to differentiate their offerings in competitive markets. Whether developing a remote patient monitoring app, a telemedicine platform, or an AI-driven diagnostic tool, startups rely on custom development to meet investor expectations, integrate cutting-edge technologies, and demonstrate compliance from day one.
Examples of critical functionality
Custom healthcare software spans a wide range of applications. Still, specific categories consistently deliver high impact:
- Electronic Health Records (EHR) are centralized platforms that consolidate patient data across specialties and facilities.
- Billing and revenue cycle management systems are built to reflect regional regulations, insurance requirements, and organizational policies.
- Telemedicine platforms are secure, scalable systems that support video consultations, e-prescriptions, and integration with IoMT devices.
- Analytics and decision support with advanced dashboards and predictive models that process large patient and operational data volumes.
Key trends in custom healthcare software development
Rising expectations for personalization, the acceleration of digital health, and the critical demand for compliance and security are reshaping priorities for providers, payers, and technology partners alike. The following trends illustrate how technology redefines care delivery, operational resilience, and the strategic direction of healthcare IT.
Predictive analytics in healthcare
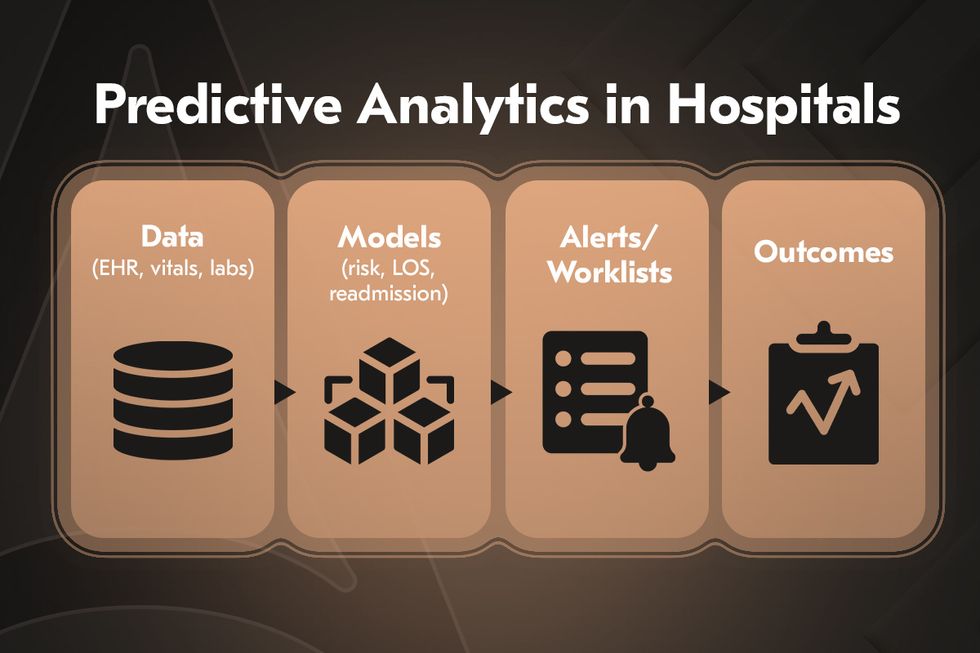
Hospitals are increasingly investing in predictive analytics to prevent overload and anticipate patient needs before crises occur. By processing large volumes of structured and unstructured medical data, predictive models can forecast demand for emergency beds, ICU occupancy, and staffing levels.
From a clinical standpoint, predictive analytics is helping identify patients at risk of complications, such as sepsis or cardiac arrest, hours before symptoms become visible. Early alerts allow clinicians to intervene proactively, reducing mortality rates and improving recovery outcomes. A typical example would be a hospital system that uses predictive dashboards to track bed capacity and flag high-risk patients in real time, enabling smoother patient flow and fewer unplanned admissions.
AI in healthcare: automation, chatbots, and virtual assistants
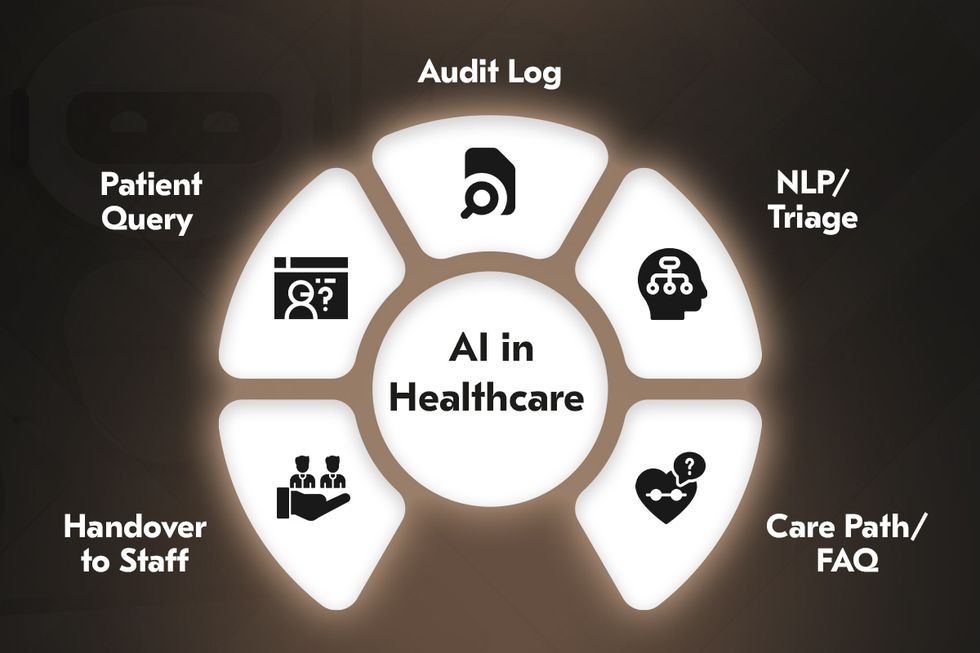
Artificial intelligence is embedded in everyday healthcare workflows. AI-powered chatbots and virtual nursing assistants are increasingly deployed across patient portals, triage systems, and telehealth platforms. Predictive analytics, powered by statistical models and ML algorithms, allows hospitals to anticipate patient admissions, forecast ICU demand, and optimize bed availability. This prevents overloads, particularly during seasonal peaks or emergencies, and improves resource allocation.
On the clinical side, predictive models help identify patients at risk of complications, enabling earlier interventions. AI-supported mammography screening and other AI-driven diagnostic systems can analyze imaging scans and pathology slides with accuracy comparable to or even exceeding human specialists. These advancements are gradually shifting hospitals toward proactive care models where outcomes are improved, and costs are reduced through timely, data-driven interventions.
Data security & compliance
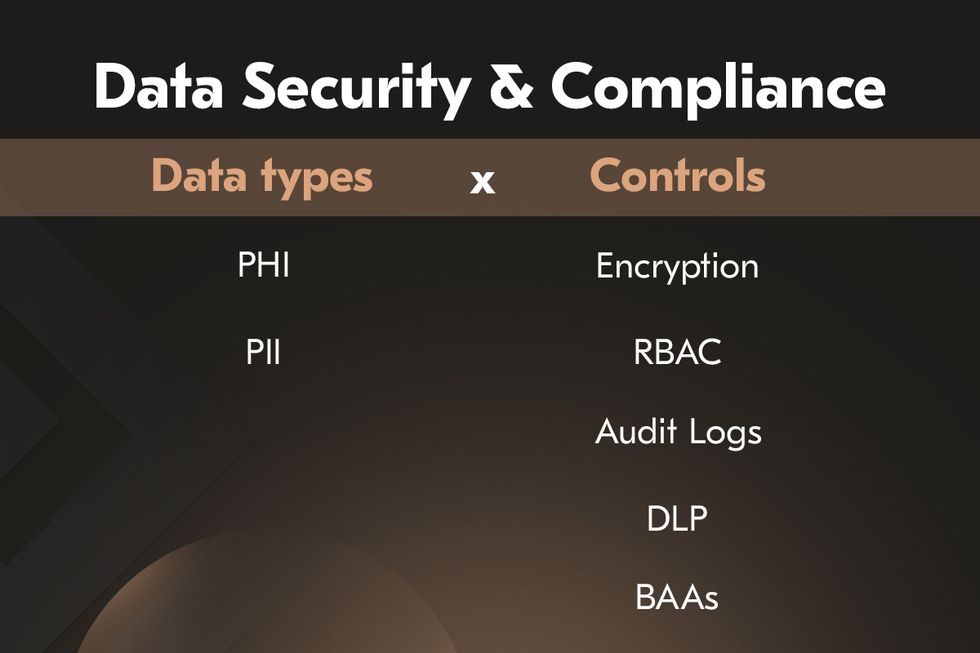
Handling sensitive patient health information demands uncompromising attention to security and compliance. Healthcare systems are frequent targets of cyberattacks, and breaches can have devastating clinical and financial consequences. Regulations such as HIPAA in the US and GDPR in the EU mandate strict safeguards for storing, processing, and transferring medical data.
For developers, compliance is not a box-ticking exercise but a design requirement. Encryption of data in transit and at rest, strong authentication mechanisms, detailed access control, and continuous monitoring must be integrated at the architectural level. A typical example of healthcare app development is a hospital adopting role-based access controls, where physicians, nurses, and administrative staff see only the data relevant to their responsibilities.
Telemedicine app development
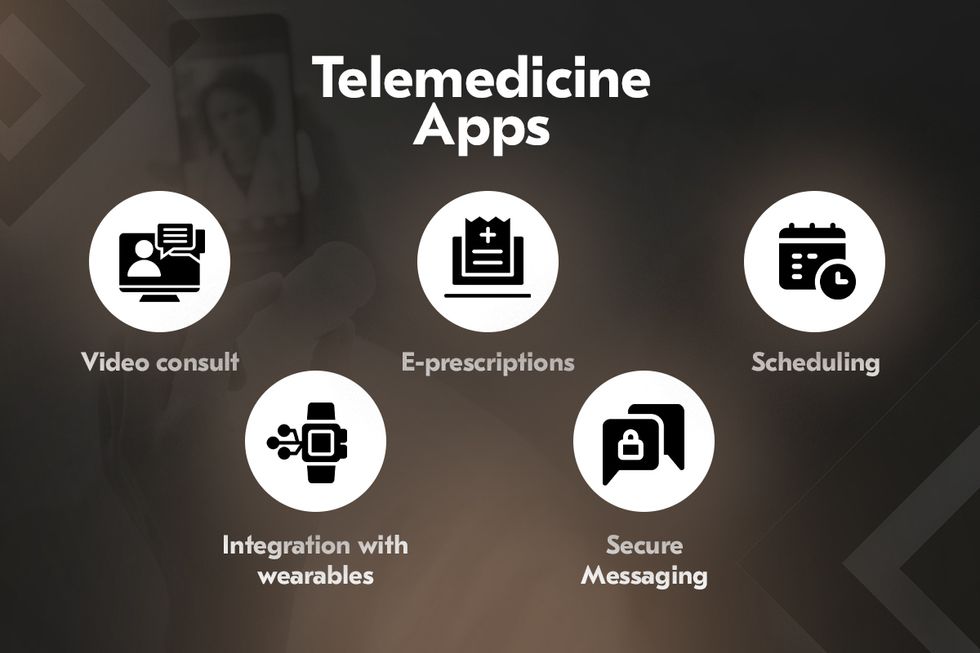
Telemedicine has become one of the most visible pillars of digital healthcare. The global market is expanding rapidly, with platforms enabling remote consultations, e-prescriptions, and integration with wearable devices. A modern telemedicine app development will support secure, high-quality video consultations, real-time messaging, and electronic prescription software transmission.
Wearables and IoMT devices have further extended the reach of virtual care. Smart insulin pens, heart monitors, and connected inhalers feed continuous health data streams into patient records, enabling physicians to monitor conditions remotely and intervene earlier. For patients with chronic illnesses, this represents a step-change in quality of care and accessibility. As telemedicine matures, the expectation is shifting toward seamless integration with EHR systems.
Legacy healthcare systems modernization
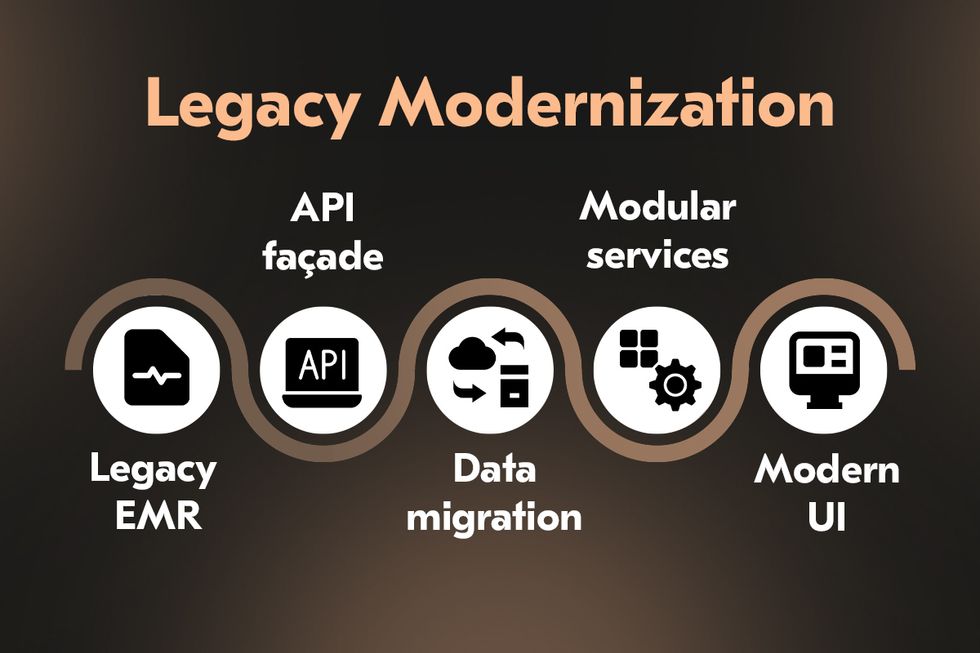
Despite the progress, many healthcare organizations rely on outdated legacy systems. These systems are costly to maintain, lack interoperability, and pose security vulnerabilities. They often create fragmented patient records, limit integration with modern applications, and introduce risks that slow digital transformation initiatives.
Legacy healthcare systems modernization is a priority, but wholesale replacement is often impractical due to operational risks and costs. The prevailing approach is phased modernization: incrementally upgrading modules, introducing middleware to bridge old and new environments, and deploying APIs that enable secure data exchange. A common example would be replacing a hospital’s outdated scheduling module with a modern cloud-based solution while maintaining the existing EHR. Such an approach reduces disruption while creating a path toward a fully integrated ecosystem capable of supporting advanced analytics, AI integration, and scalable digital health services.
Cost of custom healthcare software development
The cost of healthcare software development is not determined by a single figure but shaped by a combination of interdependent factors. Unlike other industries, healthcare adds a further layer of complexity because non-compliance with standards can result in financial losses and reputational damage.
Functionality. Project complexity is a primary driver: systems that require advanced features, custom designs, or complex integrations with existing healthcare infrastructure demand greater time and resources. Basic applications such as patient portals or appointment schedulers fall on the lower end of the spectrum. At the same time, enterprise-grade platforms that include electronic health records, AI-driven diagnostics, or hospital management software systems require larger investments due to higher complexity, integration needs, and testing demands.
Region where development takes place. Healthcare app development costs differ between the United States, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, and Asia, with hourly rates varying widely. Enterprises often balance budget considerations with access to specialized healthcare IT talent, so nearshore and offshore models remain attractive if they come with proven experience in regulated industries.
Level of security and compliance required. Building HIPAA compliant software development, with end-to-end encryption, multi-factor authentication, and audit-ready logging, requires additional time, expertise, and validation. Security architecture can represent a significant portion of the overall cost for systems handling sensitive patient data. Still, it is the most critical safeguard against financial penalties and reputational harm.
System integration. Healthcare enterprises rarely operate in greenfield environments. New applications must connect with legacy EHR systems, insurance platforms, pharmacy databases, and medical devices. Integration efforts often require custom APIs, middleware, and extensive interoperability testing with standards such as HL7 and FHIR. The depth of these integrations can significantly expand project budgets and timelines, but they are necessary to ensure the new solution operates seamlessly in real-world clinical environments.
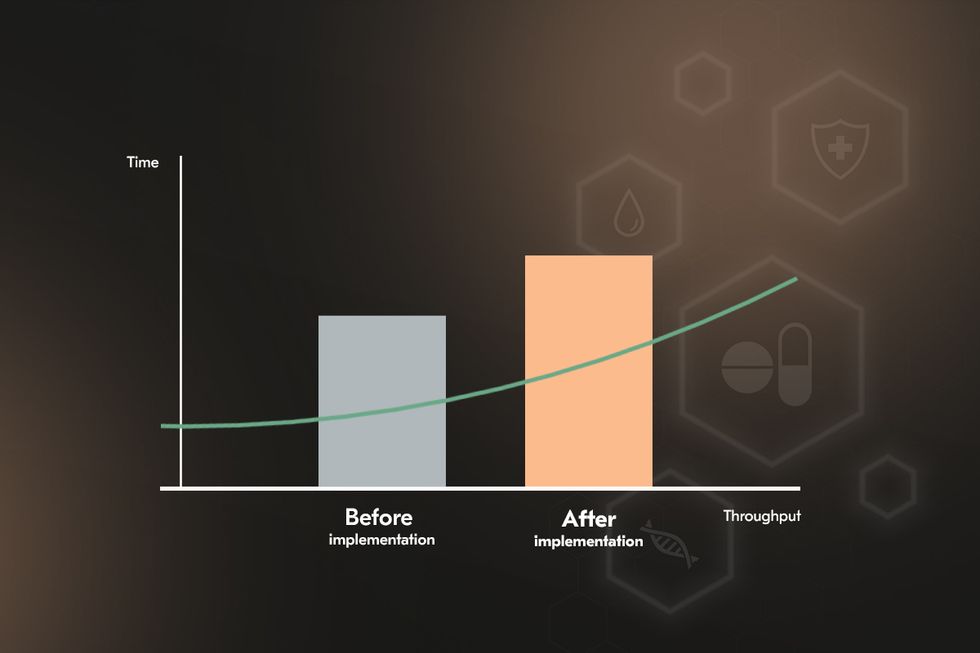
While custom healthcare software development involves substantial upfront costs, the long-term return is tangible. Healthcare automation software reduces operating costs by cutting down on manual data entry, redundant testing, and administrative overhead. Optimized scheduling and digital patient management improve patient flow, decreasing wait times and increasing capacity without expanding physical infrastructure. Predictive analytics modules further enhance resource allocation, preventing costly staffing and bed utilization inefficiencies.
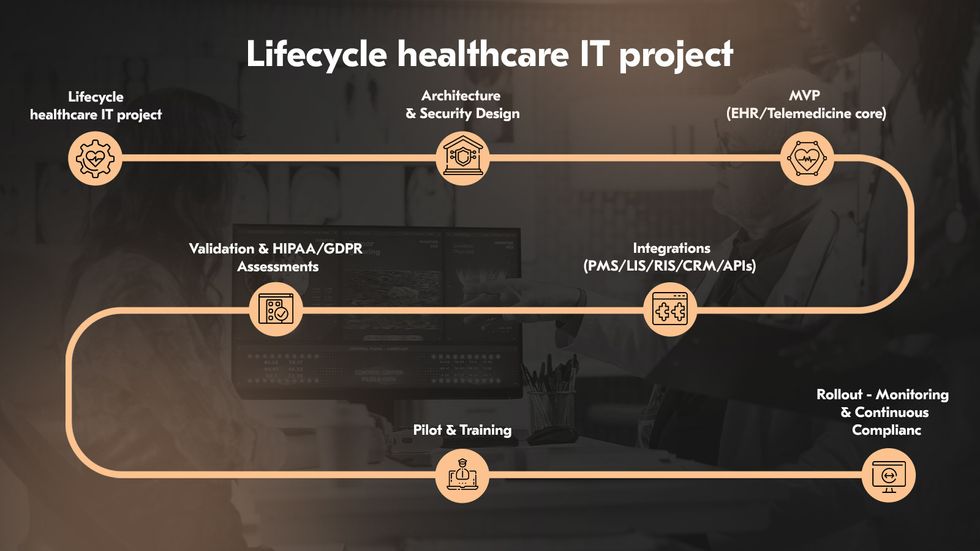
Best practices for healthcare IT solutions
Healthcare IT systems intersect with patient care, regulatory oversight, and organizational efficiency. Their development and deployment demand a disciplined approach where agility, compliance, and technological integration must coexist without compromise. Three practices are particularly critical for enterprises aiming to deliver safe, resilient, and future-ready healthcare technology.
Embed Agile and DevOps in healthcare projects
Healthcare environments are dynamic. Rigid development models often fail to keep pace. Agile methodologies provide the adaptability needed to respond to these shifts, while DevOps brings operational discipline by embedding automation, continuous integration, and monitoring into the delivery pipeline. Agile and DevOps establish a framework where features can be developed, tested, and deployed in rapid but controlled iterations.
Verify step-by-step HIPAA and GDPR compliance
Compliance is not a milestone to be ticked off but a process to be woven into every phase of the software lifecycle. HIPAA compliant software development requires strict safeguards for protected health information, including encryption, access controls, and audit trails. GDPR demands consent management, data minimization, and the ability to delete or export personal records on request. To manage these obligations, enterprises should adopt step-by-step verification: architectural reviews during design, secure coding standards during development, automated compliance testing in CI/CD pipelines, and penetration testing before deployment.
Integrate IoT and wearables
The expansion of IoT and wearable devices in healthcare creates opportunities for real-time data collection and personalized care. Yet it also expands the attack surface and introduces interoperability challenges. Best practice requires that integration with IoT and wearables is governed by standards such as HL7 and FHIR, supported by secure APIs and middleware capable of handling large, heterogeneous data streams. Security must extend to the devices through encrypted communication, secure firmware updates, and anomaly detection.
Ensure effective implementation and long-term support
Even the most advanced solution will fail if implementation is rushed or poorly supported. Adoption requires structured change management, tailored training for clinicians and staff, and clear communication of benefits to overcome resistance. Post-deployment, enterprises must demand long-term commitments from their partners for updates, patches, compliance adjustments, and performance monitoring. Continuous evaluation of usage data, clinical impact, and patient safety metrics allows organizations to refine systems, extend capabilities, and sustain value over time.
Examples from Acropolium’s portfolio illustrate this approach in practice:
In a project for predictive analytics in healthcare resource planning, long-term support ensured that hospitals could continuously optimize staff workload and patient flow, adjusting the system as demands evolved.
With an IoT-based emergency health monitoring system, post-deployment support focused on maintaining device interoperability and enhancing real-time alert accuracy, ensuring the platform’s reliability in critical care scenarios.
For a HIPAA-compliant medical app, ongoing updates and compliance monitoring allowed the client to keep pace with changing regulations while sustaining user trust and adoption.
How to choose the right healthcare software development company
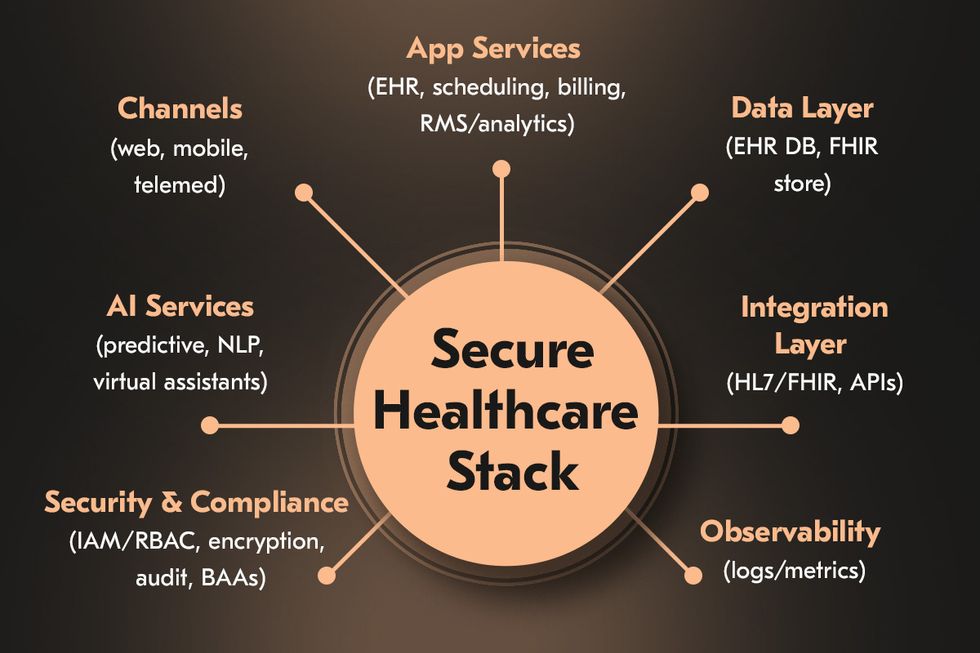
Choosing a reliable healthcare software development company is a critical decision for any enterprise, as the quality of the software directly influences patient safety, regulatory compliance, and the efficiency of care delivery. Mistakes in this domain can cause far-reaching consequences from operational inefficiencies to regulatory violations, financial penalties, and reputational harm. To mitigate these risks and maximize value, organizations should evaluate potential partners across several core dimensions.
Experience in regulated industries
Healthcare is a highly specialized field where general development experience is insufficient. A reliable partner demonstrates strong technical proficiency and an in-depth understanding of clinical workflows, compliance frameworks, and integration challenges. This expertise is best reflected in a track record of successful healthcare projects in production, delivering measurable improvements in efficiency, patient engagement, or clinical decision-making. A company’s capabilities should extend beyond coding into advanced areas such as AI for diagnostics, predictive analytics, and IoT for remote monitoring.
Demonstrated healthcare cases
Enterprises should look for tangible evidence of successful healthcare projects, whether in electronic health records, telemedicine platforms, diagnostic software, or patient engagement systems. Case studies, reference clients, and measurable outcomes demonstrate whether the partner has navigated the complexities of healthcare IT and delivered real value in production environments.
Certifications and compliance culture
Certifications are not optional in healthcare software development; they are proof of a company’s maturity and reliability. ISO 27001 confirms robust information security practices, ISO 13485 ensures compliance with standards for medical devices and related software, and documented HIPAA training demonstrates that development teams understand protected health information’s legal and ethical responsibilities. These credentials signal that a company knows the rules and has embedded compliance into its organizational culture.
Regulatory compliance and security standards
Strict regulatory frameworks govern healthcare, and compliance cannot be an afterthought. A qualified healthcare software development company must be able to build software in alignment with HIPAA and other applicable standards. Beyond this, the partner should demonstrate expertise in interoperability standards such as HL7 and FHIR, which enable data exchange across systems and institutions. Security must be treated as a core design principle, with encryption, authentication, and monitoring mechanisms integrated from the earliest stages of development.
Breadth of services and integration capabilities
Enterprises benefit most from partners that can provide end-to-end services not just in custom healthcare software development, but also with other offerings like AI, ML development, beginning with discovery and feasibility studies and extending through development, deployment, and long-term support. The supported solutions should cover the most critical healthcare systems: electronic health records, telemedicine platforms, data analytics, patient engagement applications, hospital management software systems, and medical imaging software.
Once a potential healthcare software development company demonstrates sector expertise, healthcare project experience, and compliance readiness, the focus should shift to leadership-level questions. These discussions reveal whether the partnership will deliver sustainable value, align with enterprise strategy, and withstand the pressures of regulatory scrutiny, technological change, and patient expectations.
Can the partner ensure compliance across multiple jurisdictions? Leaders must ask how the development company approaches compliance with HIPAA, GDPR, FDA requirements, and regional health acts simultaneously. The answer should go beyond checklists and demonstrate a culture of continuous monitoring, documentation, and audit readiness.
How is security embedded into the development lifecycle? Executives should ask how the partner applies encryption, authentication, and intrusion detection throughout the software lifecycle. They should also confirm whether the company conducts regular penetration testing and vulnerability scans and applies zero-trust principles.
How does the partner approach interoperability? Executives should press for evidence that the company has delivered interoperable solutions integrating EHR platforms, imaging systems, insurance databases, and medical devices. The ability to work with HL7, FHIR, DICOM, and ICD standards is critical for seamless data exchange and operational continuity.
What is the company’s track record with emerging technologies? Enterprises increasingly expect healthcare solutions to incorporate AI for diagnostics, predictive analytics for patient outcomes, IoT for remote monitoring, and blockchain for secure data sharing.
Asking these questions at the leadership level helps distinguish a vendor delivering software from a true strategic partner. The right company is one that not only meets today’s requirements but is also prepared to navigate future regulations, adopt emerging technologies, and scale with your organization’s vision.
Partner with us for secure and innovative healthcare IT solutions.








![Hotel Revenue Management Software [2025 Guide]](/img/articles/hotel-revenue-management-software/img01.jpg)

![ᐉ Why You Need Hotel Data Management to Increase Revenue [8 Examples]](/img/articles/hotel-data-management/img01.jpg)