
Key Takeaways
- Web app scalability allows it to handle growing amounts of user traffic, data, and resource demands while maintaining performance.
- A scalable web application offers companies reliability and security, high performance, enhanced user experience, easy maintenance, etc.
- Building scalable applications requires using independent nodes, caches, proxies, balancers, queues, and indexing.
Even if your app is not the second Facebook and doesn’t have to respond to billions of requests daily, it’s worth considering scalability improvement. A powerful server and a stable scalability architecture will enable gradual and consistent system growth.
In contrast, lack of scalability may cause performance failures, leading to audience loss and, accordingly, extra costs spent on attempts to improve resistance.
This post will reveal how to create scalable web application, drawing on the extensive expertise of the Acropolium dedicated team. Also, you will learn the benefits of such a solution, popular front-end and back-end frameworks, and examples of successful cases.
What is Web Application Scalability
A web app’s scalability is the product’s ability to withstand greater loads due to the increased number of users without a significant degradation in response time or overall system efficiency.
If your web app is about to serve a few hundred users with no prospects of significant growth, scalability might be an unreasonable waste of time and money. However, it’s a must-have for a modern startup or business that is about to increase the number of customers and serve a large audience’s needs.
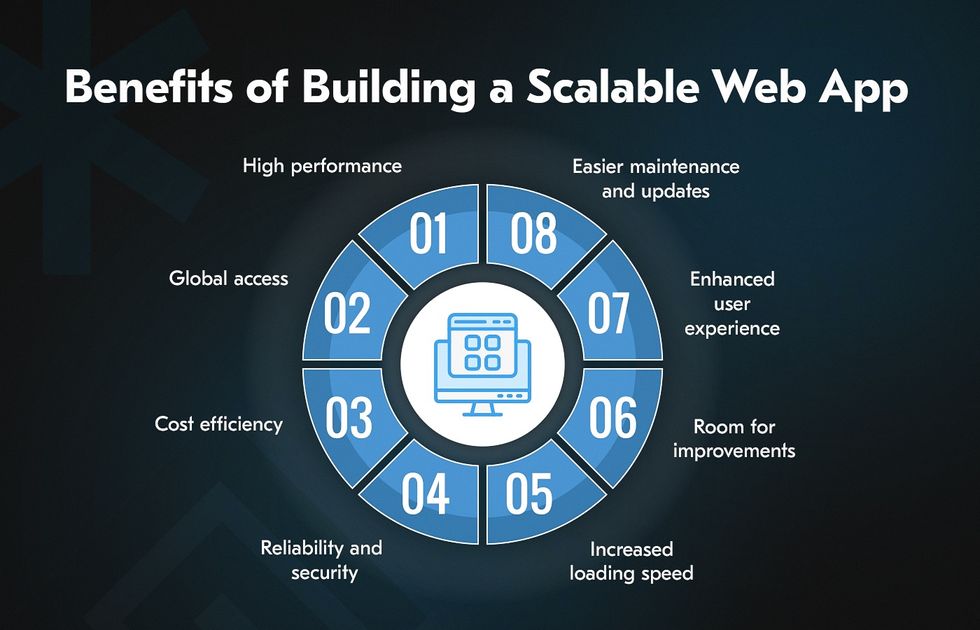
Benefits of Building a Scalable Web App
Before revealing how to make scalable web applications, let’s figure out what is special about such a product.
Lack of scalability may result in particular challenges if you don’t consider it when building an application from scratch. Whenever your web app experiences higher traffic or expands its capabilities, it might cause a loading speed decrease.
Moreover, you might need to handle constant system errors and crashes. At the same time, any changes you implement to the code and SaaS app architecture cause the system’s downgrades.
Strategic decisions — such as selecting a database system, designing the application architecture, or opting for a particular hosting environment — can have long-term consequences on your system’s ability to scale.
Additionally, external events like a viral campaign or sudden traffic spike can place unexpected demands on your infrastructure. Failing to prepare for these can harm both performance and reputation.
So, if you foresee your website growth and want to prevent the potential issues, consider the option to build scalable web applications from scratch due to its advantages:
High Performance
For large enterprises and businesses dealing with a broad audience, it’s vital to ensure the app is fully operational. Meeting the users’ needs and withstanding traffic will prevent huge revenue losses.
Scalability ensures the platform stays responsive even during usage spikes, reducing the risk of bottlenecks and downtime.
Global Access
A scalable web application can serve customers globally thanks to reliable server network solutions. Scalable infrastructures often use CDN and distributed architecture, enabling faster access for users across regions.
Cost Efficiency
The scalable system is often easier to manage and maintain, thanks to cloud solutions. Such services will normally cost you cheaper than in-house hardware and software maintenance. Rather than overspending on infrastructure upfront, scalable systems allow you to allocate resources dynamically, optimizing operational costs.
Reliability and Security
Cloud migration and multiple server solutions, with database replication and sharding, provide confidence in network security. Additionally, the system instantly recovers if anything goes wrong. Built-in redundancy and fault-tolerant systems further strengthen platform reliability, especially during unforeseen load increases.
Increased Loading Speed
One of the main causes of the users’ frustration is poor loading speed, forcing them to wait for their requests to be processed. Application scalability enables a shorter rendering time, leading to customer satisfaction and increased revenue. Fast-loading apps contribute to higher user retention and better search engine rankings.
Room for Improvements
Any changes you make to expand the system and add new features may affect its performance if your web app isn’t scalable.
With scalability in place, upgrades and feature rollouts are smoother, minimizing disruption and ensuring consistent performance.
Enhanced User Experience
A scalable web app provides a consistent and high-quality user experience, even during peak usage. Users are less likely to encounter slowdowns, errors, or downtime, contributing to overall satisfaction.
Easier Maintenance and Updates
Scalable architectures often involve modular components that can be updated independently. This makes maintenance and updates more straightforward, as you can introduce changes to specific parts without affecting the entire system.
Scalable Web App Architecture: Key Components
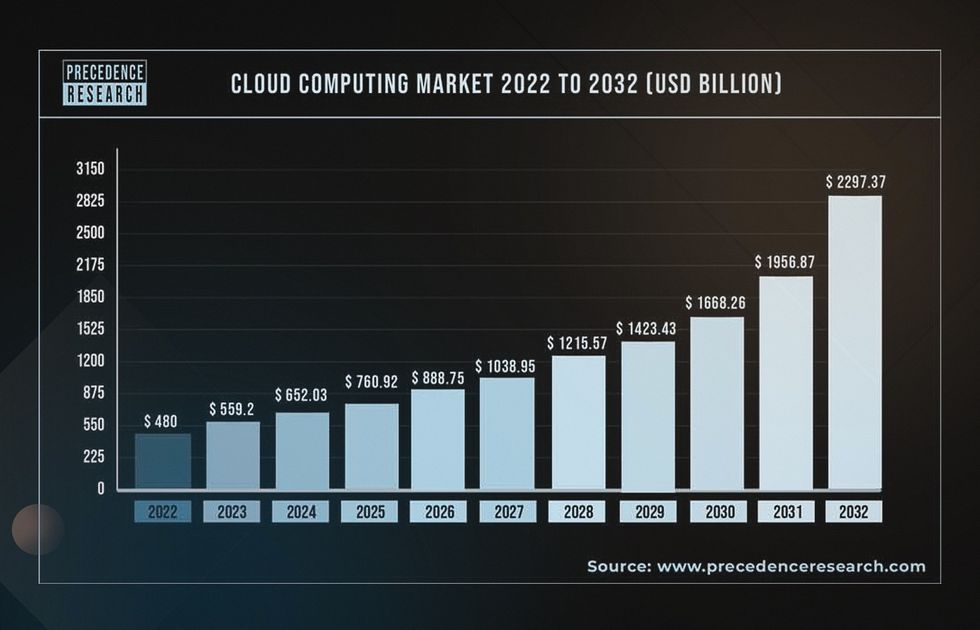
The expansion of cloud solutions is the best demonstration of the growth of interest in scalable web applications. In 2025, the worldwide cloud computing market is worth $912.77 billion. It’s anticipated to grow to $5,150.92 billion by 2034, showing a yearly growth rate of 21.2%.
Building a scalable web architecture is the key to success. Implementing core components to its structure will ensure you won’t have to rebuild the application or rewrite the code when the need to improve performance occurs.
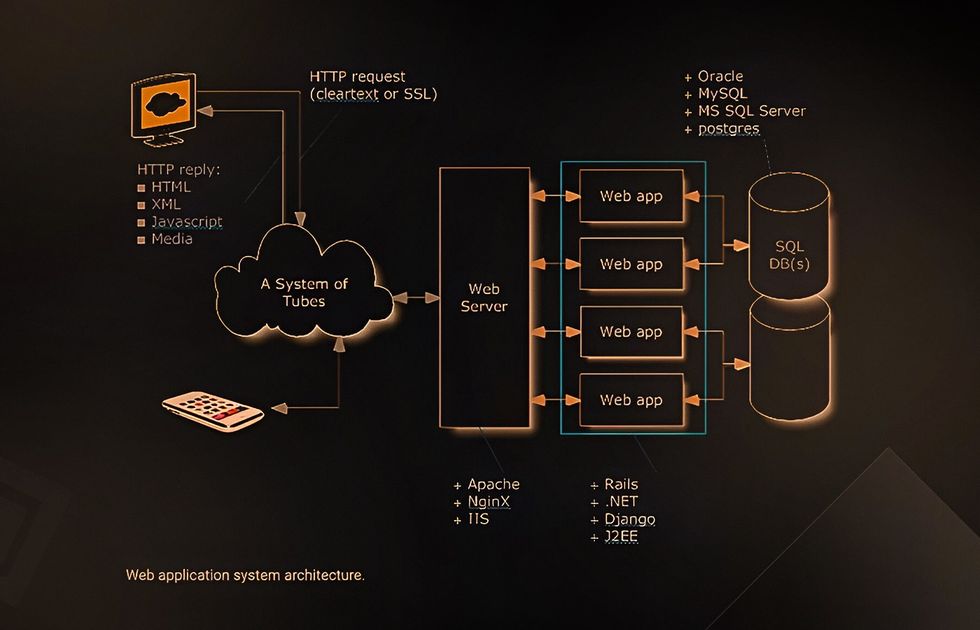
Frontend Architecture
In a scalable web application, the frontend’s efficiency entirely depends on the reliability of the backend. However, Content Delivery Network enables delivering heavy content to multiple locations via numerous servers. Thus, the end-users will be satisfied with the loading speed regardless of where the requests come from.
Moreover, modern scalable frontends increasingly rely on modular design principles, breaking UI components into independent, reusable parts that can be updated or replaced without affecting the entire system. This not only improves maintainability but also supports rapid iterations as traffic and feature demands grow.
Backend Architecture
Typically, all user requests are operated via a single server, resulting in failure and reduced loading speed. When such problems start to arise, it’s time to scale the server-side of your app. You can scale your web application’s backend in two different ways — vertical or horizontal scaling. Let’s overview them in detail.
Today, backend scalability is further enhanced through cloud elasticity, the ability to automatically adjust computing resources based on real-time demand. In this way, your application can scale up during peak traffic and scale down to optimize costs when demand is low. Elasticity is key to building responsive, cost-effective backends.
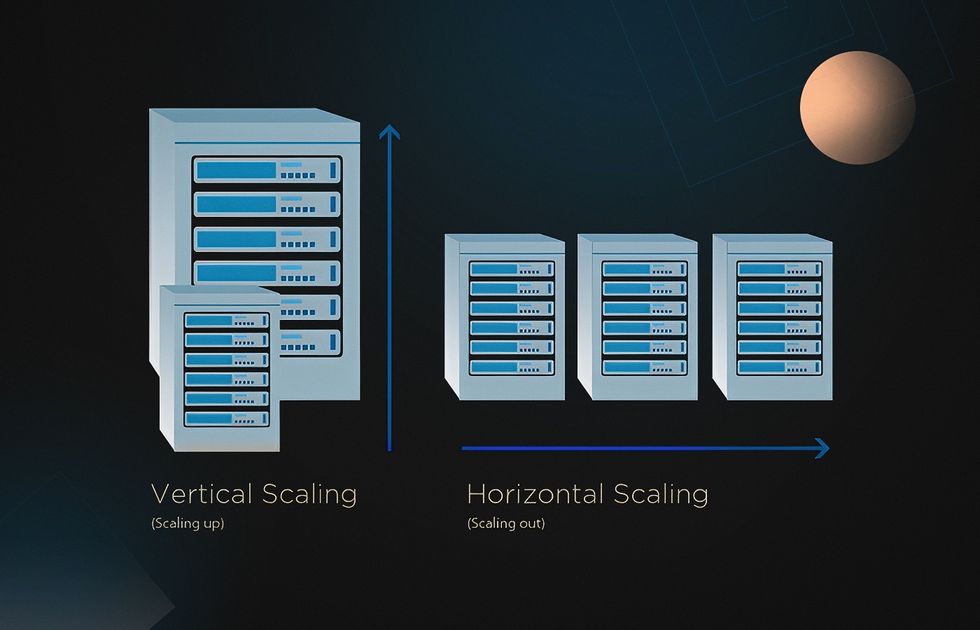
Vertical vs Horizontal Scaling
As mentioned above, vertical scaling involves enhancing the server’s, engine’s, and nodes’ capabilities to increase the application’s performance. This approach is quite efficient for solving temporary issues. However, vertical scaling won’t prevent performance challenges in the long run. Also, it doesn’t provide any alternative backing options in case of the system’s failure.
Horizontal scaling involves adding more servers and nodes to your system. Multiple servers will allow you to distribute the queries and thus reduce the load, eliminating the pressure on a single server. Moreover, if some part of your backend can’t handle the traffic, the entire system won’t crash.
It works best when paired with cloud elasticity, allowing additional resources to be provisioned or released automatically as needed. Combined with microservices and modular backend components, this setup supports continuous scaling without disrupting core functionality.
Database Scaling
Due to increased data volume and multiple simultaneous requests, the database can be difficult to manage. You can turn to the computing processes distribution like replication and sharding to address this issue.
Replication enables making database copies and processing certain parts of requests through the network. With its help, you will ensure data recovery and boost read performance.
Sharding involves distributing data via multiple databases to respond to some part of the queries. Thus, you can add more nodes when the number of users increases.
Additionally, elastic cloud databases allow you to scale storage and processing capacity independently, providing flexibility in response to workload fluctuations without compromising performance or reliability.
Multitier App Architecture
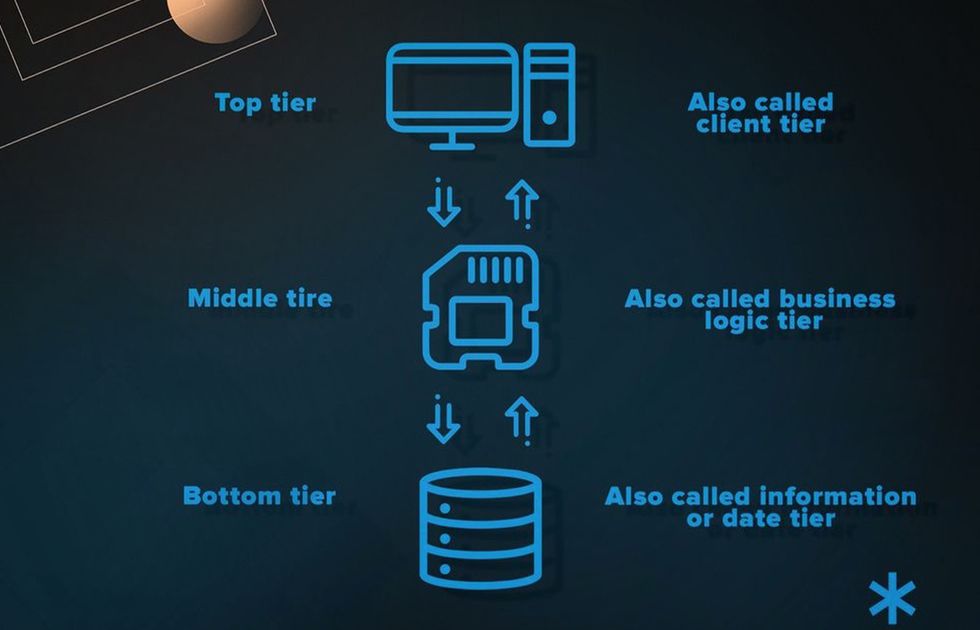
Multitier approach is often implemented to build a large scale web application architecture. Normally, it consists of three separate modules:
- The client-side server.
- The application server.
- The database server.
Every layer conducts its basic functions and isn’t overloaded with any extras. In particular, client-side modules are preliminary focused on serving the users’ direct needs. In turn, the database server runs data processing and granting access, not coping with static and middle-dynamic content.
This separation of concerns is a hallmark of modular architecture, which allows teams to scale or update each tier independently. When deployed in cloud environments with elastic scaling capabilities, multitier systems can dynamically adjust resource allocation across layers, ensuring stability and responsiveness.
How to Build Highly Scalable Web Applications
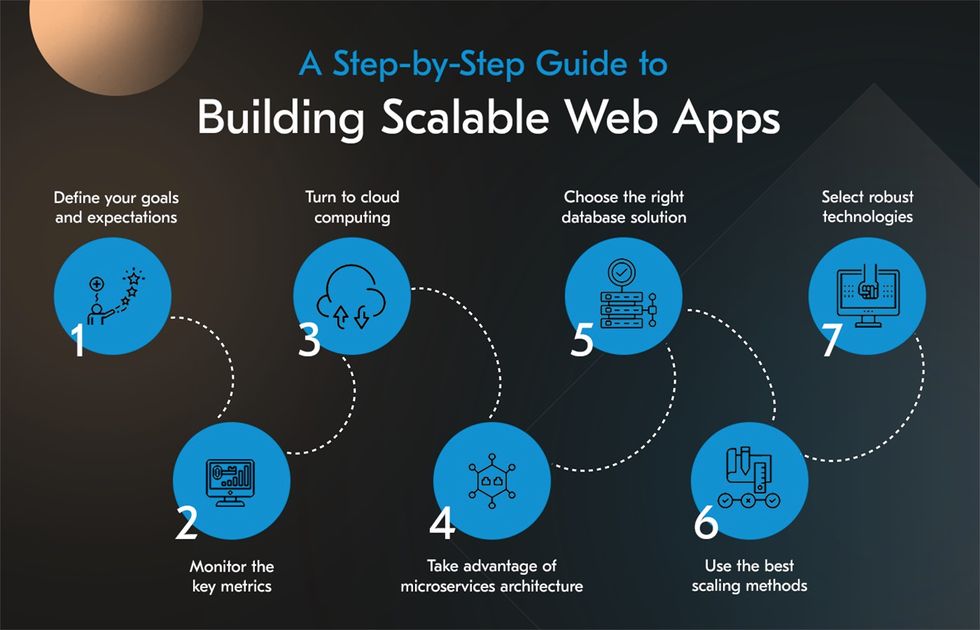
Let’s specify the key steps and efficient practices commonly used for building scalable web applications.
Define Your Goals and Expectations
Building scalable applications from scratch is quite a complex task to achieve, so you should ensure the funds and resources investments will be worth it.
- Web application scalability is crucial for a big project that experiences high traffic loads.
- Scaling your app makes the system more complex and multilevel, especially if you don’t turn to service vendors.
- Business and market research should prove the necessity to design a scalable web app.
Monitor the Key Metrics
Knowing how to build scalable applications is crucial but also you should consider their relevance through metrics and KPIs.
- CPU (Central Processing Unit) usage displays the percentage of CPU utilization over time.
- Network Input/Output shows the number of input/output operations generated by network processes that are neither reads nor writes.
- Disk Input/Output measures active disk input/output time in KB/s, including read or write operations.
- Memory utilization estimates average utilization statistics based on available memory percentage over time.
Turn to Cloud Computing
You can benefit from cloud-based services that offer options to improve the web app’s scalability for a reasonable price. Cloud providers offer networking, integrations, databases, secure storage, servers, etc. In 2024, AWS dominated the market with 30%, followed by Azure at 21%, and Google Cloud at 12%, totaling 63% of the market spending.
They will save you a lot of time and effort while improving your online platform’s manageability and performance. Moreover, you can take advantage of autoscaling. It can significantly decrease manual work and ensure scaling your app up and down when necessary.
Take Advantage of Microservices Architecture
Here are two basic tips to help you with scalable web application architecture.
- Prioritize the horizontal approach. Multiple servers will enable distributing the load and providing extra fallback opportunities. Also, they don’t restrict the scalability prospects.
- Use microservices architecture. It means that your web application’s architecture will consist of multiple independent modules, making them easier to build, deploy, and scale. According to Scholar Hat, about 73% of organizations currently use microservices architecture, while 23% of companies plan to do so.
Choose the Right Database Solution
Oracle leads as the world’s top database management system (DBMS), followed by MySQL and Microsoft SQL Server in the top three. However, your choice will depend on the data type.
If you need to store relational data, you may use MySQL, Microsoft SQL, or PostgreSQL database management systems. For non-relational data, turn to scalable NoSQL databases like MongoDB or MariaDB.
To improve efficiency and reach better scalability, you can combine SQL and NoSQL databases.
Use the Best Scaling Methods
Stick to these techniques to ensure your app’s high performance.
Independent Nodes
Separate your web app’s features and nodes into multiple modules. This approach will allow you to manage each node individually, expand the app’s functionality, and avoid contradictions between nodes and functions.
Caches
The caches may be placed in each requesting node, or you may use a global cache. It will instantly allow finding information without overloading the database. The temporary memory will constantly be updating, storing the frequently requested data only.
Proxy
Proxy servers provide a smoother gateway between users and the Internet. You can use them to coordinate requests on your multiple servers. When combining proxy and caches, you can accelerate the response time and unload the database to improve performance.
Balancers
When the number of requests per minute grows, balancers redirect them to numerous nodes. It will facilitate the routing of traffic between users and servers.
Queues
Commonly, a customer cannot complete any operations in your web app until it responds. However, a queue solution enables users to do something else and regularly check whether the system has processed the request.
Indexing
Indexing is used for efficient database management. Indexes are kept as a dataset informing about the location of certain data pieces. When a request comes, indexing directs it to the right place instead of searching it throughout the whole database.
Select Robust Technologies
Choosing the right technology to make a scalable web application is critically important. The chosen tech stack should be suitable for scaling, have a sufficient developers’ community, and completely match your product’s functional requirements.
The Most Popular Scalable Web App Frameworks
Here are the most probable technologies to choose from:

Angular
Developed and maintained by Google, Angular is a JavaScript-based web framework known for its efficiency and rapid development. It excels in building the front end of web applications, particularly single-page web applications. Choose Angular for scalability and high performance, especially in crafting interactive social sites. Google uses it for services like Google Search, YouTube, and Google Translate.
| Angular | |
|---|---|
| Pros | Cons |
| A comprehensive set of tools | Steeper learning curve |
| Simple data synchronization | Large file size |
| Strong community support | Integration difficulties |
| Cross-platform development | |
Laravel
Laravel is a leading PHP-based web development framework following the Model-View-Controller (MVC) pattern. Web developers choose it for robust functionalities like authentication, API integrations, vulnerability handling, automation web testing, and caching. Laravel is perfect for large web apps like online communities, eCommerce, social networks, CRM, and CMS systems.
| Laravel | |
|---|---|
| Pros | Cons |
| Clean and elegant syntax | Limited to server-side rendering by default |
| MVC architectural pattern | Heavyweight for small projects |
| Robust built-in tools | |
| Blade templating engine | |
| Great deployment and management options | |
React
Developed by Facebook, React is a JavaScript library for crafting user interfaces, especially single-page applications. Widely acclaimed for its versatility, React is popular with industry leaders like Facebook, Instagram, and Netflix. Opt for it to get dynamic updates in large web apps without full reloads. Also, React offers a native experience across various platforms.
| React | |
|---|---|
| Pros | Cons |
| Virtual DOM for updates and rendering | Steeper learning curve |
| Component-based architecture | It’s not a full-fledged framework but a library |
| Has a large community | Tooling complexity |
| Easy integration with other libraries or frameworks | |
| Unidirectional data flow | |
Java Spring
Spring is a popular Java framework with an impressive developers’ community. It can perform various tasks, including data processing and security. Spring technology is a great option for those who prefer the Java ecosystem and create a scalable web app with microservices architecture.
| Java Spring | |
|---|---|
| Pros | Cons |
| Well-established documentation | Complexity |
| Support provided by Oracle | Difficulties in learning |
| Huge developers’ community | |
| Flexibility and reliability | |
Node.js
Node.js is one of the most popular options used by giants like Netflix, Walmart, Paypal, etc. This framework significantly facilitates processing requests and balancing the load. Also, it offers a cluster module and an event-loop mechanism. Additionally, Node.js technology is extremely efficient in applying microservices.
| Node.js | |
|---|---|
| Pros | Cons |
| High level of scalability | Poor library support |
| Well-established performance | Unstable API |
| Caching options | Lacks heavy CPU-tasks performance |
| Multiple functions for processing requests | |
| Microservices-friendly | |
| Simple to learn | |
Django
Django is majorly used for building web applications. The main advantage of Django technology is the great variety of functions, including free API, URL routing, database migrations, etc. Besides, Django is the preferred solution for modern advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and Machine Learning.
| Django | |
|---|---|
| Pros | Cons |
| Numerous functions | Monolithic files structure |
| Advanced development capabilities | Multiple simultaneous requests incapability |
| Faster development | Lack of conventions |
| Security | |
Ruby on Rails
Ruby on Rails (RoR) is another popular choice for scalable application development, used by Shopify, Airbnb, etc. This technology is based on the principle that combines model, view, and controller. RoR is famous for its time-efficiency and impressive bunch of useful functions. Its libraries include many helpful tools to improve your code when required.
| RoR | |
|---|---|
| Pros | Cons |
| Time-efficiency | Lack of flexibility |
| Rich libraries and helpful tools | Longer performance time |
| Active community | |
| Easy to learn | |
7 Examples of Successful Scalable Web Applications
Let’s take a look at seven impressive examples of scalable websites.
Shopify
Shopify is a famous Canadian eCommerce platform used by more than 1 million clients in the United States only. Online retailers can use its marketing, payment, shipping, and customer service tools with this platform. Shopify allows its clients to start a business or move the existing one online.
Walmart
Walmart is an American retail corporation operating a huge hypermarket chain and stores. Its history dates back to 1945. The fact that Walmart is the biggest retail enterprise in the world helped it rapidly build and scale its online platform, capable of competing with web giants like Amazon.
Dropbox
Dropbox is a world-famous file hosting service. It’s especially famous for secure file storage, efficient collaboration options, and multiple features that serve numerous business needs. Currently, the Dropbox platform has over 700 million registered users around the world.
Netflix
Netflix, the renowned streaming service, excels in scalability. With 247.2 million paid subscribers, it uses cloud infrastructure and advanced CDNs for seamless streaming experiences, even during peak usage.
Airbnb
Airbnb connects hosts and travelers worldwide, efficiently managing millions of listings, bookings, and search queries. In 2022, the company had over 393 million booked nights and experiences. The scalable architecture ensures a great user experience amid high traffic and demand spikes.
Instagram handles billions of photo and video uploads, likes, comments, and messages daily. Its scalable backend, which is built on cloud services and microservices, allows it to deliver smooth performance and instant content loading for over 2 billion monthly active users globally.
Slack

Slack is a popular communication platform used by businesses of all sizes and 80% of Fortune 100 players. As it supports real-time messaging, file sharing, integrations, and video calls for millions of users simultaneously, Slack’s scalable cloud-native architecture comes as an agile, responsive tool under heavy enterprise usage.
Build a Scalable Future for Your Web Application
Scalability is not just a fashionable trend. Creating such an application will ensure you can overcome increasing traffic challenges, withstand the competition, and satisfy your users, converting these benefits into revenue.
Hopefully, our guide on how to build scalable web applications helped you realize the value of such solutions and get useful insights. But if you still have any questions related to the topic, we at Acropolium are always ready to give you a hand.
Acropolium has 20+ years of experience in delivering web apps. We serve 13+ industries, including transportation and logistics, hospitality, healthcare, fintech, retail, risk management, etc. Our developers are helpful in web app development (including Backend-as-a-Service), database management, cloud solutions, and re-engineering services.
Acropolium has helped numerous retail clients transform their omnichannel strategies and adopt AI-driven technologies to support sustainable growth. Here’s one example of how we’ve delivered measurable impact:
Dealership Management Software Modernization
A rapidly growing automotive retail chain with a vast network of European dealerships representing 20+ car manufacturers needed to overhaul its dealership management ecosystem.
Years of fragmented tools and disconnected workflows resulted in inefficiencies, inconsistent data, and delayed customer service. The client required a scalable, cloud-based solution to unify dealership operations and support long-term expansion.
Solution
We developed a centralized, cloud-native automotive dealership platform designed for operational scalability and digital transformation with the following functionality:
- Cloud migration to Microsoft Azure with Kubernetes and Docker for scalable infrastructure and reduced maintenance overhead.
- Centralized modules for inventory, sales, service, and customer management, ensuring consistent workflows across all dealership locations.
- Automated routine operations (vehicle intake, servicing, inventory updates) to minimize manual errors and speed up service.
- Real-time data synchronization, providing instant visibility into vehicle stock, service status, and customer records.
- Seamless integrations with OEM platforms and CRM systems for unified communication and personalized outreach.
- Predictive analytics to forecast service demand and optimize inventory planning.
- Mobile-optimized user portals built for both dealership staff and customers.
Results
- 20% increase in operational efficiency due to automation and real-time data access
- 15% growth in customer retention through faster service and personalized engagement
- 30% reduction in infrastructure costs following the migration from on-premise systems
- Scalable architecture enabling rapid expansion into new geographic markets
- Improved accuracy and decision-making from centralized data and integrated analytics

You can familiarize yourself with our latest cases, for example, the modernization of a legacy ERP system for an oil & gas company, digital signage bespoke software, and payment system.
Get in touch to have a consultation with our experts how to build a scalable application.







![5 Benefits of SaaS Software for Your Business [2025 Guide]](/img/articles/benefits-of-saas/img01.jpg)
![SaaS Migration Strategy: [Why Move to SaaS and How to Do It]](/img/articles/saas-business-model/img01.jpg)

![How to Build a SaaS MVP [2025 Step-by-Step Guide]](/img/articles/build-saas-mvp/img01.jpg)
![Fintech SaaS Solutions in 2025 [Custom vs. Off-the-Shelf]](/img/articles/fintech-saas-solutions/img01.jpg)
![ᐉ Choosing a Technology Stack for SaaS Development [2025 Guide]](/img/articles/technology-stack-for-saas/img01.jpg)