
Key Takeaways
- The value of the SaaS development market is expected to hit nearly $200 billion in 2023.
- There are multiple SaaS software vendors targeting different lines of business (LOBs) to help companies achieve their business goals.
- SaaS apps provide many benefits to customers, from cost efficiency to increased team productivity and operational agility.
- Still, developing SaaS software brings multiple challenges, including cybersecurity, connectivity, compliance, and data migration. Partnering with a reputable SaaS development company is one way to overcome these challenges.
Are you planning to serve small and medium enterprises by delivering SAAS solutions and now understand you need help to build a SaaS MVP? Or probably, you are looking to develop a combined solution: the one that you can use for your internal processes and deliver to other small and medium-sized businesses within the SaaS business model?
If either of your answers is yes, you’re not alone. Software-as-a-service advantages range from lower upfront investment costs to enabling remote work with higher productivity for a distributed workforce. This provides increased business agility and is a major reason for the growing popularity of SaaS solutions, with end-user spending on SaaS expected to reach nearly $200 billion in 2023.
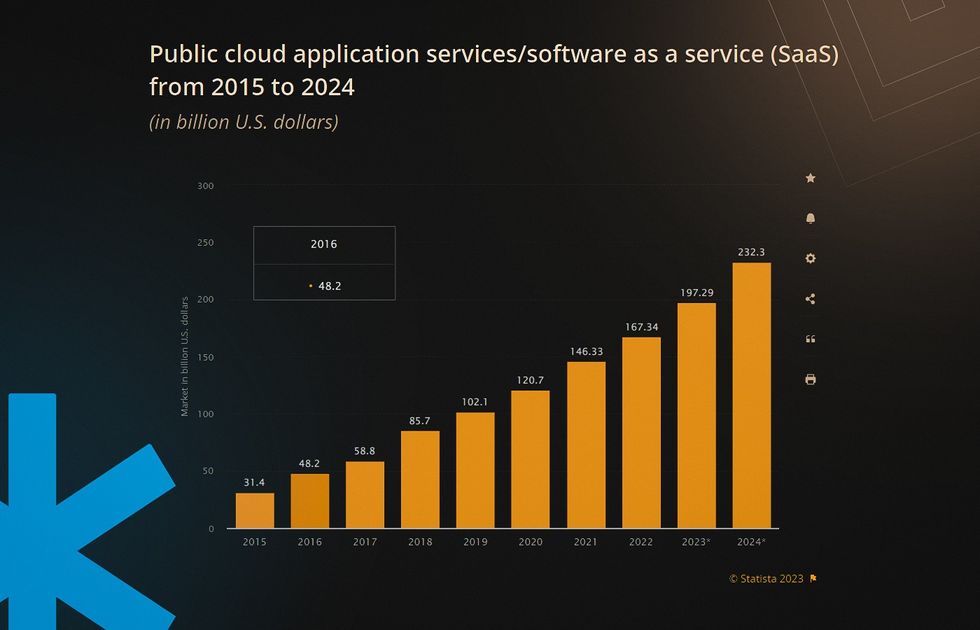
It’s normal to want to profit from the trend, but SaaS development carries its own challenges compared to developing standalone solutions. For successful sales, you also need to understand what your target business customers will expect from a SaaS solution.
This article will guide you through the basic benefits of the SaaS model, how to deliver on your promises in different lines of business, the challenges you can face, and how you can overcome them.
Understanding SaaS Software Architecture

From a technical standpoint, a SaaS-based application is a solution that’s accessible over the internet and requires no installation on the target device.
At the same time, many SaaS software solutions offer installable components and optional features, most of which are dependent on a subscription level. Therefore, SaaS app development services imply creating a modular solution, where certain features can be enabled or disabled based on the subscription type.
These requirements impose certain technical demands on SaaS software architecture. For example,
- A SaaS platform must be a cloud-based product with a separation at the database level (single-tenant or multi-tenant) and advanced security features.
- It must also be able to scale easily to meet changing business demands.
- It should also have API integration capabilities for cohesively building it into the customer’s software toolkit, as well as automated updates and built-in analytics.
These things make SaaS architecture quite different from that of on-premise software, which is usually monolithic, must be run, maintained, and updated by the user, and provides few or zero usage analytics.
Salesforce, Slack, and Zendesk are examples of widely known SaaS apps, but there are many other types of SaaS enterprise applications, which we’ll discuss later.
For now, let’s compare SaaS vs traditional software models.
What Is a SaaS Business Model, and How Is It Different From the Traditional One?

We can understand the SaaS business model better by comparing traditional software with the SaaS setup. With on-premise software, customers pay upfront for a complete app with predefined functionality, and they’re on their own after that. When customers demand new features or better performance, they have a choice — wait for a new version, or go to a competitor that provides it.
This changes with SaaS. The key differentiator of the software-as-a-service business model is that the platforms you develop run on your infrastructure, and customers only pay for the features they use on a subscription basis. This is great for customers, but creates a risk for you as a vendor, as your customers, small and medium-sized businesses, can change the software they use at any time. As a result, quality customer service and timely updates are key.
What’s more, since SaaS products are available over the web, your customers don’t need to periodically upgrade or purchase a new version; instead, the software is constantly updated over the internet.
These are two main advantages of software-as-a-service products for small and medium-sized businesses (as well the other user categories), but there are many more. Let’s take a look at them now.
The Advantages of SaaS Software for Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises
Showing you walk the talk (in terms of effectively solving the problems of small and medium-sized businesses) is essential for building trust and closing a sales deal.
Given that, you need to clearly understand the software-as-a-service benefits your solution brings about. Here are the main things to consider.
Cost-effectiveness
One of the biggest software-as-a-service advantages for small and medium-sized businesses is that they don’t need to invest in internal IT infrastructure since hosting is handled by the SaaS-based platform vendor.
SaaS subscription plans scale linearly, based on the number of users, requests, or other product-specific actions performed by customers. Software costs are predictable, so businesses using your solution can plan months ahead.
Accessibility and Mobility
With the WHO declaring the COVID-19 pandemic over, enterprise mobility is once more top of mind. Employees don’t just need access to all their enterprise systems from home — they also need access from any device, and from any location with an internet connection.
Available over the web, SaaS enterprise software ticks all these boxes, as it allows a distributed workforce to use it 24/7.
Scalability
The upcoming recession has highlighted the importance of operational flexibility. The software businesses use should be able to scale down to cut costs where necessary and rapidly scale up during peak demand periods.
One of the key benefits of the software-as-a-service approach is that different service packages can be activated or deactivated as needed. Subscription-based pricing helps businesses allocate their resources appropriately and only pay for the features they use.
Security and Reliability
Accessing corporate digital assets from a wide range of personal devices across public networks naturally raises security concerns. While addressing them may be beyond the capacity of an SME, a reliable SaaS application development company (like you) has all the necessary resources to protect business-critical data with strong security and user authentication measures, data protection compliance, and a robust recovery strategy. What’s more, automatic updates maximize reliable service delivery.
Improved Efficiency and Productivity
One of the biggest SaaS benefits for a business customer is a multitude of integration possibilities. Integrations connect disparate islands of data and functionality into a cohesive system that drives business efficiency. Streamlined data sharing with integrated applications also boosts productivity, giving your clients a competitive advantage.
Now that you have a basic understanding of why your clients across domains might want to use SaaS software, let’s answer another question: what types of SaaS software exist?
Types of SaaS Software

The key aspect of the software-as-a-service model is that every business can tailor its choice of software and features to its strategy and needs. Some SaaS software development companies provide a wide range of building blocks to cover all business requirements, while others concentrate on particular lines of business (LOBs).
Below are the most common types of software that you, as a SaaS software provider, can offer to small and medium-sized enterprises (and/or use it to streamline your internal operations).
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Software
Examples: Salesforce, Zendesk, and Zoho.
When building SaaS CRM software, it’s important to ensure it supports the revenue-making processes at the heart of every business.
This means it should provide all the required features, such as user management, access control, canned replies, integrations with the customer support center and knowledge base, and more. More importantly, it must offer flexible business rule editors, to enable the creation of bespoke business logic workflows.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Software
Examples: Microsoft Dynamics, SAP.
A SaaS ERP software solution is the tool organizations use for the daily management of various business processes, from procurement and logistics to internal training and accounting. As such, it must be able to obtain data from any system, process it, and upload the results in different formats to different destinations.
Important functions include data analytics, scheduling, paperwork automation, notifications and reminders, and task management.
Accounting Software
Examples: Quickbooks, Freshbooks, Eleven.
SaaS accounting software is essential for keeping track of an organization’s income and expenses and ensuring stable cash flow.
Key required features are general ledgers, a chart of accounts, transaction recording, management of accounts, invoicing, tax calculation, and account reconciliation. Some of these can be provided as part of a subscription package, while others will require API integration.
Project Management Software
Examples: Asana, Jira, Wrike.
SaaS project management software is important for keeping track of daily tasks, viewing staff workload, and evaluating the efficiency of resource allocation.
Thus, it must provide integration with external sources like Dropbox and Github to store attachments and code repositories. It must also integrate with various calendars and email systems to enable centralized progress tracking and support time-tracking.
Content Management System (CMS)
Examples: WordPress, Drupal, Joomla, Magento.
SaaS CMS software oversees the way a business interacts with its audience through content such as blog articles and landing pages, testimonials, banners for marketing, and knowledge bases.
As a result, it must provide features such as a WYSIWYG and HTML editor, media processing capabilities, post-scheduling, and integration with Google Analytics and other tools.
Sales, Marketing, and E-commerce
Examples: Magento, HubSpot, ClickUp.
These solutions and their features are too numerous to list, but they are hard to overestimate. Every business selling online uses some kind of SaaS e-commerce platform or sales/marketing tool, and the only way to convince them to switch to yours is to offer functionality the client needs but competitors don’t provide.
As you can see, the market is broad. Yet reaping all the benefits of the SaaS business model is hard. Let’s take a look at the main implementation challenges you might face when developing a SaaS solution.
The Challenges of SaaS Software Implementation

Developing SaaS software isn’t hard, but it’s important to understand the process. Here’s a list of the most common challenges SaaS software development presents, some of which stem fromSaaS disadvantages:
- Integration with existing systems. For successful SaaS app development, you need to ensure integration with all apps your target small and medium-sized enterprises are likely to be using. The key is to list them all from the start, and maybe include alternatives. Having ready API connectors for typical integration needs is also a good idea.
- Security concerns. Cybersecurity is an essential aspect of SaaS, as every device can become an intrusion point. Building a robust solution with all security measures in place and kept at the required level is paramount.
- Data migration. Migrating large amounts of data from existing systems to a new SaaS platform takes time and careful planning to avoid disrupting normal business operations. As is hard to do without experience in enterprise-grade data migration, you’ll probably need to empower your clients with data migration services.
- Heavy reliance on internet connection. Cloud hosting is simultaneously one of the biggest advantages and disadvantages of SaaS. The client must ensure stable uplink and availability of backup access, while you need to include failover contingency scenarios to ensure minimal downtime if the connection is lost.
These challenges are just the tip of the iceberg, as every project will face unique issues based on the client’s existing software kit, processes, business strategy, and budget. This is why partnering with a web development agency with a proven reputation can be a wise move.
Why Choose Acropolium?

With 20 years of expertise in IT outsourcing, app development, and modernization, 170+ completed projects, 50+ custom high-load solutions, and 4 customers from Fortune 500, Acropolium can lend a hand to any vendor. We can form a dedicated team of certified specialists to handle any aspect of your project and provide technical help and consulting.
Whether you need to build an MVP fast, perform a challenging legacy system modernization, or fine-tune your SaaS product technology stack, we can guarantee timely, effective, and cost-efficient service.
Final Thoughts
There are many pros and cons of SaaS software development. The ability to unite disparate islands into a cohesive system is definitely a plus. However, the reliance on internet access to use the platform poses a significant risk to operational stability.
In addition, there are many challenges to overcome, from compliance and security to handling data migration. Partnering with a reliable SaaS development company is a good way to get the most out of the benefits of SaaS for a business.
As a reliable SaaS application development services provider, Acropolium works on GDPR-compliant software under ISO-verified processes. We use cutting-edge solutions like serverless, AI, microservices, IoT, and low-code tools to deliver products that help businesses achieve their goals. If you’d like to discuss how Acropolium can help your company, get in touch today!







![AI in SaaS: [How AI is Transforming the SaaS Landscape]](/img/articles/ai-in-saas-how-ai-is-transforming-the-saas-landscape/img01.jpg)
![ᐉ Biotech Software Development: Trends & Benefits [2026 Guide]](/img/articles/biotech-software-development/img01.jpg)
![Fintech SaaS Solutions in 2025 [Custom vs. Off-the-Shelf]](/img/articles/fintech-saas-solutions/img01.jpg)
![Building Logistics SaaS Solutions [5 Use Cases & Key Benefits]](/img/articles/saas-for-logistics/img01.jpg)

![Microservices Architecture [Implementation Benefits]](/img/articles/microservices-architecture-implementation/img01.jpg)