
Key Takeaways
- The role of big data in supply chain is pivotal in improving demand forecasting, inventory management, risk resilience, and personalized customer experiences.
- Source examples of big data in supply chain include IoT devices, ERP systems, customer feedback, and external data about weather and traffic.
- Successful big data in supply chain examples are Procter & Gamble, Amazon, General Electric, Siemens, DHL, Nestlé, Walmart, UPS, and Coca-Cola.
Worried about rising shipping costs, labor shortages, geopolitical issues, and other industry disruptions? Most of the challenges can be minimized with the help of big data in supply chain management, as a leading trend that impacts the sector.
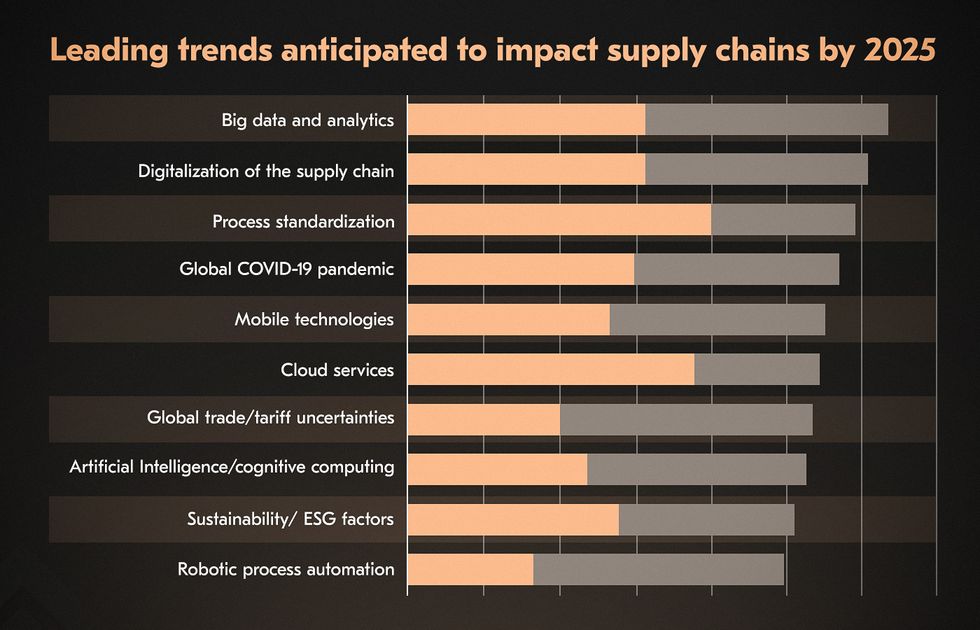
By leveraging real-time data from GPS, ERP, and social media, companies improve visibility, forecast demand, and optimize routes. Big data supply chain streamlines operations, reduces costs, and enhances customer satisfaction by enabling proactive responses to obstacles.
In this article, we will discuss how big data is used in supply chain, considering its benefits, types of data sources, popular use cases, and implementation challenges.
What Is Big Data in Supply Chain?
Big data in the supply chain refers to the structured and unstructured data gathered at various stages. It provides a comprehensive view that enhances process visibility, improves demand forecasting, and optimizes inventory management.
Typical data sources in the supply chain include:
- IoT in equipment, vehicles, and facilities tracks temperature, location, speed, and machine performance.
- ERP systems capture essential internal data, including inventory levels, order statuses, procurement, and financials.
- Data from customer reviews and service interactions provide insights into product satisfaction, delivery times, and areas for improvement.
- Weather conditions and real-time traffic are crucial for managing disruptions and optimizing routes.
Benefits of Big Data in Supply Chain

How is big data used in supply chain? Let’s find out exactly how technology overcomes industry challenges and helps companies succeed.
1. Enhanced Demand Forecasting
Big data and supply chain enable more accurate demand forecasting by analyzing historical sales data, market trends, and real-time conditions. Adjust inventory in real time to avoid overstocking items unlikely to sell and ensure that popular items are available.
2. Better Visibility and Transparency
Big data consolidates information across all supply chain stages — from raw materials to warehousing and delivery. Monitor the location and condition of shipments through GPS and IoT devices to detect delays or issues as they happen. Also, you can analyze data from manufacturing and assembly lines to identify bottlenecks or inefficiencies.
3. Inventory Optimization
By aligning stock levels with actual demand, you avoid overstocking, which ties up working capital and increases holding costs. Real-time data enables businesses to quickly restock fast-moving items and ensure products are available when customers want them.
4. Improved Logistics and Transportation
Real-time data from GPS, traffic updates, and weather conditions allow companies to adjust delivery routes on the fly. This way, you update schedules and predict delays more accurately. By tracking vehicle performance and fuel usage and optimizing routes, you will reduce expenses and stay more sustainable.
5. Risk Management and Supply Chain Resilience
Analyze patterns and external factors such as weather, political instability, or natural disasters to prepare for potential disruptions and act quickly to minimize their impact. In case of emergencies, identify backup suppliers and provide alternative transportation routes.
6. Personalized Customer Experience
Supply chain and big data enable supply chains to become more customer-centric by tailoring offerings and services. It becomes real thanks to purchasing history, preferences, and demographics. Providing timely, accurate, and personalized service builds trust and customer satisfaction, increasing long-term revenue potential.
Big Data Sources in Supply Chain
Now that you know the advantages of big data in supply chain, it’s time to figure out what sources provide this data:
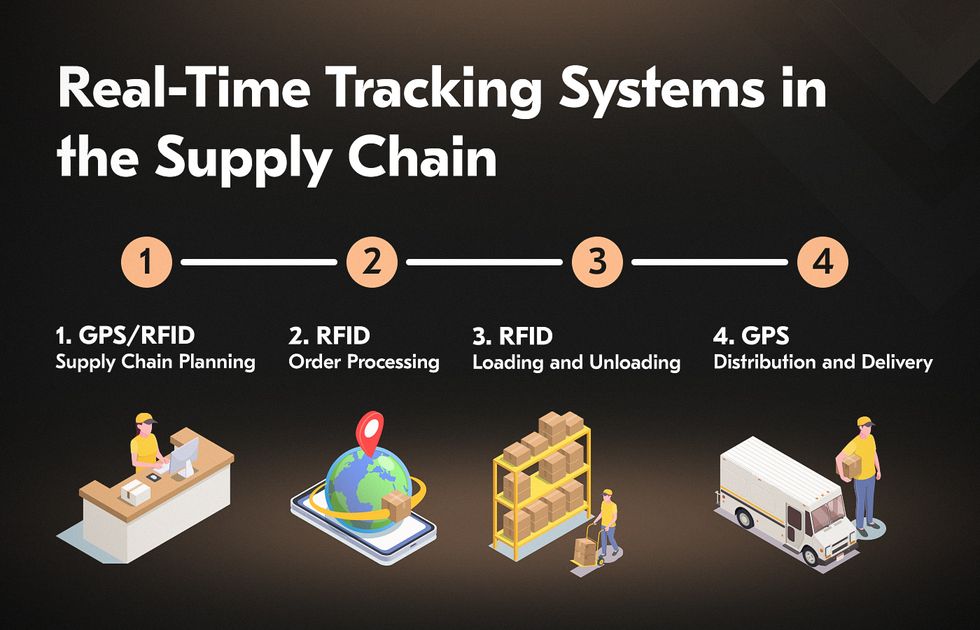
Real-Time Tracking Systems
GPS and RFID systems track shipments, helping prevent losses, manage inventory better, and quickly resolve delivery issues. Customers also benefit from real-time updates on their orders.
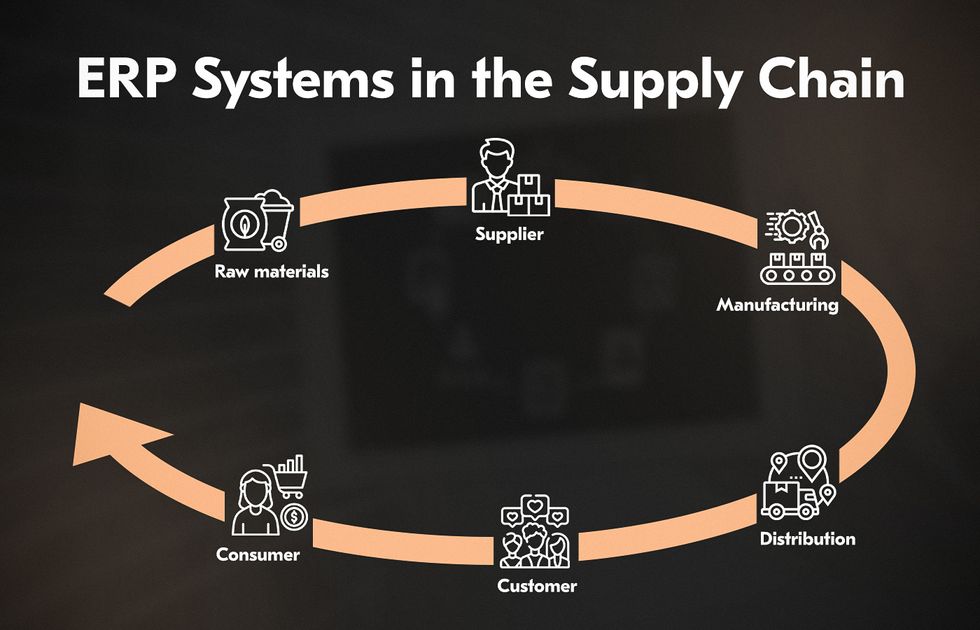
ERP Systems
ERP systems integrate data from various business areas like inventory and orders, offering a clear overview for better decision-making. This helps businesses predict demand, allocate resources, and reduce waste.
Social Media Insights
Platforms like Twitter and Facebook provide updates on market trends and disruptions like natural disasters or strikes. Companies use this information to adjust routes or suppliers, minimizing risks and keeping operations smooth.
Use Cases and Applications of Big Data in Supply Chain
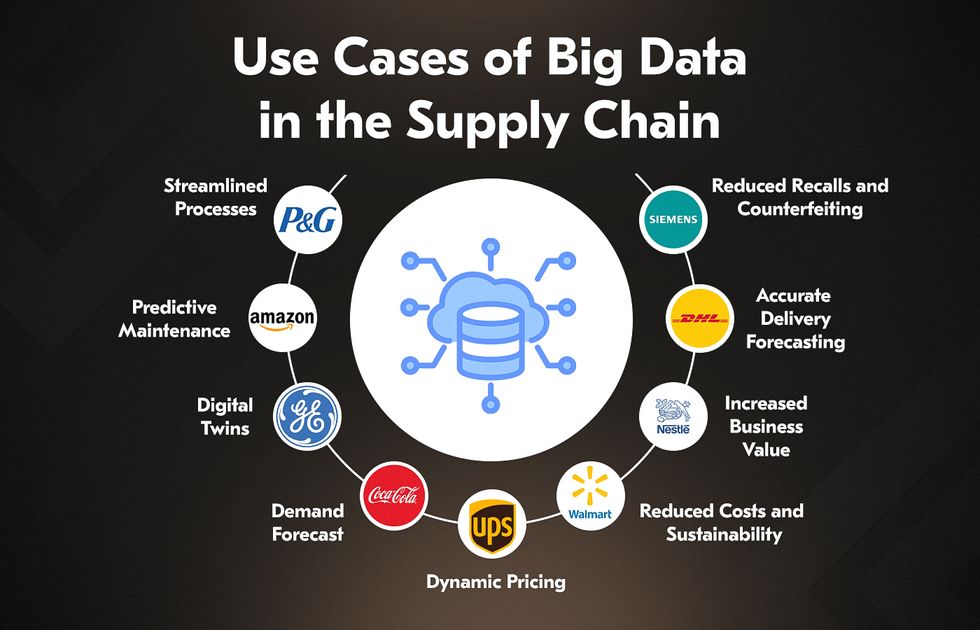
How can big data be used in supply chain? Let’s consider the most popular applications by discovering big brand examples:
Procter & Gamble: Streamlined Processes
Big data helps companies reduce unnecessary steps and integrate data-driven decisions. For example, in India, Procter & Gamble has achieved a 60% reduction in supply chain touchpoints compared to previous years. It led to faster operations, lower costs, and improved efficiency.
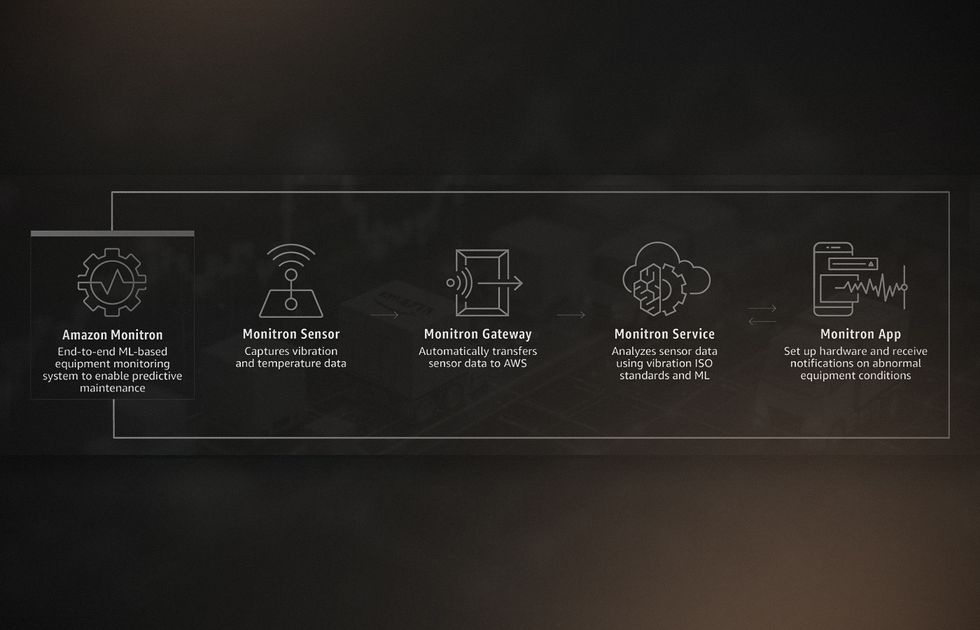
Amazon: Predictive Maintenance
Amazon deployed over 104,000 Amazon Monitron sensors to monitor 34,810 assets across 192 factories. Using big data for supply chain, the company achieved a 69% reduction in unplanned equipment downtime, saving approximately $37.83 million.
General Electrics: Digital Twins
Digital twin technology enables real-time simulation and optimization of physical assets or processes. General Electric’s Proficy CSense uses Process Digital Twins to address challenges like demand fluctuations and workforce gaps, reducing product waste by 75%, quality complaints by 38%, and increasing throughput by 5%-20%.
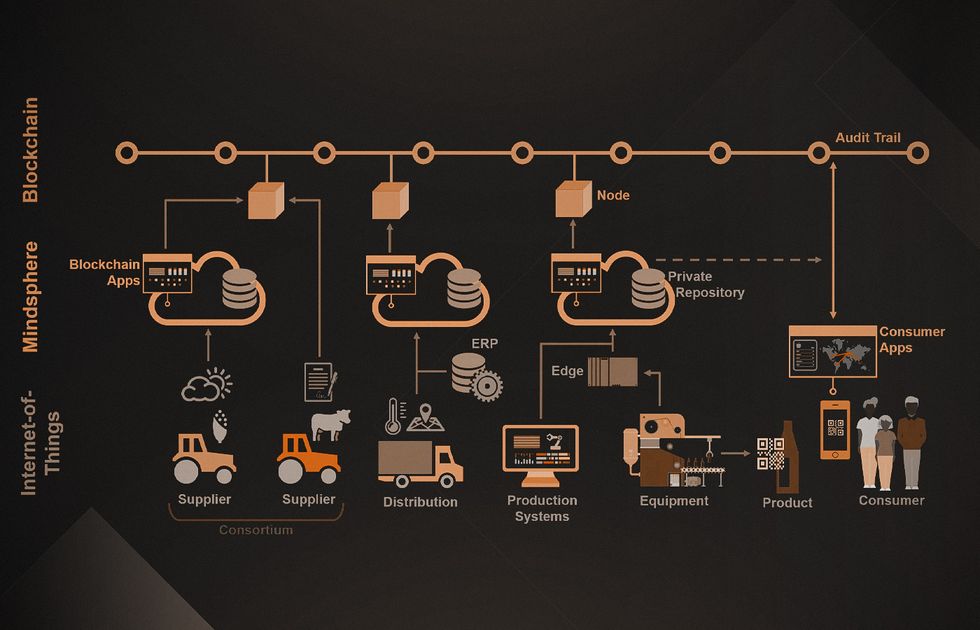
Siemens: Reduced Recalls and Counterfeiting
56% of food and beverage companies face at least one recall per year, incurring €9.5 million in direct costs and an additional €50-60 million in lost sales and reputational impacts. Siemens uses blockchain and IoT platform MindSphere to achieve full traceability and manage recalls and counterfeiting.
DHL: Accurate Delivery Forecasting
DHL forecasts delivery volumes with 90-95% accuracy, optimizing courier routes based on real-time shipment data. AI-powered software from Wise Systems then fine-tunes the route in seconds, considering delivery priorities and time-sensitive requirements.
Nestle: Increased Business Value
Deloitte and Nestlé USA collaborated to build a Microsoft Azure Data Lake, breaking data silos. The solution supported 400+ reports and integrated 15+ data sources, providing summarized reporting and insights for executives. Over four years, it has generated $200+ million in business value.
Walmart: Reduced Costs and Sustainability
Walmart’s Route Optimization technology minimizes travel miles and optimizes routes. Walmart avoided 94 million pounds of CO₂ emissions, eliminated 30 million unnecessary miles, and optimized routes to bypass 110,000 inefficient paths, winning the 2023 Franz Edelman Award.
UPS: Dynamic Pricing
UPS uses big data analytics in supply chain management through tools like Deal Manager. This system provides real-time pricing insights for small-to-medium business deals, achieving an 80% win rate. Currently, 95% of deals under $1 million utilize this tool.
Coca-Cola: Demand Forecast
By analyzing sales data and market trends, Coca-Cola forecasts demand with 90% accuracy, predicting consumer needs better and adjusting production schedules in real time. This improvement helps minimize excess inventory and associated costs while ensuring that high-demand products are available.
Сhallenges of Implementing Big Data in Supply Chain Management
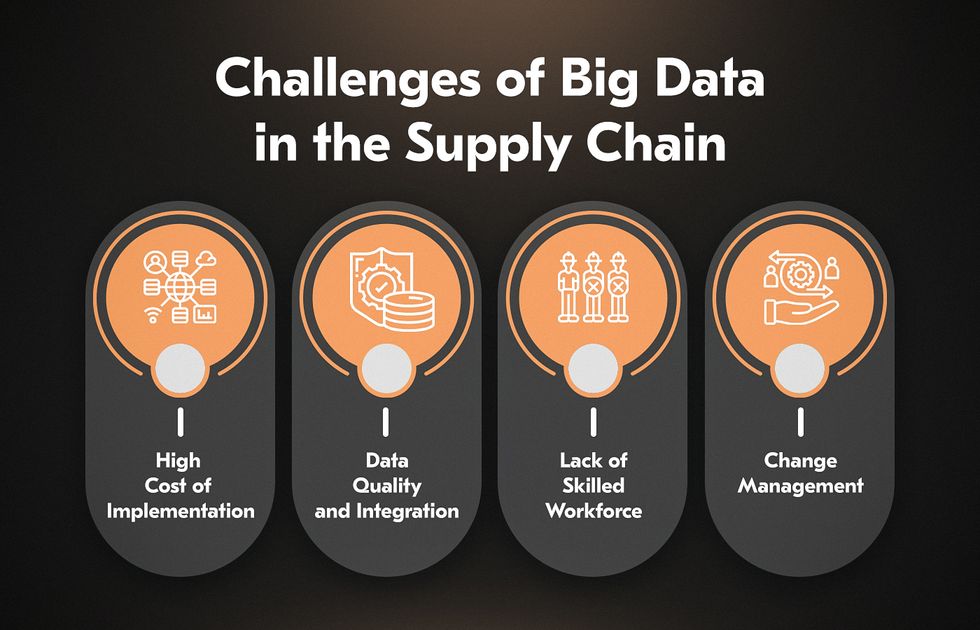
But is everything so simple with integrating big data analytics in supply chain? Of course, like with each technology, you should overcome certain difficulties:
High Cost of Implementation
Big data analytics in logistics and supply chain management often require significant upfront investment in infrastructure, technology, and training. Small and medium-sized enterprises may struggle with these expenses.
To manage this challenge, leverage cloud-based services to reduce infrastructure expenses through pay-as-you-go models. Implement incremental changes, starting with basic low-code tools and scaling up as needed. Also, partner with offshore technology vendors with affordable rates.
Data Quality and Integration
Supply chains generate large volumes of data from diverse sources, and integrating them into a cohesive format for analysis is complex. Inconsistent or poor-quality data can lead to incorrect decisions and operational inefficiencies.
To address data issues, use data integration platforms to consolidate and standardize data, apply data cleansing tools to remove inaccuracies, and leverage real-time IoT monitoring for early issue detection. APIs for seamless data exchange with partners enhance data sharing and reliability.
Lack of Skilled Workforce
Data scientists, analysts, and IT specialists are in high demand, and small and medium-sized enterprises often struggle to recruit and retain talent. This can slow down the adoption and effective use of supply chain and big data analytics.
Address this gap by investing in training programs for existing employees and leveraging automation and AI-powered tools that simplify data analysis. Cloud-based platforms often provide user-friendly interfaces that allow non-experts to work with big data analytics and supply chain management more effectively.
Change Management
Employees may be reluctant to adopt new technologies, fearing job displacement or a steep learning curve. Introducing big data requires significant shifts in organizational processes, roles, and mindsets.
Clearly communicate the pros of big data analytics for supply chain and how it will improve operations, not replace jobs. Offering training and development programs and gradually integrating new technologies can also reduce resistance.
Why Choose Acropolium?
Acropolium is your trusted IT outsourcing partner, featured by Clutch and TechBehemoths. We specialize in advanced solutions for transportation, logistics, healthcare, and hospitality, strengthening them with IoT, GPS, GIS, machine learning, and blockchain. Our developers adhere to ISO-certified processes, ensuring the delivery of high-quality, secure, and GDPR-compliant bespoke software.
Let’s dive into our latest supply chain big data use cases:
SaaS Route Planning Tool
Acropolium built a scalable SaaS solution for a transportation provider, integrating ML-driven route planning and fleet management. The software reduced fuel costs, boosting profits by 15%, while customer retention increased by 25% due to improved delivery accuracy and a 25% boost in logistics efficiency through real-time tracking.

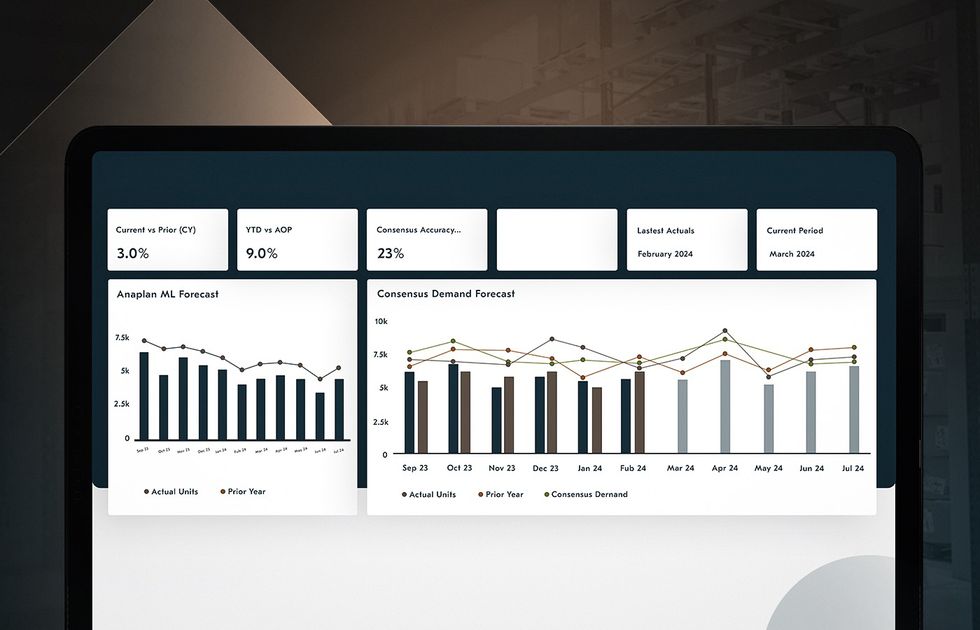
Supply Chain Data Analytics Software
We developed a supply chain analytics platform for a client managing complex networks of warehouses and hubs, integrating data from ERP, IoT, and GPS systems. The solution led to 20% less downtime, 27% improved efficiency, 15% lower inventory expenses, and a 22% increase in customer retention.
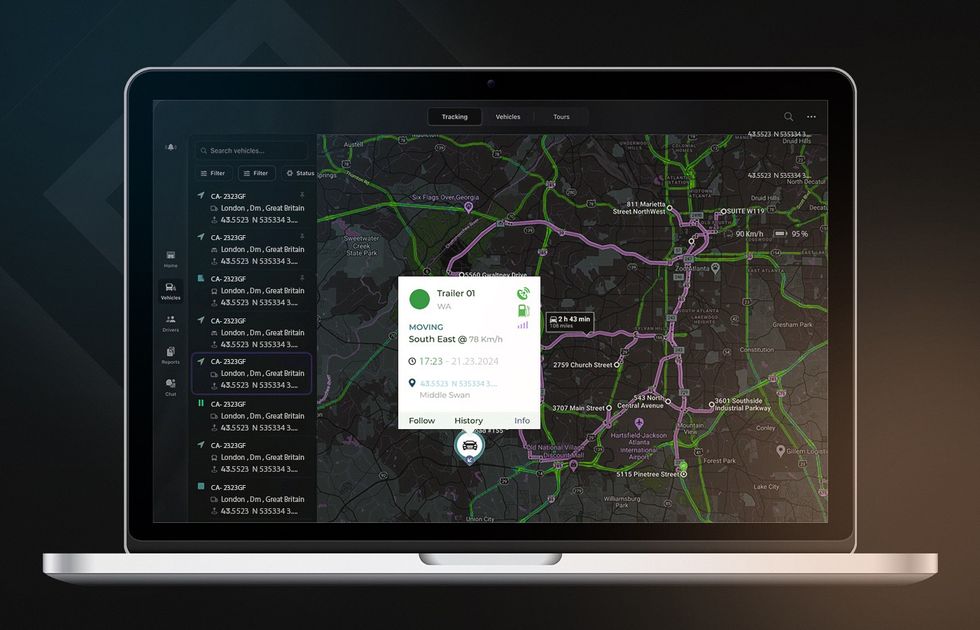
SAAS Fleet Management Software
American logistics company required a SaaS fleet management solution to optimize routes, reduce fuel consumption, and enable real-time tracking. This resulted in a 31% reduction in delivery time, 14% lower fuel consumption, a 28% boost in customer satisfaction, and improved driver behavior and safety.
Final Thoughts
Big data applications in supply chain management enable companies to analyze vast datasets for critical insights, enhancing inventory optimization, demand forecasting, and risk management. Leverage these technologies to make data-driven decisions, improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, and gain a competitive advantage.
If you don’t have enough experience and skills for implementing big data supply chain software, ask Acropolium for assistance. Our dedicated team will conduct an audit of the processes and consult where it is best to start. Contact us to discuss cooperation on a subscription basis.







![Machine Learning in Logistics and Supply Chain [7 Use Cases Included]](/img/articles/machine-learning-in-supply-chain-and-logistics/img01.jpg)

![ᐉ Warehouse Management Systems Development [2025 Guide]](/img/articles/warehouse-management-systems/img01.jpg)
![Transportation Management Software Development [2025 Guide]](/img/articles/transportation-software/img01.jpg)

![ᐉ Mapbox vs. Google Maps [Choosing a Map API]](/img/articles/map-api/img01.jpg)