Key Takeaways
- Low code supply chain and logistics involve visual development tools and pre-built components to streamline software building.
- The low-code approach enables faster app creation, cost-efficiency, enhanced productivity and collaboration, and improved operational agility.
- Low code use cases in transportation include supply chain optimization and tracking, compliance and certification, collaboration, repairs and returns, and predictive analytics.
According to Forrester, in a low-code approach, development takes less time, experimentation becomes easier, and fundamental separation between tech teams and businesses is eliminated. As supply chains are becoming more complex and less resilient, the adoption of low code logistics app development becomes a natural choice for most companies. Over two-thirds of enterprises have already incorporated low-code into their supply chain operations.
We know this because we keep a close eye on the digitalization of logistics and transportation, delivering advanced, cost-efficient products. In this article, we’ll guide you through the main reasons for using low-code applications and explore their most common use cases. We’ll also talk about the challenges your business can face when implementing low code development services for logistics. Buckle up!
Supply Chain Technology Trends
Navigating a complex global supply chain remains challenging, as nearly all businesses faced significant issues in the past year. 44% of them addressed major challenges in their supply chain footprint, leading to necessary changes. Additionally, 49% reported big planning challenges due to supply chain disruptions.
As technologies like IoT and smart sensors advance, more companies turn from linear supply chains to integrated networks, also known as Supply Chain 4.0. The new concept involves using innovative technologies for better performance and efficiency.
KPMG predicted that half of supply chain organizations will allocate investments towards applications that bolster artificial intelligence and advanced analytics capabilities. According to a recent Gartner study, almost 80% of supply chain respondents intend to pilot or implement GenAI capabilities in 2024, allocating an average of 6% of their total technology and transformation budget.
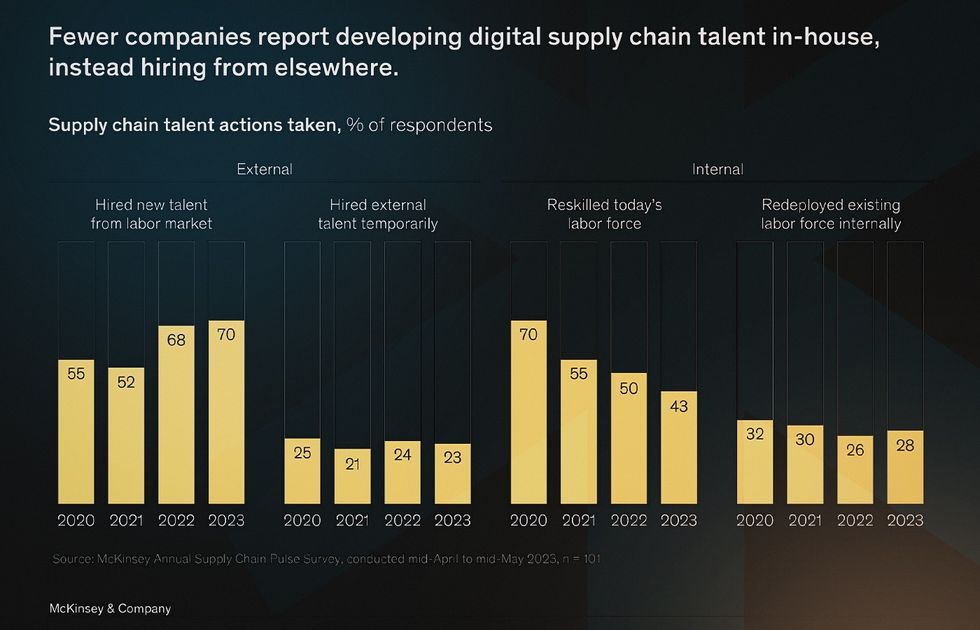
However, the high cost of implementing advanced solutions can stop the company from transformation. Another persistent barrier to technology adoption is the need for more talent. Just 8% of supply chain companies have enough in-house specialists for digitization. In the last three years, internal reskilling programs in the supply chain have decreased by 27%, while external hiring has risen by 15%.
Low or no code in transportation allows business users with limited technical expertise to rapidly create, test, and implement new capabilities. Low-code platforms automate most supply chain tasks, utilizing APIs and pre-packaged integrations to connect disparate systems. Applications include planning, manufacturing, product life cycle, supply chain collaboration, and track-and-trace. And yes, AI-powered technologies are also available in low-code solutions.
What is Low-Code Development for Logistics
Low-code development for logistics relies on a minimal amount of manual coding to create software applications tailored for industry specifics. This approach involves drag-and-drop components and pre-built elements so users can easily and quickly design, develop, and deploy the platforms.
Low code supply chain app development can address specific industry issues:
- Low-code development automates repetitive and time-consuming logistics processes like order processing, warehouse management, and shipment tracking.
- The logistics industry requires real-time visibility across the supply chain. Low-code solutions provide instant access to critical data, improving decision-making and reducing delays.
- Logistics operations vary widely, and low-code platforms allow for rapidly developing customized solutions that can adapt to specific business needs.
- Low-code development facilitates integrating different software and hardware components, fostering a seamless data flow between disparate systems.
- Many logistics tasks require mobility, and low-code solutions enable the creation of mobile applications, facilitating on-the-go access to information.
- Low-code development allows for swiftly modifying apps to comply with new regulations, reducing compliance-related risks.
- With low-code development, logistics professionals with domain expertise can actively participate in the development process, reducing dependency on IT specialists and accelerating system deployment.
4 Benefits of Adopting Low Code in Supply Chain and Logistics
Citizen development has evolved from experimentation to replacing core applications. Currently, 39% of firms use low-code to empower non-IT developers, and an additional 27% plan to do so in the next 12 months.
The worldwide low-code development technologies market is projected to hit $31.9 billion by 2024. Furthermore, by 2026, developers outside formal IT departments will constitute at least 80% of the user base for low-code development tools, compared to 60% in 2021.
No wonder low code in supply chain industry is advancing so fast — it gives businesses more control over the applications they’re going to use. Here’s how this can benefit your business.
Improved Operational Agility
In 2022, McKinsey found three crucial elements for resilient supply chains: end-to-end visibility, high-quality master data, and effective scenario planning. A year ago, two-thirds achieved visibility, just over half had good, not legacy data, but only 37% routinely used scenario planning in supply chain operations.
Low-code platforms enhance end-to-end visibility and big data quality by integrating diverse systems. Additionally, these platforms facilitate effective scenario planning through rapid application development, enabling quick adjustments to evolving market conditions.
Faster Digitalization
With low-code platforms, making changes and applying new technologies is easier because supply chain teams don’t need to go through the lengthy process of logistics software development and testing. Meanwhile, IT departments can free up their time for implementing artificial intelligence (AI) and robotic process automation (RPA) into the company’s workflows.
Enhanced Productivity and Collaboration
Low code in transportation management automates freight broker tasks such as digitizing paper-based documentation, including manuals, guides, instructions, and audit reports. They can also be used for addressing specific problems, for example, to eliminate silos resulting from different systems used in warehouses. This leads to a more optimized supply chain and less untapped capabilities.
Users can focus on important tasks and new business initiatives rather than routine supply chain management. Real-time sharing of information related to orders, payments, shipping, and delays improves collaboration between teams and allows vendors to make their lines of communication wide open.
Cost-Efficiency
Develop simple solutions for particular problems without hiring top-notch software engineers. Though you still need specialists with a certain level of coding skills to build a full-fledged supply chain application, you can save time and effort when searching for candidates.
Unlike lengthy full-cycle building, low code development for logistics is fast and simple. It provides companies with a variety of tools to build and deploy applications on multiple platforms, saving development and maintenance costs.
6 Low-Code Use Cases for Logistics and Supply Chains
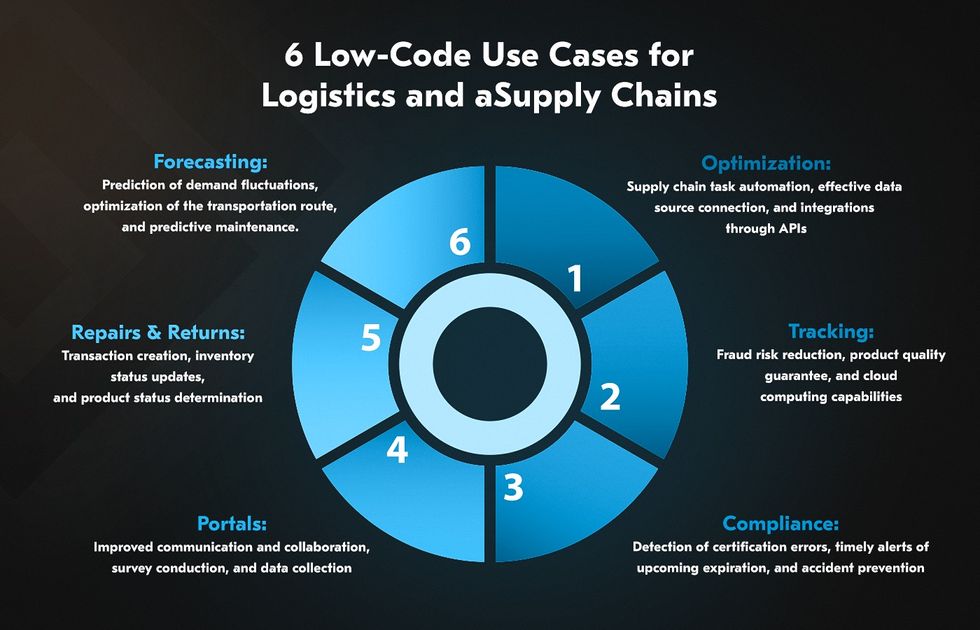
Low code use cases in logistics and supply chains are almost the same as in traditional development. The difference lies in the level of customization, development speed, and functionality. Here are a few low code examples in logistics.
Supply Chain Optimization
Low code transportation app development allows you to automate most supply chain tasks, such as invoicing, warehouse management, and receiving the goods.
Supply chains involve multiple systems of records (applications and databases) that can be a valuable source of data for analytics and machine learning algorithms. Unfortunately, the complexity of most supply chains doesn’t allow companies to connect data sources efficiently.
Low code in transportation industry, on the other hand, can accelerate integrations thanks to application data model consistency and a wide range of Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) and prepackaged integrations.
Supply Chain Tracking
43% of organizations possess limited to no visibility into the performance of their tier-one suppliers. In industries like food, consumer goods, and drugs, supply chain tracking is critical for ensuring the high quality of provided products and services. For example, in pharmaceutics, manufacturers, distributors, and pharmacists integrate solutions for GPS vehicle tracking to monitor drugs in real-time, reducing the risk of fraud.
Enhanced integration capabilities of low code development in supply chain enable businesses to establish better connections across various systems. Also, companies can benefit from cloud solutions that unlock maximum supply chain transparency, IT governance, and integrated cyber-security.
Compliance and Certification
Many manufacturers still manually track lapsed certifications, social, labor, and environmental audits, as well as employee safety training compliance. However, with a few dozens of warehouses, document management becomes cumbersome and slow. This increases the risk of non-compliance fees due to expired or missing certifications.
Among other low code examples in supply chain, this approach enables companies to create a centralized information bank across all warehouses. Applications can identify certification errors, timely alerts about upcoming expirations, and provide the necessary information about employee safety training. Also, they help businesses meet changing compliance requirements.
Supply Chain Portals
Customer portals are a great example of no code supply chain. They can improve communication and collaboration between the involved parties: raw material suppliers, warehouse managers, importers, logistics companies, and distributors.
At the same time, conducting surveys and collecting data for analytics becomes easier, resulting in better planning and data-driven decision-making.
Repairs and Returns
Returns and repairs always pose significant challenges for supply chain companies, as manual processes are labor-intensive and prone to errors. Low code development in transportation enables the automation of these tasks, leading to significant cost reductions and improved efficiency.
Generate transactions, update inventory status, and track product movement in real time. Such accuracy is essential for determining the condition of returned products and deciding whether to repair, restore, or replace them. Streamlining the returns and repairs process contributes to faster turnaround times, enhancing customer satisfaction. Also, you can easily inform clients about the status of their returns or repairs.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics enables logistics companies to anticipate demand fluctuations more accurately. By analyzing historical data and external factors, organizations optimize inventory levels, reduce excess stock, and minimize stockouts. At the same time, predictive analytics helps reduce fuel consumption by route optimization and minimizing downtime with predictive maintenance.
Low code application development in logistics enables professionals to harness these benefits without extensive coding knowledge. How? Specific platforms provide intuitive visual interfaces and pre-built components to create AI-powered predictive models and applications.
Challenges of Low Code for Logistics and Supply Chains
Though more enterprises are integrating low or no code logistics, it can’t fully replace experienced developers:
Limited Capabilities
As the business grows bigger, low or no code for supply chain can no longer meet all project requirements. To minimize this risk, the leading low-code platforms like Mendix, Topo, and JourneyApps use open technologies.
Besides, developers can extend the functionality of low code examples in transportation by adding their own UI components or code (for example, JourneyApp enables to use React for this).
Lack of Low-Code Specialists
Low-code platforms are designed to be used by even non-technical people. However, users should understand a visual language like Business Process Modeling Notation (BPMN) that platforms for no code in supply chain rely on.
At the same time, the user-friendly interface, plenty of tips and prebuilt patterns, along with the drag and drop function, significantly reduce the learning curve for your dedicated team.
Vendor Lock-in
Some platforms can restrict the export of application code to local databases or even prohibit access to source code. In other cases, exported code isn’t clean and readable enough to be reused.
The challenge can be addressed by partnering with reliable vendors who know a thing or two about developing low or no code in logistics. In this way, you can guarantee full access to the source code and export capabilities.
How Acropolium Can Help You With Low-Code Development for Supply Chain and Logistics
Low code improves the resilience of the software solution and swiftly reacts to dynamic environments and compliance requirements. In modern supply chains, fast and agile development drives the company’s growth and digital transformation.
With almost 20 years of expertise in software development and consulting, Acropolium knows how to accelerate your supply chain modernization and automate the development process. Our IT outsourcing company has hands-on experience across logistics, hospitality, healthcare, fintech, and other industries and can build a comprehensive low-code application according to your industry standards.
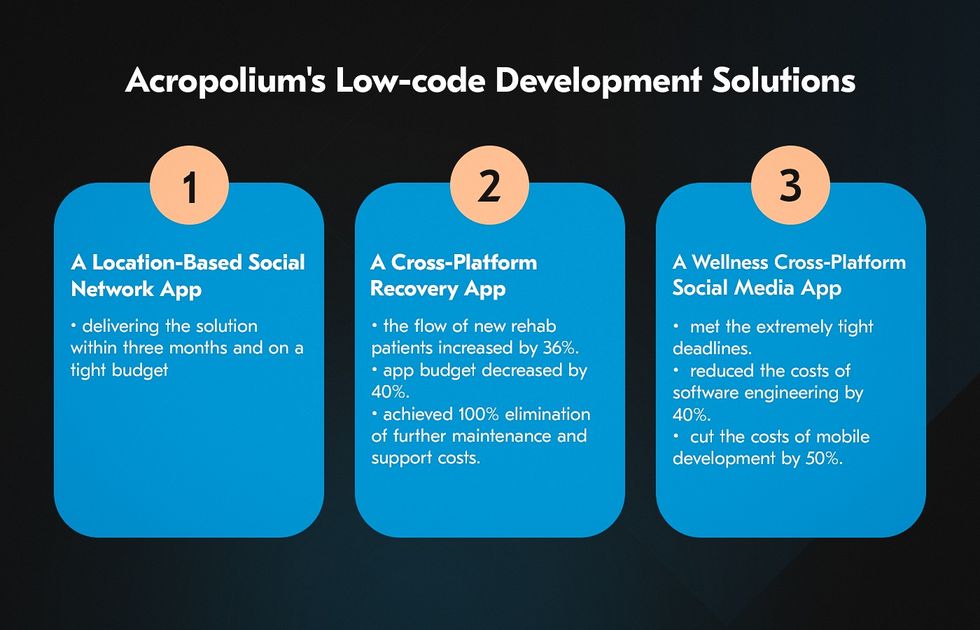
Our low-code projects include the following cases:
- The client had an idea for a location-based social network app and needed a fast MVP to test hypotheses. The low-code option allowed us to deliver the solution within three months and a tight budget.
- A private psychological help center for addiction needed a cross-platform recovery app for iOS and Android. The low-code system led to a 36% increase in new rehab patients, a 40% reduced app budget, and a 100% elimination of maintenance and support costs.
- The client sought rapid development of a wellness cross-platform social media app to eliminate stressful experiences. Using low code, we met tight deadlines, reduced software engineering expenses by 40%, and achieved a 50% cost reduction in mobile development.
Contact us to learn more about our low-code development services for logistics and supply chains on a subscription basis.







![Low-Code in Healthcare [5 Use Cases]](/img/articles/low-code-healthcare/img01.jpg)


![15+ Low-Code Use Cases [Real-World Examples Included]](/img/articles/low-code-use-cases/img01.jpg)

