Key Takeaways
- Data security ensures the protection of sensitive information. It prevents financial losses, preserves software integrity, and maintains customer trust and loyalty.
- Common data security threats include SQL injection, command injection, and cross-site scripting (XSS), which compromise sensitive data.
- Best practices for data security involve encryption, access control, regular updates, employee training, and strong authentication measures.
Efficient cybersecurity is critical for software development and IT operations. As a result, global spending on information security is expected to reach $212 billion in 2025. The key reasons for this boost include emerging threats, cloud adoption, and talent shortages.
At the same time, the costs of data breaches are also rising. According to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report, the global average spending on a data breach reached $4.88 million in 2024 — a 10% increase from last year and the highest total ever recorded.
But don’t worry; there are plenty of ways to make your solution safe. Allow us to show you the most practical, secure software development practices and regulations. You’ll also learn how to find a reliable outsourcing company and make sure it keeps software development secure.
What Is Secure Software Development?
Security in software development is designing, coding, and testing software with built-in security measures. Its purpose is to prevent vulnerabilities and cyber threats. Appropriate security measures ensure data protection, system integrity, and compliance with industry regulations throughout the development lifecycle.
We can distinguish four elements of data security:
1. Confidentiality — providing access to data only to authorized users and services
2. Integrity — storing files in a secure storage where third parties can’t modify them
3. Resiliency — backup and recovery tools to prevent loss of data
4. Availability — ensuring all of your data is readily available and visible
Importance of Data Security for Businesses

In Q3 2024, data breaches compromised over 422 million records globally. Not too encouraging, right? So, let’s see how implementing secure software development best practices can help mitigate the problem.
Protection of Sensitive Data
46% of breaches involved customer PII, including tax IDs, emails, phone numbers, and addresses. IP records accounted for 43% of breaches, with their cost rising to $173 per record from $156 last year. You also risk exposing this information when outsourcing if you don’t work with a secure development company.
Prevent Financial Losses
The healthcare sector has the highest charge of a data breach, at $9.77 million, compared to $10.93 million in the previous year. The average global cost of a data breach in the financial industry reached $6.08 million, 22% above the worldwide average.
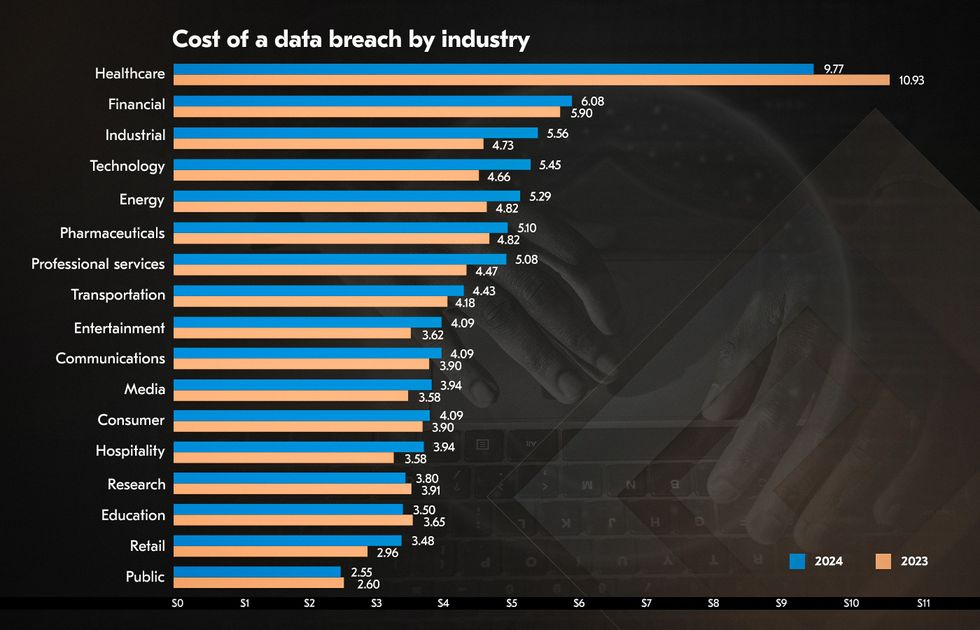
Organizations that extensively used security AI and automation saved an average of $2.22 million compared to those that didn’t.
Early Identification of Cyber Threats
Organizations that employed advanced technologies extensively detected and contained an incident, on average, 98 days faster than organizations lacking them. Internal detection (by own security teams or tools) rose to 42% (up from 33%), cutting breach time by 61 days and saving $1M per incident.
Availability and Reliability
Business depends on data reliability. When breached, breakdowns range from minor issues to complete operational shutdowns. Nearly 70% of organizations faced significant disruptions, and about one-third of them fully recovered within over 150 days. For 24%, the recovery took 126 to 150 days.
Industry Regulations and Standards
Suffering a data compromise due to non-compliance with government regulations can lead to severe fines or legal responsibility. Lehigh Valley Health Network (LVHN) settled a $65 million class action lawsuit. The 2023 hack exposed about 600 sensitive data records of patients and employees, including personal and medical information.
Customer Trust and Loyalty
Companies implementing robust cybersecurity practices protect their customers’ personal and financial information from breaches. This approach prevents reputational damage and fosters long-term relationships with clients.
Common Cyber-Attacks for Software Development

First off, let’s overview some of the freshest and most significant data breaches:
A LockBit ransomware attack on Infosys McCamish (a service provider of Bank of America) exposed the personal data of 57,028 clients. Notification was delayed 90 days after the breach. This attack demonstrates how a minor vulnerability in affiliate networks may lead to severe financial and reputational damage.
Dell is investigating a breach affecting more than 10,000 employees. It exposed sensitive data like IDs and names and posed a risk of phishing and identity theft. The database is being sold for $0.30, increasing the threat. HR teams need to enhance employee security awareness.
MediSecure confirmed hackers stole the personal and health data of 12.9 million Australians in April. That included 6.5 terabytes of sensitive information, such as names, addresses, and medicare numbers. The company is no longer part of Australia’s digital health network.
What causes such cases? Here are some common cyber-attacks often leading to the damage:
SQL Injection (SQLi)
Attackers inject malicious SQL code through user input to manipulate queries, access or alter databases, and retrieve sensitive data (usernames, passwords, and personal information). To prevent SQL injection, ensure all user inputs are validated and sanitized. Also, use prepared statements with parameterized queries.
Command Injection
Malicious users exploit vulnerabilities to execute unauthorized system commands. This way, they gain complete control over the server. To avoid this outcome, sanitize and validate all user inputs without passing them directly to shell commands. Also, employ secure APIs and avoid using unsafe system calls.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
This threat involves malicious scripts injected into web pages and executed in users’ browsers. It can lead to stolen session data or redirection to malicious sites. Use a Content Security Policy (CSP) and HTTPOnly/Secure flags to block JavaScript access and limit attack vectors.
Exploitation of Known Vulnerabilities
Attackers exploit unpatched security flaws in libraries, frameworks, or even the operating system. They do it to execute low code, escalate privileges, or cause a denial of service (DoS). Regularly update and patch all software components to fix known vulnerabilities and prevent exploitation.
Memory Safety Exploits
Hackers manipulate memory through techniques like buffer overflows, causing unexpected behavior, crashes, or remote code execution. Mitigate risks within your software development budget with the help of memory-safe programming languages. Also, enforce secure coding practices.
Best Data Security Practices and Tools

Here are the web development security best practices to help you ensure a secure, compliant, and resilient IT environment. Consider them from the discovery phase:
Authorization Controls
Authentication verifies a user’s or service’s identity, and authorization assigns a unique access token based on the privileges. Fine-grained access controls specify detailed rules based on location, time, or role to enhance security. When adopting a zero-trust model, the system doesn’t grant access to all entities from inside or outside the network perimeter by default.
Multi-Factor Authentication
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) requires users to provide extra verification factors (one-time passwords, biometrics, etc.) in addition to their login and password. Pairing MFA with adaptive authentication adds an extra security layer by adjusting access requirements. These are typically based on the user’s location, device, time of access, or unusual behavior.

Automated Security Tests
Integrate validation tests and vulnerability scans to identify security flaws early on. Looking to cover backend and runtime environments? Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) simulates attacks on running applications to identify runtime flaws. In contrast, Software Composition Analysis (SCA) scans third-party libraries for known vulnerabilities, reducing risks from outdated dependencies.
Monitoring and Intrusion Prevention
Traditional monitoring focuses on detecting suspicious activity. However, it often lacks the ability to correlate data from multiple attack vectors. Intrusion prevention systems (IPS) block known threats but struggle with detecting evolving sophisticated attacks.
Extended Detection and Response (XDR) enhances security thanks to monitoring, threat detection, and automated response across multiple attack vectors. It unifies data from endpoints, networks, and cloud environments, enabling faster threat identification and mitigation.
Encryption
Data encryption, a key aspect of architecture, means converting readable data into an unreadable format you can decipher with a security key. Also, consider investing in post-quantum encryption (PQE) to protect data from future attacks. Companies increasingly adopt NIST-approved algorithms like CRYSTALS-Kyber to stay ahead of evolving threats.
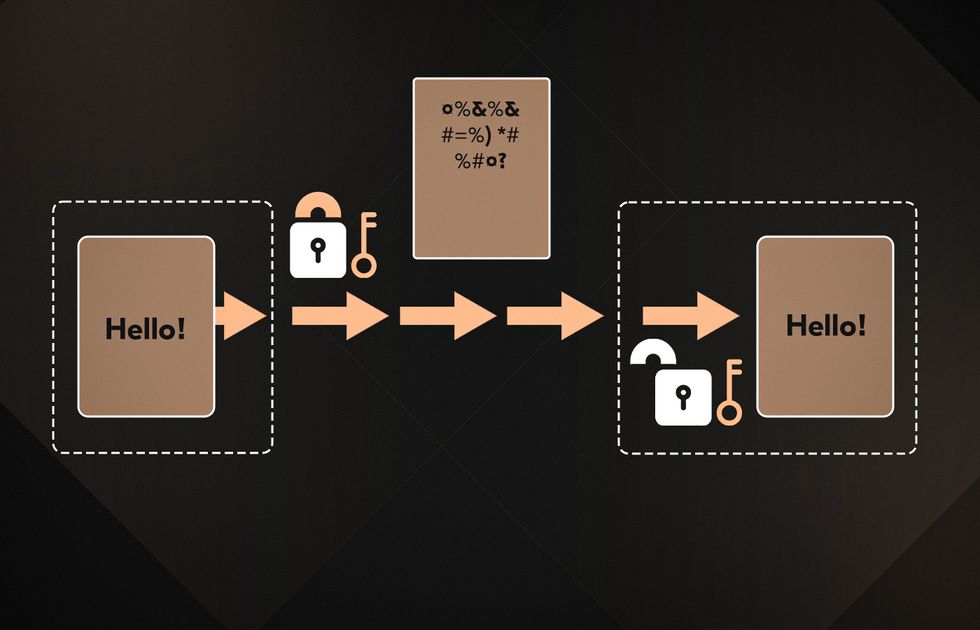
Tokenization (Data Masking)
Tokenization replaces data with an unreadable token stored externally for security. Unlike data encryption, tokenization changes the values in files in a way that’s impossible to reverse-engineer. Format-preserving encryption (FPE) keeps the data’s original structure while encrypting its contents. It’s perfect for applications requiring specific formats, like credit card numbers or healthcare records.
Role-Based Access Control
Role-based access control restricts access to your servers, applications, and data based on the user’s role and responsibilities. However, this approach often lacks flexibility. In turn, replacing it with attribute-based (ABAC) or policy-based access control enables dynamic decisions based on user attributes, location, and data context.
Backup and Recovery
Data backup software regularly copies files and databases to secure cloud and physical environments to make them easily restorable. Implement immutable backups to prevent unauthorized modifications and ensure data integrity. Ransomware-proof recovery systems enable swift restoration without compromise.
Data Classification
Enterprises should classify their data according to its type, confidentiality, and value to the company. This lets you set up security measures for specific categories of files. Your employees can classify files manually every time they create, edit, or release a document. Automate data classification with AI-driven tools to ensure faster, more reliable categorization of sensitive data.
Data Erasure
Industries like healthcare even force providers to destroy personally identifiable information and health data they haven’t used for more than six years. So, you should regularly erase data you no longer need for your business activities. Cryptographic erasure encrypts and deletes keys to securely destroy data and make recovery impossible.

Documented Security Policies
It’s necessary to document all cybersecurity, privacy, risk tolerance, and mitigation rules and keep them up to date. Make security policies dynamic by integrating them into DevOps through security as code. This way, you reduce the need for manual updates. Make sure your security policies are automatically applied, updated, and enforced across environments.
Cybersecurity Training
Employee training is the leading factor in reducing average data breach costs (by $258,629). It remains a critical component of secure development practices (particularly for identifying and preventing phishing attacks). Gamified platforms boost engagement and retention of security principles, making learning more interactive and productive.

DevSecOps Integration
82% of organizations use 6 to 20 security testing tools. While offering broad coverage, it increases complexity and integration challenges. 60% of respondents report that 21% to 60% of test results are noise. It often leads to alert fatigue and inefficient resource use.
DevSecOps integration embeds security into every development lifecycle stage. It ensures continuous testing, automated security checks, and real-time feedback. Hire a DevOps engineer with a security background to reduce complexity, improve teamwork, and overcome false alarms.
Common Data Security and Privacy Regulations

Compliance with regulatory requirements is difficult to navigate as it depends on your industry, company’s location, and customer’s residence. So, let’s look at the most significant and widely applicable laws you should consider when adapting software security best practices.
GDPR
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) obliges organizations to implement technical and organizational safeguards to protect the information of European Union users from unauthorized access. Among other things, it requires you to request consent when collecting data, anonymize confidential information, and notify users in case of a data breach.
GDPR retained its effects in the United Kingdom after Brexit. The UK GDPR shares the same principles as the original law but with several implications for cross-country data transfer and controlling establishments.
CCPA
California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) regulates how businesses can collect the personal data of California residents. It gives consumers the right to know the information you collect and lets them prohibit selling it to third parties. However, the law applies only to companies that possess data of at least 50,000 Californians or have over $25 million of yearly revenue.
HIPAA
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) defines the security and privacy requirements for managing personally identifiable health data. It applies to healthcare providers (clinics, pharmacies, doctors, and others), insurance companies, and other entities that process US patients’ data. Violation of this law can lead to severe penalties, including fines of up to $1.5 million and criminal charges.
SOX
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) requires public organizations and private companies to maintain secure financial reporting control to prevent inaccuracies and fraud. To ensure compliance, you must validate their security configurations and implement access management mechanisms. The law also requires you to audit changes that impact financial data, transactions, and compliance processes.
ISO/IEC 27001
ISO/IEC 27001 is an international standard for maintaining, establishing, and improving data security. This certification is not specific to any industry and is not obligatory. Still, ISO 27000 shows that a company follows the best practices for security software development and data management.
PCI DSS
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) applies to all businesses that process credit or debit card transactions. Some essential safeguards you need to apply to get certified include encrypted transmissions, network monitoring tools, and secure access to cardholder data.
FISMA
The Federal Information Security Management Act of 2002 (FISMA) applies to federal agencies and organizations that provide them with IT systems. Under this law, you should have advanced data classification systems and access controls.
You may need to follow other regulations based on your type of software and target markets. But if you cooperate with experienced BaaS and custom development vendors, they will keep everything in check.
Ensure Data Security and Compliance with Acropolium
Hiring a reputable outsourcing provider is the easiest way to create secure and compliant software: Experienced providers use software development security best practices such as encryption, access control, and compliance checks. They also separate environments to minimize unauthorized access risks.
Professional teams apply shift-left and DevOps methods to identify and fix security issues early, enhancing code quality.
Outsourcing teams integrate compliance checks to prevent misconfigurations, guaranteeing adherence to security and privacy standards.
For two decades, Acropolium has delivered top-tier solutions in fintech, healthcare, logistics, HoReCa, and more, earning long-term trust from clients across industries.
With ISO 9001:2015 certification, our dedicated team ensures compliance with regulatory standards, enforces role-based access management, and maintains strict control over the software development lifecycle. Our transparent process offers 24/7 project tracking and direct access to skilled engineers. We prioritize data security with features like Single Sign-On (SSO) to securely manage project data.
Each of our software developer cyber security ensures continuous support, uptime monitoring, and security upgrades, with a warranty for any reported bugs, minimizing IT outsourcing risks.
Final Thoughts
Data security is critical for all organizations that manage customer information, intellectual property, and other restricted data. Even a seasoned outsourcing provider can’t guarantee security if you neglect essential practices during software development.
Acropolium can assess your IT infrastructure, patch the vulnerabilities, and help you adopt the latest security tools before the start. Our company also provides a full range of development services with the SDaaS (Software Development as a Service) model for a fixed monthly fee.
If you need to implement best practices for secure software development and comply with regulations, reach out to us so we can talk business.







![How to Write Software Requirements Specification [SRS Document Template]](/img/articles/software-requirements-specification/img01.jpg)


![Retail Software Development Guide for 2025: [Features + Cost]](/img/articles/custom-retail-software-development/img01.jpg)
![Blockchain App Development [7 Reasons to Build a Blockchain App]](/img/articles/blockchain-application-development/img01.jpg)
