Key Takeaways
- SaaS tenant is the customer or user of the application, operating within their own isolated portion or instance of the software.
- A single-tenant architecture offers enhanced data isolation, ensuring advanced data security, complete control over customization, and reliable performance.
- Multi-tenant architecture provides cost-efficiency and scalability, allowing multiple customers to share common infrastructure and resources.
- When choosing multi vs single-tenant SaaS, define your priorities. Consider single-tenant architecture for enterprise with control and robust security or a multi-tenant database if your small or mid-sized company requires a scalable, affordable solution.
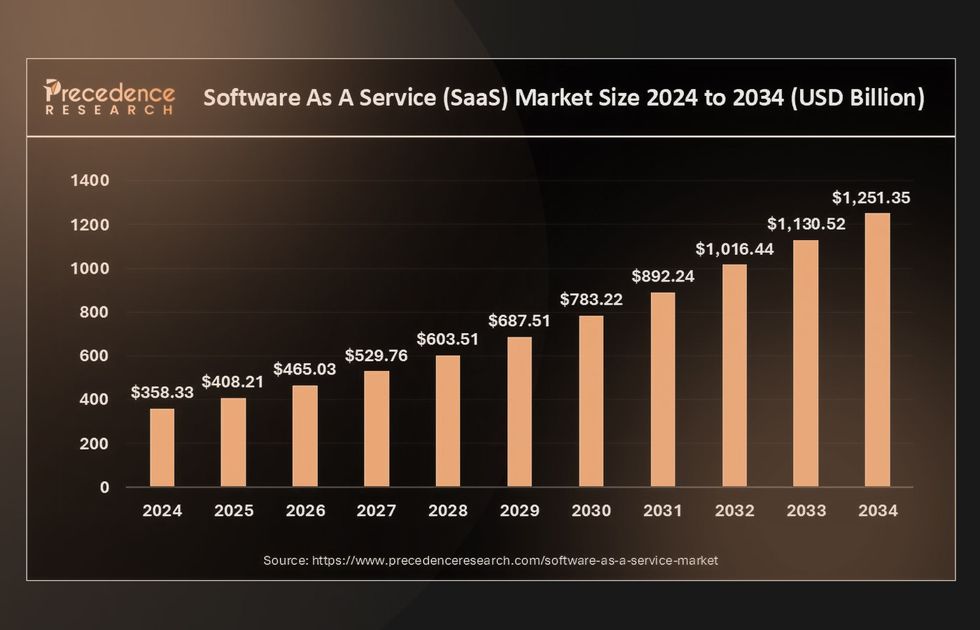
The SaaS market continues to skyrocket and will reach $1.251 billion by 2034, increasing by 13.32% annually. You may be planning custom software development and want to know more about single-tenant vs multi-tenant pros and cons to make the right choice. Or switch from one database type to another.
Acropolium is a SaaS development company with more than 16 years of experience and over 175 delivered solutions with different architecture types. But what is single-tenant and multi-tenant? In this article, we’ll discuss definitions, pros and cons, as well as explain how to migrate an isolated infrastructure to a scalable multi-tenancy environment.
What is Single-Tenant Architecture?
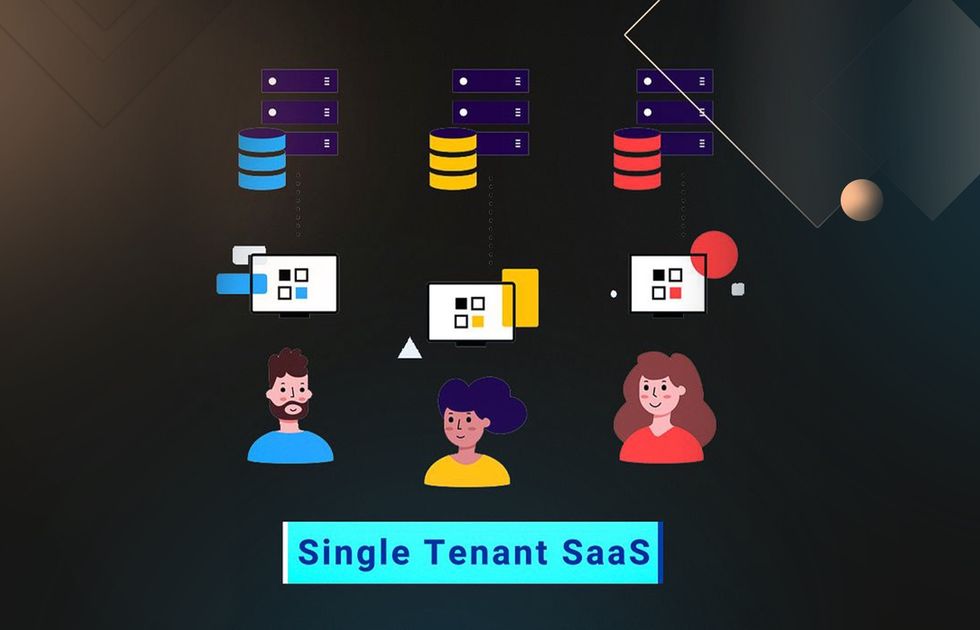
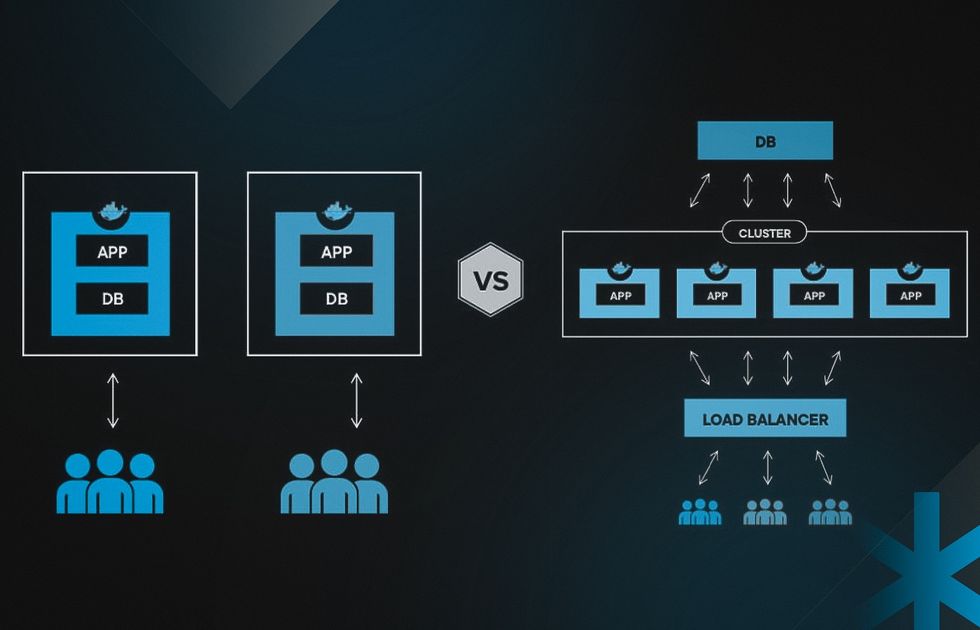
You may wonder: what is multi-tenant and single-tenant architecture? Single tenancy refers to a cloud architecture where each tenant operates in a fully isolated environment, without any shared resources. This setup is comparable to residing in a standalone home, offering dedicated infrastructure and enhanced control over data and security.
Your data and computing resources are located in clusters, separated from other tenants. This allows you to fully customize, upgrade, and manage your environment.
Single-tenancy is typical for private cloud environments and enterprise-grade SaaS services. While offering enhanced data protection and flexibility, single-tenancy typically involves more complex deployment processes and higher operational costs.
- For example, Oracle Cloud hosts segregated compartments with isolated resources and granular access control. Every customer has a different product version and has to upgrade it manually, making it a single-tenant platform.
- SAP S/4HANA Single Tenant Edition (STE) is one of SAP’s cloud offerings provided to a single tenant in a dedicated landscape. The solution supports all industries, and the configuration is available for personnel, finance, sales, procurement, etc. You can run your systems on not only SAP HEC (HANA Enterprise Cloud) but also AWS, GCP, and Microsoft Azure.
- ServiceNow is a SaaS platform that streamlines and automates business processes. Core services include HR, IT, customer support, security, and business applications. ServiceNow allows you to run a separate instance for each customer and perform tasks without mixing client data together.
Single-Tenant SaaS Architecture Pros
Let’s overview single-tenant SaaS benefits:
Advanced Data Security
Single-tenant architecture customers store their application instances and databases on dedicated servers. They can also implement proprietary security tools, role-based access control, and multi-factor authentication to boost cybersecurity.
Complete Control
Single-tenancy SaaS users can purpose-built their software around their business needs and have complete control over the customization. You can upgrade your software individually and implement any custom and third-party modules.
Reliable Performance
Single-tenancy customers benefit from isolated cloud environments with dedicated databases, applications, memory, and CPU. This means other clients’ problems and resource consumption won’t affect you. Plus, you are less likely to use overhead resources during SaaS app development.
Single-Tenant SaaS Architecture Cons
Here are some of the cons associated with a single-tenant SaaS architecture:
Higher Cost
Managing individual instances for each customer means extra server resources, maintenance, and operational costs.
Slower Scaling
Adding new clients often means provisioning new servers or resources, which takes time and effort.
Complex Onboarding
Single-tenant platforms have a complex onboarding process because the SaaS provider and your team must configure the infrastructure around your needs.
Complex Maintenance
Maintaining multiple instances, each with its own configuration and customization, can be complex and prone to errors. Updates and patches must be applied individually to each of them.
Increased Risk of Data Silos
Single-tenant architectures can lead to data silos, where each customer’s data is isolated. This can make it harder to gain insights from the data and implement cross-client features.
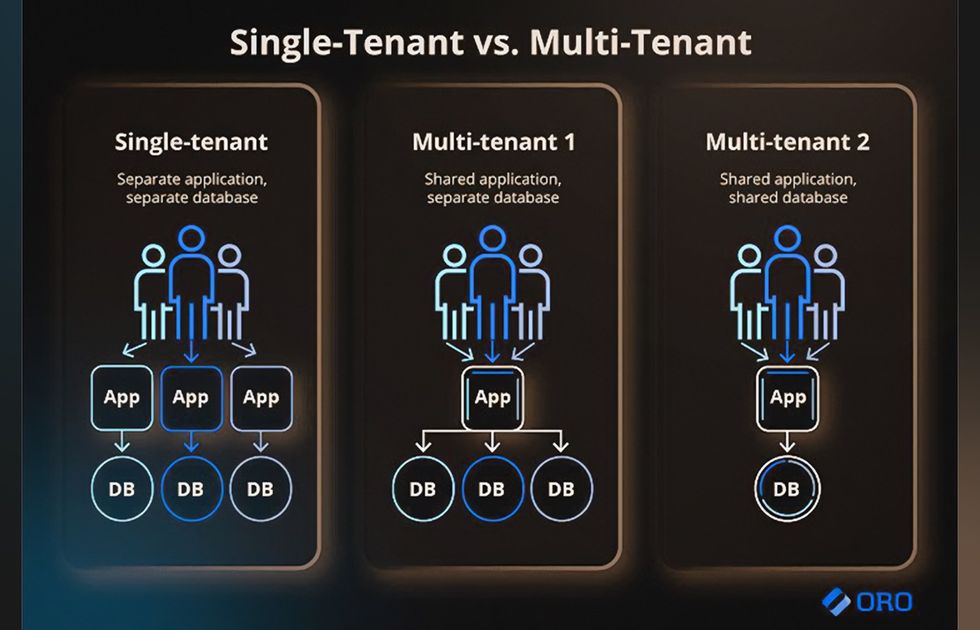
What is Multi-Tenant Database Design?
What is multi-tenant architecture? Multi tenancy implies a cloud environment where multiple customers share software instances and the supporting infrastructure.
Each tenant’s data is logically separated, ensuring privacy while benefiting from a shared system. This model offers greater scalability and cost efficiency, making it a common choice for SaaS providers.
However, customizability may be limited, as changes often affect all users. The shared infrastructure simplifies deployment but requires a robust security model to manage access controls and data segregation.
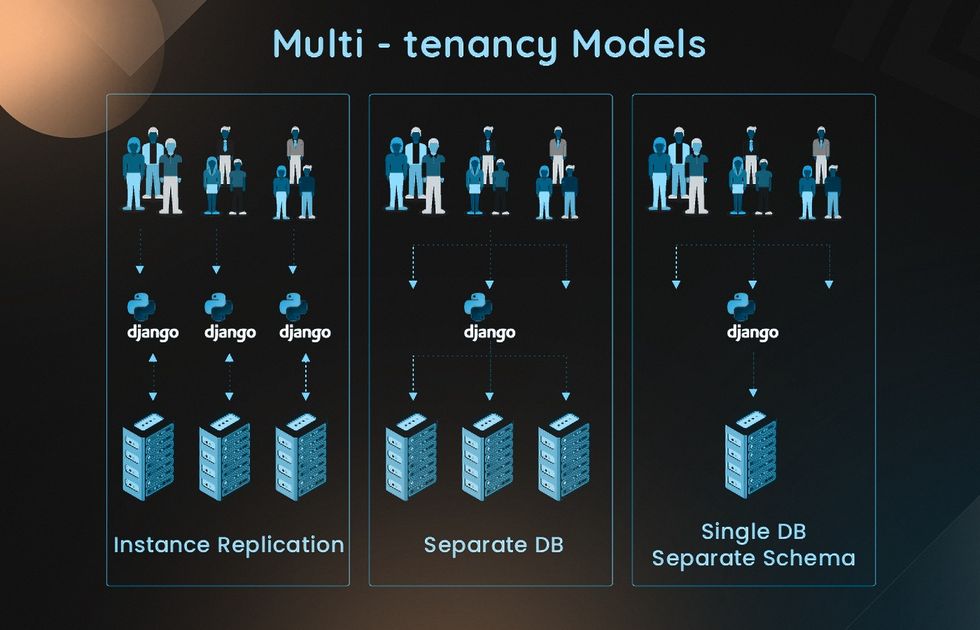
What is multi-tenant database? While tenants use the same software and database, their data is logically isolated, ensuring privacy and preventing unauthorized access across accounts. SaaS providers actually use different strategies to isolate tenants:
- Shared database. Tenants share resources and storage with a single database divided into identifier columns (one for each client).
- Dedicated database. The model consists of resource groups, with each tenant having a separate database. The vendor moves these databases between resource groups to optimize their usage.
- Sharded databases. Tenant data is split into movable “shards” across several databases.
- Hybrid-sharded databases. This strategy is better suited for platforms with subscription tiers (for example, a free tier and enterprise-level plans).
Security is paramount in multi-tenant architectures, as customers share the same infrastructure and resources. Here are several key security measures you can use:
- Tenant-specific data, configurations, and user accounts
- Role-based access control (RBAC) and permissions
- Encrypting databases, backups, and communication between different system components
- Authentication and authorization
- Firewalls and network segmentation
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS)
- Certifications like SOC 2, ISO 27001, or HIPAA
- Tenant-level customization to meet specific needs without affecting other tenants
The common examples of multi-tenant SaaS include non-corporate email clients (Gmail and Yahoo), cloud hosting services (Google Drive and OneDrive), and website builders (Shopify). Enterprise-level platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS) offer a multi-tenancy infrastructure but have dedicated single-tenant and mixed options.
Let’s look at some multi-tenant SaaS solutions in more detail:
- Salesforce is an outstanding example of a successful cloud computing platform and application ecosystem. It helps create popular business applications, industry solutions, and special programs and extensions for unique use cases. Salesforce’s multi-tenant architecture isolates and supports different tenant requirements that can customize user interface and business logic using metadata.
- Microsoft 365 for enterprises uses a combination of applications, services, and cloud products. In particular, it provides access to Microsoft Teams, Outlook, Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and other capabilities. Each Microsoft 365 customer is unique and separate from all others. At the same time, you can enter restrictions and additional considerations when managing them and providing services.
- Slack is a collaboration platform that allows teams to communicate in real time. Its services operate on a multi-tenant architecture, meaning they work both at the platform and infrastructure levels. It lets you separate and limit access to the data you and your users provide through Slack.
Benefits of Multi-Tenant SaaS Architecture
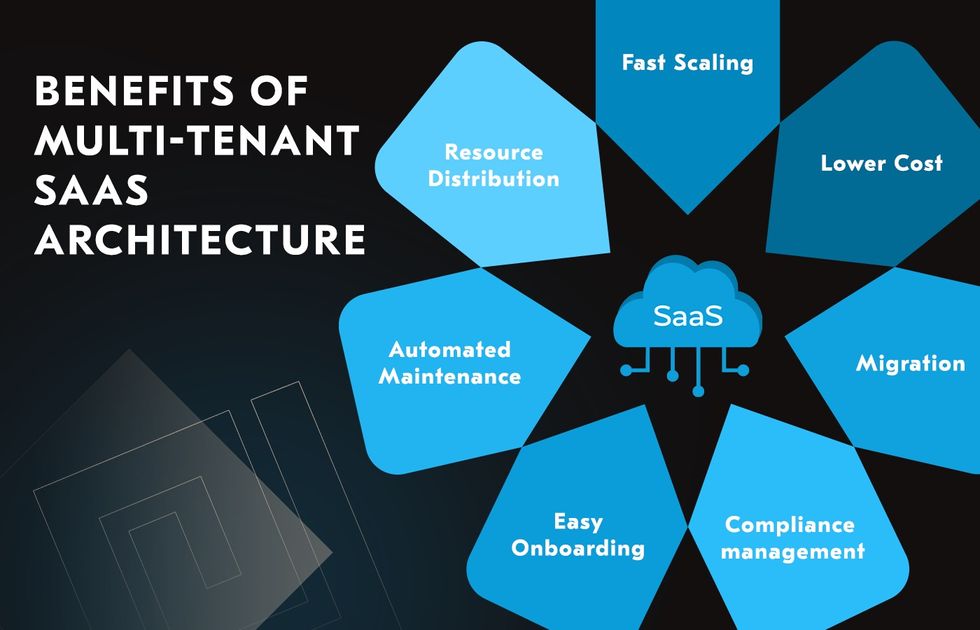
So, what are the benefits of multi-tenant architecture? Let’s go through the main ones:
Resource Distribution
Multi-tenant SaaS providers use load balancers to allocate application data between databases and servers. This guarantees that the infrastructure makes the most available resources to handle heavier workloads.
Fast Scaling
Scaling has fewer infrastructure implications for multi-tenancy because clients use the same software and hardware. You can quickly add or remove resources based on your computing and business needs.
Automated Maintenance
Maintenance is included in the price of the subscription in multi-tenant SaaS models. The vendor takes care of the servers, security, and software updates, so their tenants can focus on other goals.
Lower Cost
Multi-tenancy platforms give you access to complex infrastructure with large amounts of computational power for a smaller price. For example, a single Amazon data node can hold application data for millions of tenants. As you can imagine, maintaining one node with multiple clients is far cheaper than taking care of every client individually.
Compliance management
Multi-tenancy platforms adhere to major regulatory standards, so you don’t have to worry about compliance. Some SaaS solutions offer policy templates to help you develop compliant software (for example, PCI DSS for FinTech or HIPAA for healthcare apps).
Easy Onboarding
Multi-tenant SaaS environments have straightforward setup and configuration processes. The user-friendly interface allows you to easily customize the accounts, add users, and implement third-party services without the provider’s administrative support.
Migration
A multi-tenant infrastructure isn’t tailored for specific configurations. This means you don’t have to re-architect your environment when migrating your workload to another platform.
Disadvantages of Multi-Tenant SaaS Architecture
Comparing single-tenant SaaS vs multi-tenant solutions, it would be fair to discuss some disadvantages of the latter:
Limited Customization
Multi-tenant systems often prioritize standardization, limiting the customization available to individual tenants. Single-tenancy, in contrast, supports greater customization, allowing businesses to modify applications, deploy unique configurations, and integrate tools without affecting other tenants.
Compliance Challenges
Multi-tenant architecture can pose compliance issues, as shared infrastructure makes it harder to implement tailored security controls and meet standards like HIPAA or GDPR.
Single-tenant environments, with isolated resources, offer better support for strict regulatory requirements.
Data Security Concerns
Shared infrastructure increases the risk of data breaches, as a security incident in one tenant’s data can potentially impact others.
Performance Variability
In multi-tenant environments, users can face the “noisy neighbor” effect when one tenant’s excessive resource usage negatively impacts the performance experienced by others sharing the same infrastructure.
Resource sharing among tenants can lead to performance variations, where high resource usage by one tenant may temporarily affect others’ performance.
Data Portability
Extracting data from a multi-tenant SaaS application for migration or backup purposes may be complex and require the provider’s assistance.
What is a Mixed Tenancy Model?
In a mixed tenancy model, hosting providers strike a balance between shared and dedicated infrastructure. Certain parts of the application, often those requiring high levels of customization or security, are allocated exclusively to each client. Meanwhile, other components, such as core services or backend systems, remain shared across all users.
This hybrid approach is gaining popularity as it blends the strengths of both single-tenant and multi-tenant architectures. Clients benefit from the efficiency and scalability of shared environments, while still maintaining the control and isolation of dedicated resources where it matters most.
The Difference Between Multi-Tenant and Single-Tenant Architecture Types
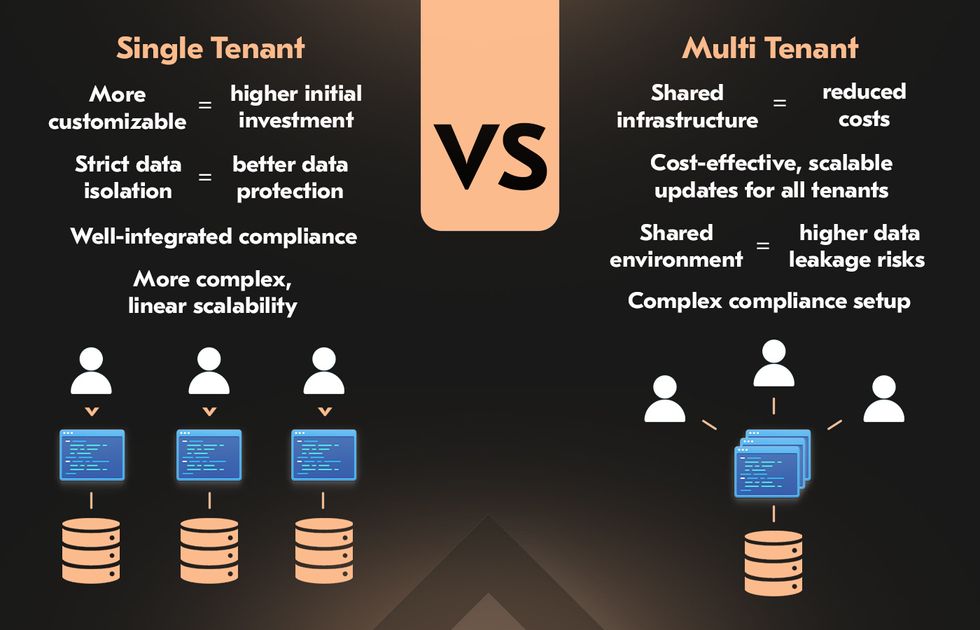
When choosing between multi vs single-tenant architectures, your technical decision should depend on how the chosen option affects cost, scalability, security, and compliance. Here’s a quick breakdown of how each model stacks up in these key areas.
Cost Efficiency
Multi-tenant systems reduce costs by sharing infrastructure. Providers spread DevOps and maintenance efforts across all users, resulting in lower per-customer expenses. Single-tenant setups, while more customizable, require isolated environments for each client, driving up costs and complexity.
Scalability
Multi-tenancy benefits from economies of scale. Providers can serve more customers without scaling infrastructure linearly, making it cost-effective and easier to roll out updates. Single-tenancy lacks this efficiency, often requiring duplicate systems per client.
Security & Data Isolation
Multi-tenant architectures carry a higher risk of data leakage due to shared environments. Without strict isolation, sensitive data may be exposed. Single-tenancy offers dedicated resources and stronger data separation, lowering that risk.
Compliance Simplicity
Single-tenancy simplifies compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. Isolated environments help manage data residency, access controls, and user rights more directly. In multi-tenant setups, compliance demands tighter controls and added complexity.
For your convenience, we compare multi-tenant vs. single-tenant architecture and summarize it in the table:
| Single-tenant SaaS | Multi-tenant SaaS | |
|---|---|---|
| Isolation | A dedicated software application, server, and database for every client | A single database or application instance shared between clients |
| Affordability | Premium price and the need to invest in maintenance, setup, hosting, and infrastructure updates | Clients spend less money because providers maintain and update the infrastructure |
| Performance | The application’s performance doesn’t depend on other clients | The application performance depends on your tier, provider, and resources used by other clients |
| Security | Reliable and isolated databases with convenient backup solutions | Clients share the same environment and depend on the vendor’s security measures |
| Scalability | Reliable and isolated databases with convenient backup solutions | Clients share the same environment and depend on the vendor’s security measures |
| Customizability | Clients can fully customize their software and user interface | Customization is limited but easier to implement with supported tools |
| Onboarding | The onboarding process is costly and time-consuming | Multi-tenant solutions have automated setup and intuitive configuration |
Should You Choose Single-Tenant vs Multi-Tenant SaaS?
Single-tenant SaaS works for large enterprises that want full control and robust security. This model works for healthcare and FinTech companies responsible for client’s personally identifiable information. Single-tenancy is also an excellent solution for B2B businesses whose eCommerce platforms rely on complex workflows and ERP tools.
On the other hand, a multi-tenancy database design is perfect for companies that want an easily configurable and reasonably priced solution with fewer hardware requirements. This option is great for startups, medium businesses, and larger companies that constantly readjust their scaling expenses.
However, it’s not necessary to choose between single tenant vs multi-tenancy. A hybrid approach combines elements of both architectures to strike a balance between customization, efficiency, and SaaS cost.
How to Implement Multi-Tenant Database Architecture
As more businesses shift to SaaS models, multi-tenant database architecture is becoming a go-to approach for scaling fast while serving several tenants.
However, the right setup depends on your goals, technical needs, and the industry you’re in:
- Healthcare. Choose schema-based or hybrid tenancy to meet HIPAA requirements and maintain strict data separation.
- Finance. Emphasize encryption, compliance auditing, and tenant-specific data access to meet regulations like PCI DSS.
- Education. Use row-level tenancy for scalability across schools or campuses, with access policies tailored to academic roles.
- Retail & E-commerce. Optimize for high concurrency and usage spikes, using shared resources for catalog search and dedicated space for customer data.
- SaaS Platforms. Prefer database-per-tenant for high-paying clients and shared models for SMBs to balance performance and cost.
- Government. Focus on maximum data isolation — schema-per-tenant or database-per-tenant — to meet strict national security and privacy laws.
- Manufacturing. Combine tenant-specific analytics with shared operational databases to track inventory and supplier performance securely.
- Legal Services. Prioritize confidentiality and auditability. Hybrid models work well for secure document storage and client case tracking.
Businesses can use on-demand cloud computing platforms like AWS to build a multi-tenant SaaS application:
- Amazon ECS (microserver architecture). ECS has a loosely coupled architecture, giving your teams the possibility to code, scale, and deploy code independently.
- Amazon EKS (Elastic Kubernetes Services). EKS adds a layer of complexity to Amazon ECS and allows deeply customizable SaaS configurations. You can also isolate tenants in different Kubernetes clusters to boost security.
- Amazon Serverless Computing. Serverless is a fully scalable and cost-effective AWS architecture where they charge based on the resources you use.
You also need to implement an authorization server and domain route module to segregate users in your SaaS application.
Authorization (Identity) Server
When someone wants to access your environment, the authorization server must check his affiliation and role in the organization. Then, the system passes the information to the application and issues a token based on the user’s access rights.
Companies use third-party tools to optimize resource-heavy authentication & authorization processes. Many of our clients rely on AcroSSO — a backend authorization management service made by Acropolium. This solution is designed to easily manage and control user and service rights in corporate information networks (primarily multi-tenant SaaS environments).
Domain Route
You need to implement the right URL design for a multi-tenant SaaS. Organizations with fewer clients can use logical and keyable URLs to separate their domains. But global businesses prioritizing security can go with cryptic address lines or block access requests made without a valid session.
Migrating from Single-Tenant to Multi-Tenant Cloud Architecture
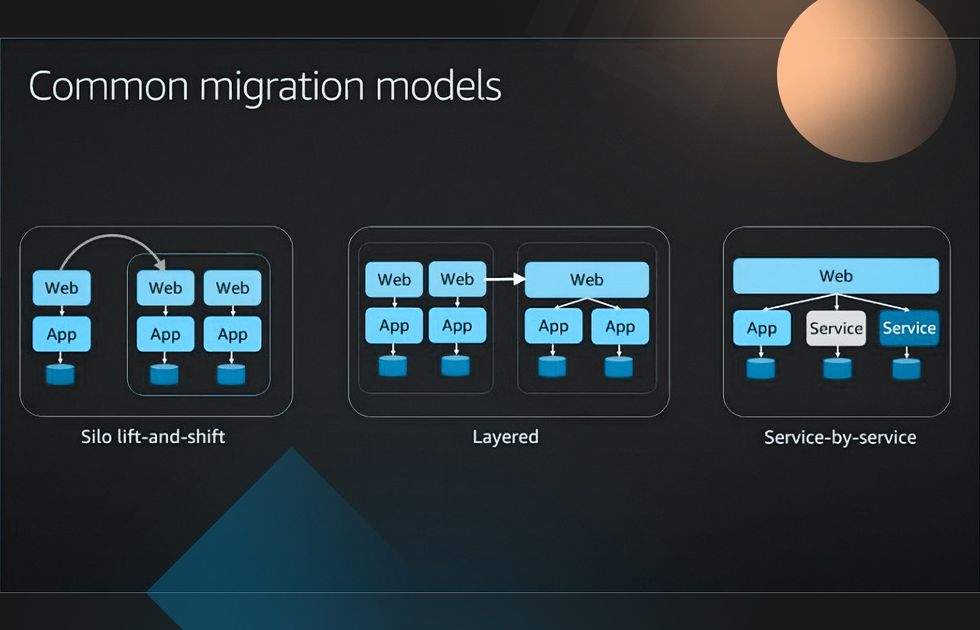
To convert your on-premise or single-tenant infrastructure to a multi-tenant environment, you have to start with the migration model and methodology. The common approaches include:
- Silo migration: moving the existing stack with minimal restructuring
- Layered migration: moving web and app tiers and partially optimizing them in phases
- Service-by-service migration: restructuring and optimizing every component of your architecture in increments
You’ll have to choose the database isolation model based on the number of user groups and the required level of security. Next, you’ll need to add the authorization server and ensure its compatibility with all your apps or services that access dedicated databases or a shared one.
Lastly, you can always consider mixed tenancy. Hybrid tenancy models offer a smart balance with dedicated resources where needed, shared ones where possible.
They’re ideal for industries like healthcare, finance, and government that require strong data isolation, while still benefiting from shared infrastructure for less sensitive tasks.
Company Experience
Acropolium is a certified SaaS development vendor in many markets, including healthcare, retail, fintech, risk management, supply chain, logistics, etc.
Our company can supply you with a dedicated team of cloud computing consultants, web developers, architects, and project managers. With our skills and tech stack, you can migrate your entire infrastructure or build a successful multi-tenant data architecture from scratch.
Let’s take a look at our actual case studies:
Biotech Enterprise SaaS Development
A corporate medical equipment supplier needed a reliable multi-tenancy solution for remote device management. At the same time, it was important to automate the audit of all incoming assets, their certification and marking, quantity and quality control. Also, SaaS was supposed to bring vendors and technicians together to improve communication and collaboration.
As a result, the SaaS solution helped the company increase sales by 65%, user loyalty by 75%, and attract 30% of new customers.
Accounting Multi-Tenancy SaaS
Our client provides accounting SaaS for small and medium-sized companies and enterprises. For them, we developed a multi-tenant solution with various payment methods, customizable reports, and document templates. The use of SSL encryption and adherence to industry standards was also crucial.
After five months, we presented the SaaS MVP with a quick user setup in five clicks. The decision was successful because the conversion rate from the free demo to the paid plan reached 30%.
Conclusion
There’s always a tradeoff when selecting an architecture type. You must choose between the flexibility and cost-efficiency of a multi-tenant vs single-tenant solution with its security compliance and reliability.
It is important to consider resource usage needs, budget, partition (isolation) model, and cybersecurity tools. Thankfully, IT outsourcing with Acropolium can help. We deliver consulting and web development services using a subscription-based model. That means you should pay monthly, optimizing the allocation of resources.
Get in touch to see what we have to offer!








![AI in SaaS: [How AI is Transforming the SaaS Landscape]](/img/articles/ai-in-saas-how-ai-is-transforming-the-saas-landscape/img01.jpg)
![SaaS ERP vs Cloud ERP: [Which Works Best for You?]](/img/articles/saas-erp-vs-cloud-erp/img01.jpg)
![ᐉ SaaS Development Outsourcing: [How to Scale Faster and Cut Costs]](/img/articles/outsource-saas-development/img01.jpg)
![Microservices Architecture [Implementation Benefits]](/img/articles/microservices-architecture-implementation/img01.jpg)
![Fintech SaaS Solutions in 2025 [Custom vs. Off-the-Shelf]](/img/articles/fintech-saas-solutions/img01.jpg)