
Key Takeaways
- Cloud-based systems enable remote access to patient records and healthcare applications from anywhere with an internet connection, improving accessibility and flexibility for healthcare providers.
- By adopting cloud computing in healthcare, medical businesses can replace expensive on-premise infrastructure maintenance with pay-as-you-go, cloud-hosted pricing models.
- The healthcare cloud computing market is valued at $70.6 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach $171.16 billion by 2030.
The adoption of cloud computing in healthcare has significantly boomed in the past few years, with most medical businesses relying on patient data security. The need for automation and real-time data analysis has fueled the rapid digitalization in the healthcare industry, making cloud migration a vital step toward transformation.
In this article, we’ll run you through the most common medical cloud computing use cases and market trends. We’ll also give you a short overview of the benefits of cloud adoption and share some practical tips on overcoming its challenges.
What is Cloud Computing in Healthcare?

Cloud computing in healthcare refers to the use of remote servers hosted on the Internet to store, manage, and process healthcare data and applications. Instead of relying on local servers or physical infrastructure, healthcare organizations leverage cloud-based services to access computing resources. This includes storage, processing power, and applications available on-demand over the Internet.
With cloud computing in the healthcare industry, medical providers can efficiently manage patient records, collaborate with colleagues, and deploy healthcare applications while ensuring scalability, flexibility, and security.
Healthcare Cloud Computing Market Trends
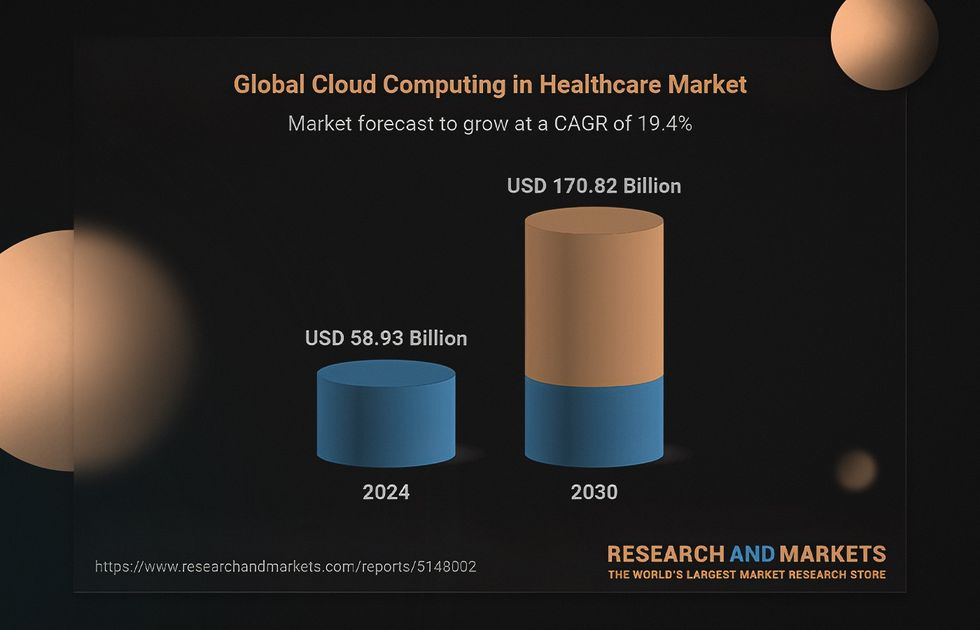
Indeed, the future of cloud computing in healthcare is promising. The healthcare cloud computing market is valued at $63.55B in 2025. Currently, it is projected to grow to 197.45B by 2032, with a CAGR of 17.6%.
According to HIMSS, over 82% of healthcare organizations migrated to the cloud in 2025. With SaaS going hand in hand with cloud solutions, medical businesses continue to invest in SaaS-based software. We can also see the increasing adoption of real-time big data analytics, remote patient monitoring, the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT), and chatbots within mobile apps.
Each of the abovementioned healthcare applications is based on cloud computing. In fact, study found that organizations using cloud-based services experienced a significant 43% decrease in security incidents. Along with cloud computing for healthcare, organizations are planning or already using machine learning, artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and IoT in 2025.
Moreover, modern hospitals, surgery centers, and rehabilitation institutions are increasingly investing in robotic process automation and blockchain technology. The blockchain in the healthcare market, valued at $831.54 million in 2024, is projected to soar to $178.91 billion by 2034, with the United States at the forefront of technology adoption.
How Cloud Computing is Used in Healthcare
Cloud computing allows healthcare facilities to centralize large volumes of electronic health records (EHR) coming from different sources and make the records accessible to all parties.
At the same time, 80% of healthcare IT leaders say cloud is the most secure way to manage sensitive patient data, with 67% using cloud applications and 63% planning to adopt cloud-based EHRs. Their main motivators include scalability (61%), cost savings (58%), data storage capacity (52%).
Better management and interoperability of data result in more accurate forecasting and decision-making. With access to specific records, healthcare specialists can make data-driven decisions, improve treatment results, and even forecast seasonal disease outbreaks.
Moreover, organizations report cost reductions of ~12%, with public cloud favored for its flexibility and affordability.
Cloud Computing Use Cases in Healthcare
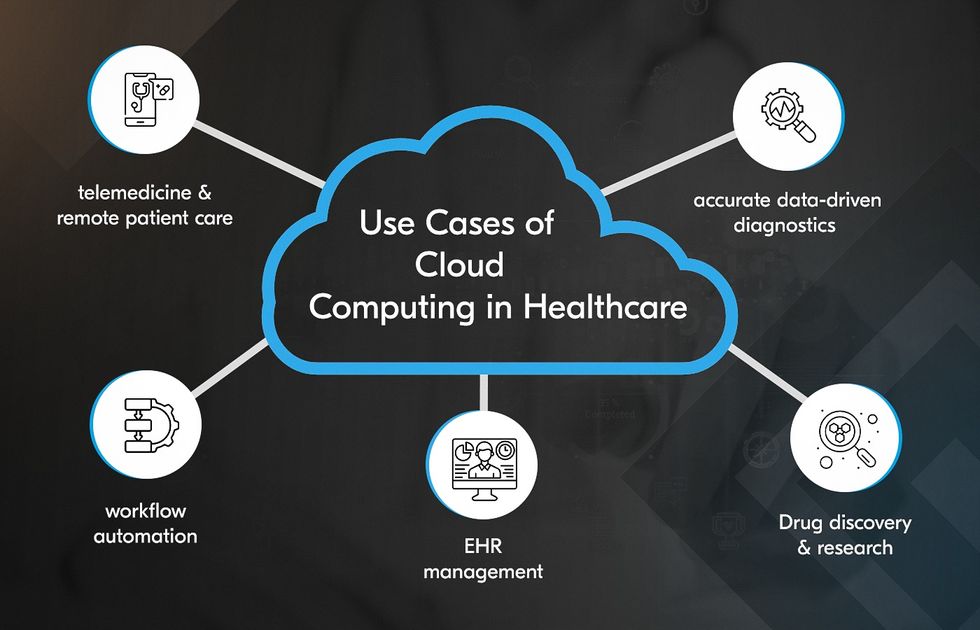
The use cases of cloud computing are countless thanks to the advantages this technology brings to the table. But how can cloud computing be used in healthcare applications? Let’s take a closer look at the three most promising examples.
Telemedicine & Remote Patient Care
Telemedicine is an excellent alternative to traditional in-person consultations. Today, patients can receive medical advice and access their health records, lab results, and prescriptions remotely via cloud-based platforms. Thanks to telemedicine, healthcare professionals can monitor chronic illnesses, provide remote care, and even carry out surgeries.
Thus, CareCloud delivers cloud-based practice management and telehealth solutions that allow providers to conduct virtual visits, manage patient workflows, and access medical data remotely. By integrating scheduling, billing, and patient communication on a single platform, the product enhances access to care while improving operational efficiency.
Electronic Health Records (EHR) Management
Electronic Health Records (EHR) Management systems represent the disruptive impact of cloud computing on healthcare. It involves the use of cloud computing to store, manage, and access patient health records electronically.
In this use case, healthcare organizations leverage cloud-based EHR systems to securely store comprehensive patient information, including medical history, treatment plans, test results, and medications. Healthcare providers can efficiently access and update patient records, streamline clinical workflows, and improve care coordination across different healthcare settings.
Additionally, cloud-based EHR systems like ClearData facilitate interoperability and data exchange between healthcare providers. The product specializes in healthcare cloud compliance and security, providing HIPAA-compliant cloud environments for EHR hosting, backup, and analytics. Their platform enables healthcare organizations to safeguard sensitive patient data while leveraging cloud scalability.
This enables seamless sharing of patient information to support better decision-making and patient outcomes, which is usually not supported by most legacy systems.
Accurate Data-driven Diagnostics
Accuracy in diagnostics remains a critical challenge in modern healthcare. A landmark JAMA study estimates that in the U.S. each year, nearly 800,000 patients suffer serious harm — death or permanent disability — as a result of diagnostic errors. Of these, approximately 371,000 die and 424,000 experience lifelong disabilities due to misdiagnoses related to conditions like stroke, sepsis, pneumonia, venous thromboembolism, and lung cancer.
However, AI-based cloud solutions like clinical decision support systems (CDSS) collect relevant data in a single place, helping healthcare specialists improve the accuracy of their diagnoses and make their decisions data-driven. AI also enables predictive analytics to identify risks and trends before they grow into serious issues.
For example, AI-driven predictive analytics enabled researchers to develop deep neural networks for forecasting the risk of patient death based on their ECG results. The model identifies patients at risk before any pathological signs develop.
PathAI leverages cloud computing combined with artificial intelligence to assist pathologists in diagnosing diseases more accurately. It analyzes pathology images in the cloud, improving diagnostic precision, reducing errors, and accelerating turnaround times for conditions such as cancer.
Workflow Automation for Hospital Management
Cloud computing in healthcare improves hospital management on many levels. With centralized cloud data storage and a network of connected devices, healthcare organizations can monitor patients in real-time and automate medical supply chain management.
Healthcare organizations can instantly access and share medical data, track inventory and equipment locations, and easily manage doctors’ schedules without overlaps. This proactive monitoring also contributes to a better risk management strategy.
Cloud computing fuels machine learning and AI, which can automate and optimize routine operations. For example, document auto-filling, billing, and reporting are areas where technology does all the heavy lifting.
Medsphere offers cloud-based hospital information systems that automate workflows including clinical documentation, patient scheduling, and supply chain management. Their solutions help hospitals reduce administrative burdens and improve care coordination.
The importance of cloud computing in healthcare is hard to deny. Some companies migrate to the cloud to streamline data management, while others use this technology as a foundation for further innovations. Let’s take a more detailed look at why companies choose cloud computing.
Clinical Development and Research
Cloud computing reimagines clinical development by powering collaborative, secure, and efficient drug research. As of 2025, the global market for cloud-based clinical trial systems is projected to reach $2.5 billion, having grown robustly from around $2.0 billion in 2024.
Meanwhile, the broader AI-driven clinical trials market hit $1.35 billion in 2024, with estimates showing growth to $2.60 billion by 2025 and an impressive 27% CAGR through 2034.
A notable example of cloud computing in action comes from Pfizer’s COVID-19 vaccine development. By leveraging AWS’s cloud infrastructure, Pfizer reduced the time needed to process clinical trial data, enabling faster decision-making and real-time trial adjustments. This shift allowed researchers across continents to securely collaborate, monitor safety data, and make protocol updates without the delays traditionally caused by siloed systems.
Beyond vaccines, cloud-based platforms are streamlining recruitment, monitoring, and data analysis in trials targeting oncology, neurology, and rare diseases. Researchers can now use AI to identify ideal participants from EHRs, forecast dropout risks, and automate data collection
Drug Discovery and Research
Drug discovery and research is a place where healthcare and cloud computing meet to unleash new opportunities for pharmaceutical companies. Research institutions and biotechnology firms utilize cloud-based platforms and tools to accelerate the drug discovery process, conduct genomic research, and facilitate clinical trials.
Generally, cloud computing provides scalable computing resources, storage capabilities, and collaboration tools. All this enables researchers to analyze large datasets, simulate drug interactions, and model complex biological systems.
Cloud-based platforms and pharmacy apps also support data sharing and collaboration among researchers, allowing for real-time collaboration across geographically dispersed teams.
At Johns Hopkins Medicine, researchers harness cloud-based platforms to fast-track drug discovery and clinical studies. By using scalable data analytics and machine learning in the cloud, they sift through enormous datasets — from genomic profiles to trial outcomes — spotting potential therapeutic candidates more quickly and crafting more effective study protocols.
Benefits of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
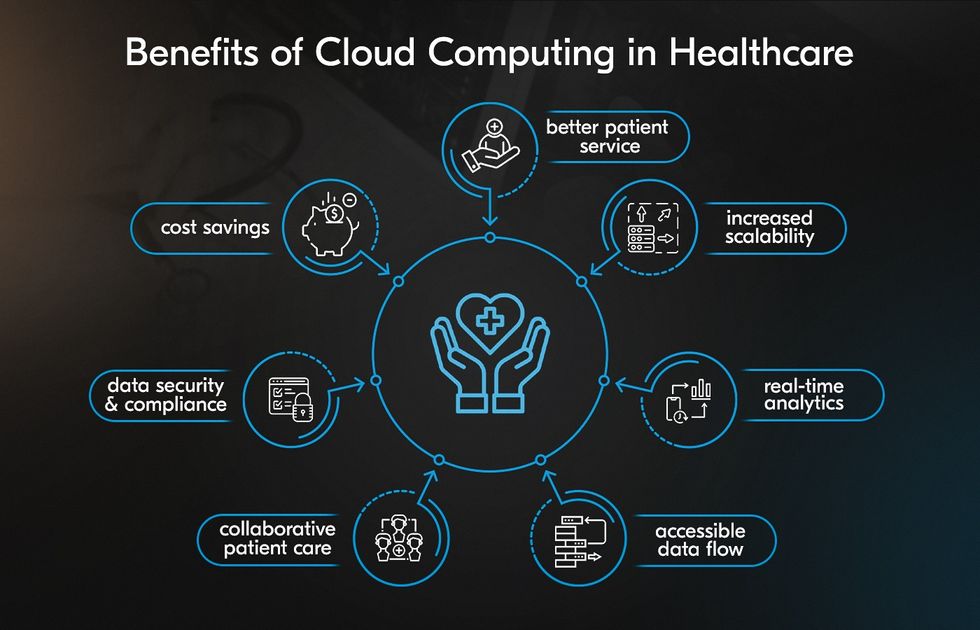
Cloud computing impacts both providers and patients by cutting down expenses while improving care quality. Though it can be hard to distinguish the benefits of cloud computing from those of other technologies it enables, we’ve chosen the six benefits that are most often mentioned by our customers.
Cost Savings
With cloud computing services, you pay for the resources you use. Cloud service providers are fully responsible for administration, maintenance, and availability, so your healthcare organization can focus on patient care instead of worrying about setup and hardware management. After all, not every clinic has an IT department.
Cloud service providers make sure the technology they use is top-notch. Plus, they follow foolproof security practices to protect your data from cyberattacks and subsequent money loss. This is an obvious advantage in the highly competitive and regulated healthcare industry, where the cost of a single data breach is approaching $10.93 million annually.
Infrastructure efficiency, workflow optimization, better patient management, and other indirect benefits of cloud computing for the healthcare industry also help save providers’ money and, thus, reduce care costs for patients.
Better Patient Experience
Patient expectations and the need for more personalized care are growing. Nearly 90% of health system executives expect the expanding adoption of digital tools, connected care delivery, and virtual health for tailored treatments in 2025.
Modern patients require medical providers to address their needs with personalization, and this kind of load often requires cloud computing.
Cloud computing facilitates real-time availability of doctor’s notes, test results, and treatment histories directly to patients. With this transparency, they can actively engage in their care decisions and communicate more effectively with their physicians.
The cloud also makes the entire patient journey clearer and more manageable, from initial appointments to insurance processing and easy access to health records.
More accurate diagnosis and illness prediction also improve treatment outcomes and, with it, patient satisfaction.
Increased Accessibility & Patient Data Ownership
Cloud computing in healthcare offers the opportunity to empower patients by giving them greater control over their own medical data. This shift encourages patients to take an active role in their health decisions, enhances their understanding of medical information, and supports improved health outcomes.
Essentially, storing digital health records in the cloud allows for seamless archiving and easy retrieval of data. Increased system availability minimizes data duplication, and with less strain on the system, restoring information becomes more efficient and reliable.
Data stored in the cloud is properly secured and can be easily accessed by authorized users from any device with an internet connection. Real-time updates ensure that all records are consistent and up-to-date. What’s more, cloud computing increases data interoperability, enabling data integrations across healthcare systems. Simply put, your data is always available for sharing and use.
AI and ML Innovations
AI and machine learning have become essential tools for managing the complexity of healthcare data. These technologies can rapidly analyze vast amounts of patient information, medical images, and lab results with high precision, reducing human error and speeding up diagnosis.
Healthcare providers benefit from AI’s ability to process diverse data types while maintaining consistent accuracy, even as case volumes fluctuate. Whether it’s a sudden outbreak or routine patient care, any outbreak requires flexible support for decision-making.
Unlike traditional manual methods, AI and ML systems can quickly adapt to varying data inputs and clinical scenarios, enhancing diagnostic efficiency without sacrificing quality.
Increased Scalability
In healthcare, scalability has historically been a serious challenge to cope with. Healthcare software should process large volumes of multiformat data while maintaining high availability and uptime. At the same time, healthcare isn’t a stable industry. Even minor disease outbreaks can require you to scale up your applications fast, while more calm periods may force you to scale the system down to optimize costs.
Unlike on-premise servers, cloud computing services are highly flexible and scalable, helping your clinic to swiftly adapt to new circumstances, be it flu season or a pandemic.
Real-time Analytics
Cloud computing technology allows storing terabytes of data and processing millions of requests in seconds. Coupled with AI, it creates more opportunities for real-time data analytics, delivering opportunities for more accurate diagnostics and personalized treatment plans.
But the use cases of real-time analytics go far beyond patient care. Analytics powers medical research, clinical trials, and drug discovery. For example, cloud computing is used as a platform for DNA analysis and collaboration. The research claims that cloud computing will likely remain a solid foundation for large-scale genomic collaboration.
Data Security and Compliance
Cloud computing in healthcare offers robust data security and compliance measures, ensuring that sensitive patient information remains protected and adheres to regulatory standards such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in the United States.
By leveraging advanced encryption techniques, access controls, and regular security audits, cloud providers safeguard healthcare data from unauthorized access, breaches, and cyber threats. Cloud platforms also offer built-in compliance features and certifications, assuring healthcare organizations that their data management practices meet industry-specific regulations.
Enhanced Collaboration
Implementing cloud solutions in healthcare significantly enhances collaboration and streamlines the storage of Electronic Medical Records (EMRs). This eliminates the need for patients to carry physical records during every doctor’s visit.
Through cloud technology, physicians can effortlessly access a patient’s medical history, review past treatment results, and share data instantly with other care providers. Using kiosks in hospitals, patients put their data into the medical databases, giving doctors instant access to essential records.
A laboratory can upload a patient’s test results, MRA images, and other data, which will be immediately available to nurses and physicians. Finally, physicians can share data with pharmacists and work together to create better medication plans.
These benefits clearly show why the role of cloud computing in healthcare departments is widely acknowledged. Still, cloud migration isn’t as smooth as we would like.
Challenges of Cloud Computing Implementation in Healthcare

Cloud computing is an excellent solution for healthcare, but before committing to it, you should know about the challenges of cloud implementation.
Security
Despite the advanced approaches and strategies, security remains the biggest setback for cloud implementation. Sensitive health data attracts cybercriminals, who are getting craftier with time. The HIPAA Journal reports a record-beating number of 720 cyberattacks in 2024, with ~50 attacks taking place monthly in 2025.
As we mentioned above, medical data management and storage should comply with numerous regulations, including General Data Protection Regulation. Though cloud providers can simplify compliance with access control and encryption, data security falls under the responsibility of a healthcare organization. Thus, one has to make sure to hire cloud engineers who know all these peculiarities and specialize in crafting cloud computing for healthcare.
Unrealized Cloud Potential
McKinsey’s research shows that cloud computing in healthcare can generate for the industry an economic value of up to $140 billion by 2030. This value is largely driven by the innovation and digitalization capabilities (IoT, automation, analytics) that the cloud unlocks.
However, despite the promising numbers, healthcare organizations often treat cloud computing as a more cost-effective IT operating model, limiting the opportunities this technology can bring to their businesses.
Cloud migration should be a part of comprehensive digital business transformation if you want to get the most out of it.
How Acropolium Can Help You Adopt Cloud Computing in Healthcare
Cloud computing helps healthcare organizations save costs, improve patient and facility management, make use of heaps of data and medical collaboration. What’s more, the technology can become a basis for all kinds of software and hardware integrations, allowing your clinic to stay ahead of trends and beat the competition. You just need the right guidance on your way to cloud migration.
Acropolium has over 20 years of experience in software development and consulting across 20 industries. But more than that, we have 13 years of hands-on experience with healthcare solutions. In our recent cooperation with medical providers, we have helped our clients thrive by:
- Developing a cloud, blockchain-based EHR software with robust integration capabilities and HIPAA compliance protocols.
- Delivering a SaaS-based appointment scheduling software that decreased patient no-show rates by 30% and cut patient wait time by 25%.
- In the latter case, the client saw a 40% increase in patients accessing their records using the system.
Thanks to our expertise in cloud computing, IoT, AI, big data, and blockchain, we can move your infrastructure to the cloud or build a new one that will meet your business needs and capabilities.
Contact us to learn more about our cloud computing services for healthcare.







![Doctor On-Demand App Development [2025 Guide]](/img/articles/doctor-on-demand-app-development/img01.jpg)

![EMR/EHR Software Development: [Benefits & Best Practices]](/img/articles/emr-ehr-software-development-implementation-tips-and-cost/img01.jpg)
![ᐉ⭐ Blockchain in Healthcare: [6 Real Use Cases Included]](/img/articles/blockchain-technology-in-healthcare/img01.jpg)
![Online Pharmacy App Development [2025 Guide]](/img/articles/pharmacy-app-development/img01.jpg)